The Demographic Divide: What It Is and Why It Matters
(2005) Public attention has begun to focus on the "demographic divide," the vast gulf in birth and death rates among the world's countries.
(2005) Public attention has begun to focus on the "demographic divide," the vast gulf in birth and death rates among the world's countries.
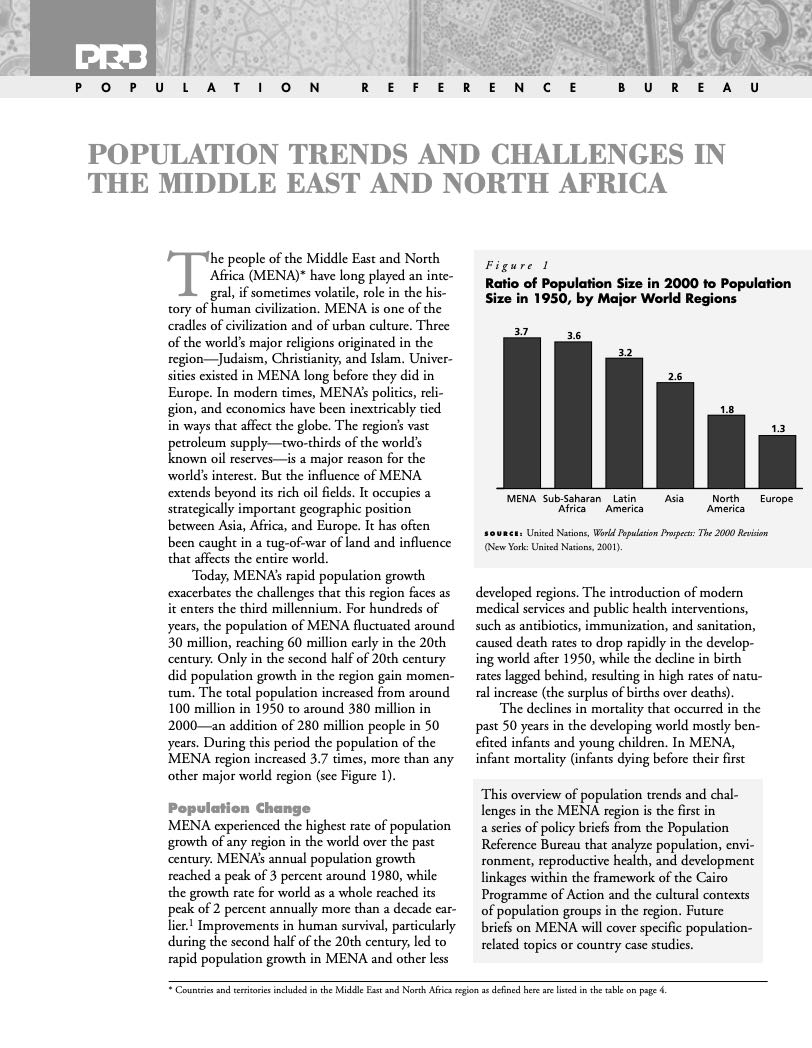
(2001) The people of the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) have long played an integral, if sometimes volatile, role in the history of human civilization. MENA is one of the cradles of civilization and of urban culture. Three of the world's major religions originated in the region — Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Universities existed in MENA long before they did in Europe.

(2000) At the beginning of the 21st century, demographic trends seem to many Americans to signal new, potentially disquieting changes in the U.S. population.
Enhancing research and policy communication in population, reproductive health, and economic development.
Project: Center for Public Information on Population Research (CPIPR)
The mortality rate for Black Americans in non-pandemic years is higher than the mortality rate for white Americans who died from COVID-19 and all other causes in 2020.

(2016) Latino children currently account for one-fourth of U.S. children under age 18, and by 2050 they are projected to make up nearly one-third of the child population. Of the 18.2 million Latino children currently living in the United States, 95 percent are U.S.-born citizens.
Water and sanitation play a crucial role in the transmission of diarrheal disease. These environmental factors contribute to approximately 94 percent of the 4 billion cases of diarrhea that the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates to occur globally each year.

Since 2010, homeownership rates for most racial/ethnic groups have held steady or increased, but the rate for blacks has continued to drop, especially among young adults.
(2010) Many developing countries adopted policies to slow population growth in the latter half of the 20th century in response to population growth rates that had risen to three or more times greater than those ever observed in industrialized countries.