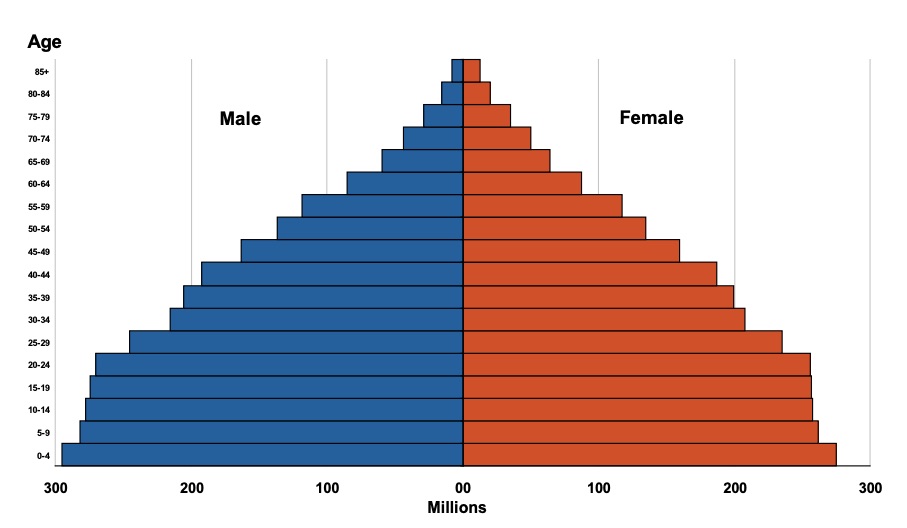
Population Bulletin vol. 64, no. 2: Urban Poverty and Health in Developing Countries
(2009) The era in which developing countries could be depicted mainly in terms of rural villages is now in the past. A panoramic view of today's demographic landscape reveals a myriad of cities and towns.