Mark Mather
Associate Vice President, U.S. Programs

In the United States, over 24 million people provide unpaid care for older adults—a 32% increase from a decade ago
March 18, 2025
Associate Vice President, U.S. Programs
Contributing Senior Writer
As the large Baby Boom generation enters advanced ages, more family members and other unpaid helpers are stepping in as caregivers. In just over a decade, the number of family caregivers regularly assisting older adults with daily activities at home grew by 32%, increasing from 18.2 million to 24.1 million between 2011 and 2022.1
While the caregiving cadre has grown, who’s getting care has also changed. Older Americans receiving family care are younger, better educated, and less likely to have dementia than they were in 2011, report Jennifer L. Wolff of Johns Hopkins University, independent consultant Jennifer C. Cornman, and Vicki A. Freedman of the University of Michigan.
The increase in family caregiving partly reflects the rising share of older adults with multiple chronic conditions, such as heart disease, hypertension, stroke, and cancer. And while the share of older adults with dementia has declined, unpaid caregivers average twice as many hours each week caring for people with dementia than without dementia (about 31 hours versus 14), Wolff and team found (see Figure 1).
In addition, a new study estimates that the number of new dementia cases will double over the next 40 years as the population ages—setting the stage for more demands on dementia caregivers and more changes to the caregiving landscape.
“Understanding the changing composition and experiences of family caregiving has never been more important, but it is challenging to assess,” the researchers write. “[It] requires consistent measurement for well-characterized, generalizable samples of people who receive and provide help.”
The nationally representative National Study of Caregiving and the National Health and Aging Trends Study offer important insights. The two studies provide a snapshot of the family caregivers that help Americans ages 65+ who live in the community (i.e., at home or with a relative) or in a residential care setting other than a skilled nursing facility, such as an assisted or independent living facility, a personal care home, or a continuing care retirement community.
Family caregivers include relatives and unpaid helpers, like neighbors and friends, who assist with personal care tasks like bathing and dressing; mobility tasks like getting out of bed and getting around the house; and household activities such as laundry, food preparation, shopping, and managing money.
On average, the time that family caregivers spent helping older adults with dementia increased by almost 50% over the decade, rising from 21.4 hours per week in 2011 to 31.0 hours in 2022. By contrast, time spent assisting older adults without dementia fell from 15.3 hours a week in 2011 to 13.9 hours in 2022 (Figure 1).
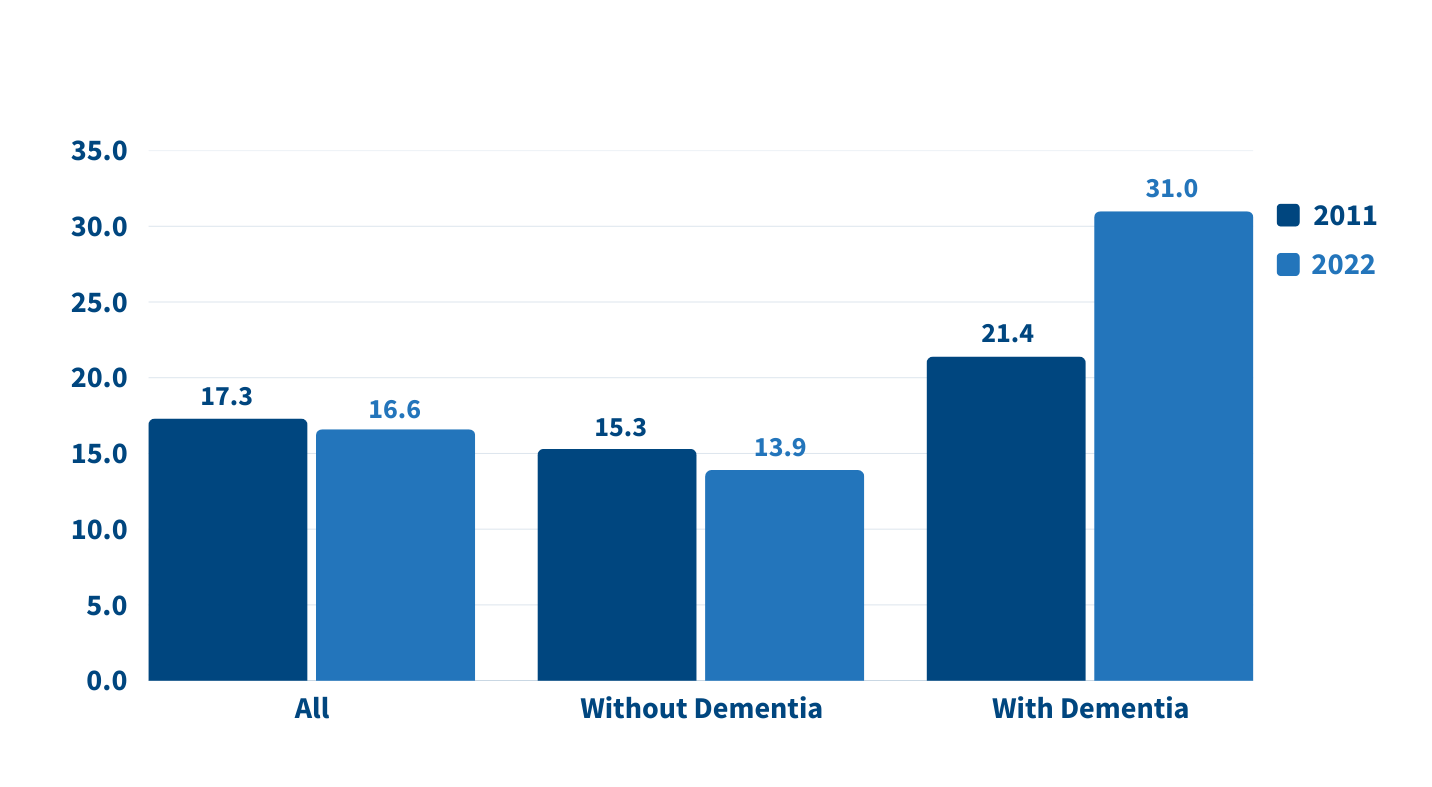
Source: Jennifer L. Wolff, Jennifer C. Cornman, and Vicki A. Freedman, “The Number of Family Caregivers Helping Older US Adults Increased From 18 Million to 24 Million, 2011–22,” Health Affairs 44, no. 2 (2025): 189-95.
People caring for older adults with dementia have high—and increasing—demands on their time. More than half (51.7%) of dementia caregivers lived with the person they were caring for in 2022, up from 39.4% in 2011, Wolff and team report. And the share able to hold jobs—outside their caregiving work—dropped from 42.5% to 34.6% during the same period.
Among caregivers with formal jobs, the share who reported challenges with their employment—including working fewer hours or being less productive—increased over the decade, regardless of whether they cared for someone for dementia.
“Challenges are exacerbated when caregivers are in poor health themselves; have a lack of choice in assuming the caregiving role; and, for the substantial proportion of family caregivers who are employed, work in low-wage jobs with limited flexibility,” the researchers note.
Which older Americans get family care? As in the past, they tend to be female, non-Hispanic white women who are married or widowed. But growing numbers of family care recipients are male and have some college education. More are also separated and divorced compared to 2011, reflecting national trends.
Who’s providing care? Family caregivers continue to be largely female and married, and most report being in good health. In 2022, adult children still made up the largest share of family caregivers for older adults, at 40.7%, but this represents a significant decline since 2011 (Figure 2).
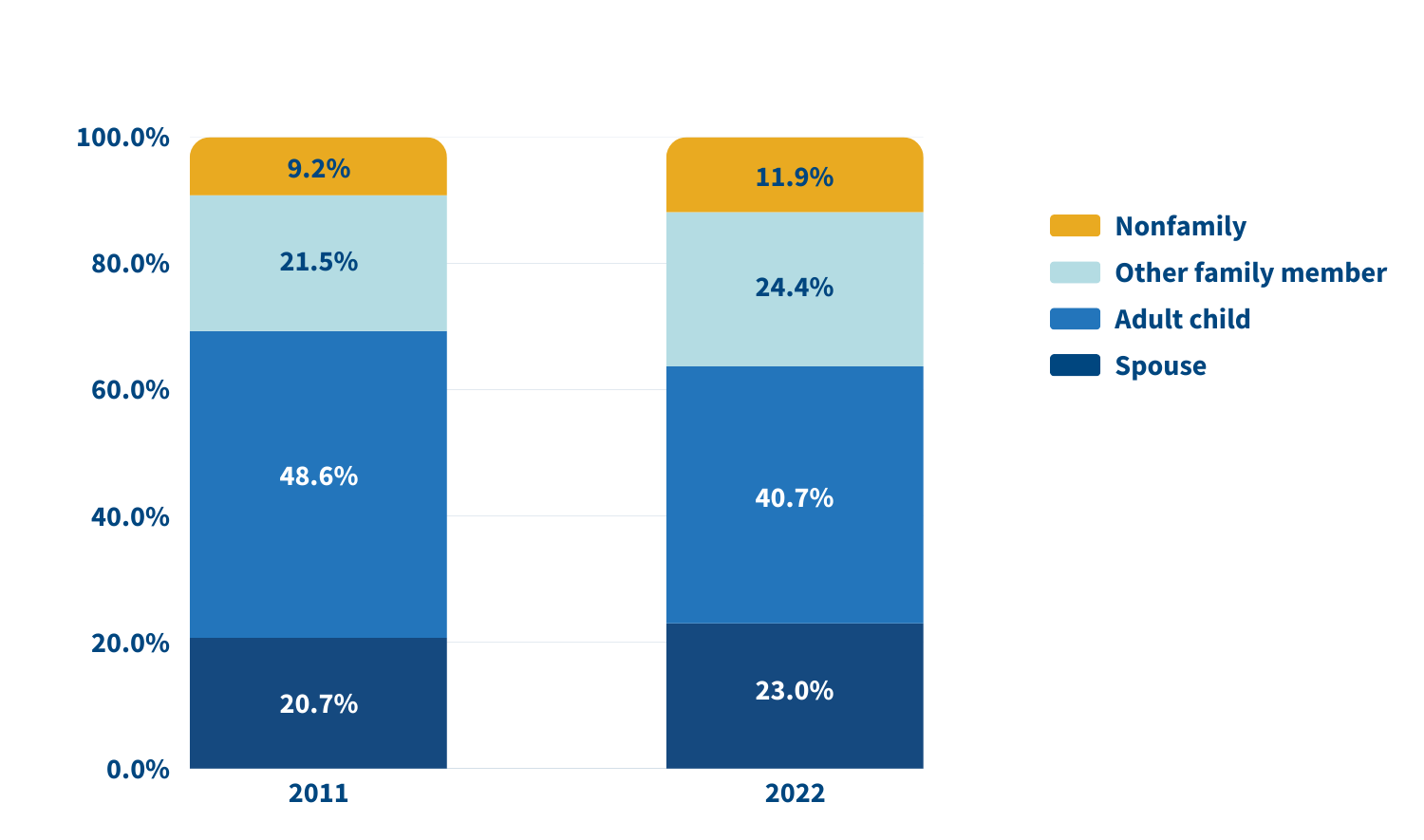
Source: Jennifer L. Wolff, Jennifer C. Cornman, and Vicki A. Freedman, “The Number of Family Caregivers Helping Older US Adults Increased From 18 Million to 24 Million, 2011–22,” Health Affairs 44, no. 2 (2025): 189-95.
In 2022, adult children accounted for about half (49.1%) of family caregivers for older adults with dementia, compared with 38.4% of caregivers for those without dementia. Just 17.7% of family caregivers for older adults with dementia were spouses, compared with 24.5% of family caregivers for people without dementia.
A sizeable share of family caregivers (17.0%) had children under age 18 at home in 2022, and 6% to 13% viewed their care responsibilities for older adults as a source of financial, physical, or emotional difficulty.
Despite these challenges, the researchers report a decline in the use of support groups (4.1% to 2.5%) and respite services (12.9% to 9.3%) between 2011 and 2022.
Many caregivers face extraordinary demands and should be the focus of support services, Wolff and colleagues say. They single out those caring for older adults with dementia or nearing the end of life, as well as caregivers “from racial and ethnic minority groups who are more likely to assist people who have extensive care needs in circumstances that involve scare economic resources.”
Family care needs are likely to rise as the number of U.S. adults ages 85 and older is projected to triple by 2050. The researchers note that the number of family caregivers rose even as the long-term use of skilled nursing facilities among older Americans dropped and community living increased. The challenges these caregivers continue to face is “sobering,” they write, including competing time demands from work and child care while spending an average of 17 hours per week on care. In addition, about 1 in 8 family caregivers report financial, physical, or emotional difficulties related to their caregiving roles, percentages that were largely unchanged over the 11 years examined.
Policies and programs to help reduce the financial, physical, and emotional burden of caregiving exist, but do not represent a coherent strategy, the researchers say. “Local, state, and federal policies are a patchwork that is uneven in availability and largely symbolic in magnitude,” they argue. Addressing the needs of family caregivers will require a “cohesive framework in support of the care economy.”
1. Jennifer L. Wolff, Jennifer C. Cornman, and Vicki A. Freedman, “The Number of Family Caregivers Helping Older US Adults Increased From 18 Million to 24 Million, 2011–22,” Health Affairs 44, no. 2 (2025): 189-95.

March 18, 2025
In this March 4, 2025 webinar, three researchers discussed how social media and new technologies may enhance—or limit—social connectedness and emotional well-being among older adults.
This webinar was hosted by PRB and the Coordinating Center for the Centers on the Demography and Economics of Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias, with funding from the National Institute on Aging.

December 2, 2024
In this Nov. 14, 2024 webinar, two distinguished researchers discussed how U.S. state policies and systems can affect racial and regional inequities in health and longevity.
This webinar was hosted by PRB and the Coordinating Center for the Centers on the Demography and Economics of Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias, with funding from the National Institute on Aging.
Mark Mather, PRB: Hi everyone, thank you for joining today’s webinar on how state contexts impact Population Health. I am Mark Mather. I’m with the Population Reference Bureau, or PRB, and I work in collaboration with the Coordinating Center for the Demography and Economics of Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias at the University of Michigan. And our goal is to help publicize research on health and well-being, especially among older adults. I also want to acknowledge the National Institute on Aging for making this webinar possible, and my PRB colleague, Toshiko Kaneda, for helping us to organize this event.
I’m excited to introduce our two speakers today. We have Dr. Tyson Brown, who’s a Professor of Sociology, Associate Professor in medicine, and Associate Scientific Director of social sciences of the Duke Aging Center at Duke University and Dr. Jennifer Montez, who is a Professor of Sociology, Gerald B Kramer faculty scholar in aging studies, Director of the center for Aging and Policy Studies, and Co-director of the Policy, Place and Population Health Lab at Syracuse University.
We’re also going to put two links in the chat, I’m not going to read their long bios, but if you’re interested in learning more about the speakers and their research, we will be putting links in the chat where you can get more information. And finally, just a couple of housekeeping notes; we’re going to hold the Q&A until the end. But if you do have a question, you can type it into the Q&A box at any time during the webinar. And finally, this webinar is being recorded, we will send you a link to that recording after the event, probably within a day or two. And with that, I will go ahead and turn it over to you, Tyson.
Dr. Tyson Brown, Duke University: Well, thank you so much. I look forward to hearing your feedback during our presentation. I will go ahead and just start sharing my screen. Again, thank you so much for inviting me to present my work, and I’m really excited to talk with you all today about how we can operationalize state level structural racism and its impact on population, health and aging. And as a race scholar, gerontologist, and population health scientist, you know, the primary focus of my research is on quantifying and mapping structural racism, as well as estimating its impact on aging and health equity. And so today, I’ll be giving an overview discussing what I see as important theoretical and methodological issues, as well as promising avenues to address them, and in doing so, advance the scientific study of structural racism and health.
So, before discussing the role of states, I think it’s really useful to zoom out to highlight how various frameworks can help us better understand how social context influence health. So, the social ecological model emphasizes that population health is shaped by complex interplay of social factors across multiple levels, from individual behaviors to broader societal forces. And this model highlights how health outcomes are not solely a product of individual choices, but are influenced by interpersonal relationships, community structures, institutional policies, and broader sociopolitical contexts. And by analyzing each of these, we gain insights into how policies, societal norms, and community structures can either benefit or harm population health. And this is true for many social forces, including structural racism.
And so, most of the research on links between structural racism and health have focused on structural racism at the neighborhood or the county level, which are really important context and really sort of the micro-level, or rather the more proximate contextual sources or determinants of health. However, other special units and policies such as states have received comparatively less attention. And this is a really major limitation in literature, because U.S. states obviously are important legal, administrative and political units and states have always provided an important context for racial stratification, including the roles that they most obviously played with respect to chattal slavery, Jim Crow and anti-miscegenation laws. So importantly, states continue to have a great deal of autonomy, and they’re heterogeneous in terms of the racialized policies and practices. This is evident with respect to things like disenfranchisement laws, aggressive policing practices, punitive sentencing, as well as the expansion or contraction of safety net resources.
And so, as a result, my research focuses on conceptualizing states as racialized institutional actors that influence population health.
So, in several recent studies, my research team scopes the literature on social racism to really identify the central tenets of structural racism theories and draw upon them to study state level structural racism. We highlight how the analytical crux for measuring structural racism, which is a complex, interconnected and dynamic network, really lies in examining its features and mechanics that undergird racial inequalities.
And so, failure to align measurement tools with these core features compromises the validity of research. Because measures that are incongruent with salient aspects of structural racism can distort findings. So, to address this issue, we draw on interdisciplinary theories and evidence to really dissect core features of social racism, with a focus on their implications for measurement and modeling.
And so, our studies on and the broader literature really underscore the importance of measuring modeling core features of structural racism, including things like the fact that it’s a distributional system, involves relational power dynamics, manifestations of racial inequities, that it’s a multi-level phenomenon operating at macro and micro level contexts, that it’s multifaceted and interconnected in nature. And this plays out across societal domains, that there are specific racial actors implicated, that it’s an institutionalized phenomenon that it involves racial schemas, logics, as well as socio historical context and intersections with other systems of oppression. And so structural racism is embedded in major political, economic, medical, criminal, legal and numerous other social institutions and aspects of society. So, in these forthcoming articles that are listed here, we offer concrete recommendations for conceptualizing, measuring, and modeling structural racism in ways aligned with theory. And so, the aims of these studies is to provide field guides for rigorous, theory driven measurement approaches, proposing best practices for the scientific study of structural racism in health research.
And to provide a couple concrete examples of ways to measure structural racism, as well as its effects on health, I’ll briefly describe several recent studies in this vein. And so, the first one addresses two main research questions. The first is, does state level structural racism across societal remains reflect an underlying latent construct? And latent constructs are phenomena that are not directly observable but can be estimated through statistical approaches that really capture manifestations of the phenomena. And then secondly, the question is structural racism associated with worse health outcomes among Blacks and whites in the U.S.
So, to examine variability in state level structural racism and its relationship with health among Black and white adults, we combined indicators of structural racism from several sources of publicly available data. And then we link these to geo coded individual health and demographic data from the Health and Retirement Study, as well as CDC data on COVID mortality, as well as the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance study. And so, this table shows each of the domains and indicators of structural racism that we examine. We use publicly available data to examine structural racism for the year circa 2010, spanning several domains including the criminal legal system, education, economic resources, political participation, as well as residential segregation.
And so, I should mention that this measurement approach is informed by theoretical perspectives as well as previously validated measures of state level structural racism.
So, the next step is to test whether state level structural racism reflects this underlying latent construct. And so, we’re especially interested in measuring structural racism in ways that are in line with structural theories, as I mentioned. And a latent variable approach is well suited for minimizing measurement error and capturing conceptual properties of a complex system that’s difficult to quantify or directly measure, such as structural racism. And so along those lines, the nine indicators of structural racism that I mentioned were used to develop a latent measure of structural racism. And we used confirmatory factor analysis to measure the extent to which structural racism across these domains are reflective of an underlying construct of structural racism and doing so we systematically evaluated model fit using varying model specifications related to correlated errors and also dimensionality. This figure here illustrates the factor structure of the latent construct. These correlated errors are all intended to address common sources of variation that are independent of the effects of structural racism on the various indicators. And so all consider the measurement model that allows for other common sources of variance in the indicators that are largely conceptually motivated, has a good fit with the data, and it generates reasonable parameter estimates. Furthermore, this measurement approach is largely consistent with many of the theoretical tenets that I outlined above. And I should note that we made this measure publicly available from the journals website in case you’re interested in exploring. So now we’ll turn to addressing the second research question, which is how does structural racism shape health among Black and white adults? Eco social theory has become a leading framework for understanding how macro level discriminatory environments impact health, and the theory suggests that structural racism has deleterious effects on Black people’s health. That part’s pretty much straight forward. We would anticipate that from the theory. And there are competing hypotheses about how structural racism may influence the health of whites, with some suggesting that whites benefit from sexual racism, while others are positing that they’re harmed by it, and others suggesting that their health may be unaffected by structural racism. I’m glad to talk more about these competing hypotheses during in more detail during the Q&A, if you’d like.
But let’s go ahead and jump into the results. What’s going on here? I’ll explain it in just a second. But one of the things I want to mention is that, you know, since replication is a hallmark of good science, we examine the relationship between structural racism and six different health outcomes in both the Health and Retirement Study and the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance study. For a little bit of context, the HRS is considered one of the premier data sources for studying health among adults over the age of 50 in the U.S. is nationally representative over samples of Black adults and the birth. This is the largest health survey in the in the United States. So, you have over 300 respondents. So, you’ve got tremendous statistical power. And so, we found remarkably consistent results across health outcomes and across the two data sets. And six out of the six cases, you can see that there are that higher levels of structural racism are predictive of worse health among Black people, remarkably consistent. But we see a very different story for whites. And one instance, structural racism exposure at the state level is predictive of better health for whites and in five out of six cases, there is no statistically significant relationship between structural racism and whites’ health. So, you find, you know, shockingly consistent results and just, you know, these health outcomes are some of the most commonly used, especially when studying older adults. And so, I think that there’s this, you know, there’s a real signal that we’re picking up. And we had much more confidence in our findings because it was so consistent across these health outcomes and across these health studies. So, in a recent study, we also examined the relationship between a latent measure of structural racism and Black-white inequities in Covid 19 mortality rates. Right.
So, the regression estimates indicate that the relationship between social racism and Black, white inequality in Covid 19 mortality is positive and statistically significant, both in the bivariate model and net of covariates. And so, this again is a state level measure and collectively the findings you know, I would argue that the collectively our findings across these studies suggest that our latent variable approach has really strong predictive validity and we actually did measure it against benchmarked it against other metrics such as sort of a summative index that assumed equal weighting of the indicators and did not take into account correlations between their errors when we found that the latent measure actually explained more variation in health outcomes and also explained significantly more variation of any of the individual level indicators. And so that again, provides some evidence that there’s really there are some real benefits to taking a latent measurement approach. So, I think it’s also essential to measure and map cultural forms of racism that reflect racial schemas, logics and practices.
So broadly you know, we really need to be considering the roles of things like racialized violence, animus, resentment, hate speech, and biases, all of which have been shown to vary by place including across states. And so, in addition to well-established survey data resources, we should also be utilizing data and methods to capture utilizing, you know, more innovative data measures to capture anti-Blackness through geo coded data from things like internet search engines and computational approaches, scraping websites and even experiments. So, this map shows the spatial distribution of a latent measure that Reid DeAngelis and I are developing using these types of data and measures. And preliminary results show that it’s predictive of population health inequities. And so, we’re really encouraged about the possibility of combining these latent measures of racial schemas and logics, sort of cultural measures with the more institutional measures and looking at how the interplay between them and their relative contributions to population health inequities.
I should also mention that in a recent study published in the Journal of Health and Social Behavior, Patricia Home and Brittany King and I, we introduced a state level structural intersectionality approach to population health. And what it does is it really demonstrates an application of social intersectionality using administrative data sources similar to the ones that I discussed in the previous studies. To examine the relationship between macro level structural racism as well as structural sexism and economic inequality and looking at how they interplay between them, as well as their joint and individual contributions to health inequities across U.S. states. Right. And so, this study, I think, can really serve as a springboard and a data source for similar studies that are aiming to extend this research, in studying how state level structural, intersectional oppressions differentially shape health outcomes for various demographic groups. I should also note that numerous studies also really highlight the dynamic role that policies and politics play in shaping health inequities.
Obviously, Jennifer Montez is a new data set, is an excellent resource for studying the role of states in this regard. There are also some studies by biomedical engineer Jackie John and other colleagues that used novel, a novel database on racism related laws which has been shown to predict health. So, these and other data sources on racial policies such as three strikes laws, welfare reform, banning critical race theory and racialized disenfranchisement can really serve as important resources for research on health inequities. And, you know, the history of structural racism in the U.S. has really important implications for how we should really be approaching the measurement of it and quantifying its effects on these inequities. And there is suggest that historical racism directs, constructs and continues to mold contemporary structural racism as well as health outcomes. And so, in that vein you know, there have been several empirical studies that have shown that polities that had larger enslaved populations in 1860, have greater present-day inequities and poverty and economic mobility and also higher levels of contemporary pro-white bias, and that these can be linked to contemporary health outcomes as well, and that historical redlining practices underlie contemporary residential segregation patterns. This is becoming a well-documented social fact, as well as the fact that New Deal policies expanded the white middle class and are directly implicated in modern Black-white inequities and wealth. And so, it really shows the long arm of history in shaping contemporary health outcomes and moving forward. I think a couple of examples of measures to consider include variation and exposure to things like slavery, Jim Crow, lynchings, anti-miscegenation laws, stunned downtowns, the number of folks who are doing really good work in that space. We can think about exclusion from the economic benefits of the New Deal and GI bills, as well as racialized voter suppression.
And so, in many respects, I think what this literature is showing is that what’s past is prologue. And we’re seeing this with new laws, for example, the disproportionately disenfranchised Black and brown Americans. And in closing, I’d just like to highlight a couple, what I see as exciting opportunities for future research that I think will really advance our understanding of the links between racism and aging, health inequities, which I think can be used to inform ultimately efficacious racial equity solutions. So, for example, future studies should really better utilize longitudinal data to better understand the temporal dimensions of the relationships between structural racism and health such as the potential impacts of things like sensitive periods, durations of exposure, as well as causal effects. Right.
And moving forward, you know, I plan to use system dynamics modeling to explicitly model interdependence between forms of structural racism as well as feedback loops and lagged effects. I think that’s a really exciting area that we can start to really overlay temporal dimensions and a life force perspective with our understanding of the processes that ultimately lead to these wide health inequities that get larger and larger throughout the life course.
And also, multilevel research are really needed in this space in order to better understand the cross level structural races and linkages and the joint effects on racial stratification. So obviously, my talk here has been highlighting the role and really funny evidence of the role of states, which are really key. I hope that made that is clear, but of course, other levels also matter, right? and ultimately, you know, this is multifactorial and we should really be thinking about how structural racism across different levels, including state level influence, health.
And then, you know, as the data ecosystem is rapidly expanding, scholars are increasingly calling for a wider use of new sort of big data sources and social science research. And so, I’d just like to echo and expand upon these calls by recommending the use of these new approaches to address salient new research questions about how structural oppression shapes racial inequality.
And so harnessing digital trace data is especially useful as traditional data sources become increasingly costly, increasingly logistically complex and are becoming less representative of the target populations due to declining response rates as well as other selective forces. Also, moving forward, you know, I’d recommend testing the extent to which structural oppression affects inequality indirectly through intermediary social pathways such as unequal access to resources, things like education, income, health care, autonomy, and also exposure to risks, things like toxins, housing instability, victimization, as well as involvement in the criminal legal system and other pathogenic social conditions.
And so ultimately, this is really important. And to do this, we really need to address the and build upon really strengthen the data infrastructure on linking structural racism to health and the current data landscape for structural racism is rather confusing and scattershot.
As I alluded to at the beginning of the talk, you know, we’re willing to build a publicly available data infrastructure on structural racism to catalyze future research on its effects. And creating a data hub will reduce inefficiencies by increasing data sharing, coordination and innovation and so it’s essential that the data include contextual information at multiple spatial and temporal scales, obviously, including the state level. And I see a number of challenges and opportunities to really build a user-friendly data resource like this.
And currently, the process of linking existing data sets to contextual data can be cumbersome, but there are some wonderful opportunities and some recent examples of innovations that reduce these barriers and make it a lot easier, which Professor Montez will be discussing with us. So, I look forward to the Q&A.
Mark Mather, PRB: Great. Thanks so much, Tyson and as a reminder, if you do have a question, we have a Q&A box. So, I encourage you to type your questions into that box at any time. We’re going to take all of those questions at the end of the webinar. So, I will now turn it over to you, Jennifer.
Jennifer Karas Montez, Syracuse University: Great. Thank you. Tyson, I really appreciate your presentation. I love the historical perspective. It’s so important. And I can’t wait to read the 2025 annual review piece.
So, what I’m going to do with my time is give a high-level summary of some of the work that’s been going on using U.S. states to understand why U.S. life expectancy has not been keeping pace with other high-income countries over the last several decades. I don’t know if you can see this thing here where I’m going to try to hide it. Okay, great.
So, this work I’ve been involved in for several years now with this wonderful team. And I want to acknowledge also the funding that we received from NIA to do this work. So, I want to start off by just talking about why we’re focusing on states and state policies. If our goal is to understand what’s going on for the U.S. overall. Um, Just touch on some of the key learnings that we’ve uncovered over the last 5 or 6 years. Talk about how did we get here? Like, how did state policies end up being so important in explaining U.S. population health? And then where do we go from here? So, why are we focusing on states to understand U.S. Life expectancy. Well, this figure you’re looking at here has a line, a wiggly line for all 50 states. It shows their life expectancy trends from 1959 to 2019. And I pointed out Connecticut and Oklahoma, and I’ll do that a lot during the presentation because there are really interesting case study pretty illustrative of what’s happening. So, you can see these two states that we think of today is wildly different in so many ways, they weren’t always that different. So in1959, these two states had the exact same life expectancy. But you can see they’ve taken very different trajectories over this time period. And you’ll notice that, you know, there are some states, like Connecticut who, you know, are approaching, you know, 80, 81, 82 in terms of life expectancy. But there’s a lot of states that have kind of flatlined, if you will, since the mid-80s. And our thinking, our team’s thinking is that if we can explain why we have this divergence in life expectancy across states and why we have so many states that just really haven’t made progress in decades, then that gives us another piece to the puzzle in terms of why U.S. life expectancy is not doing what we’d like it to do.
So, I want to give you one other view of the same data, and in this view, instead of plotting all 50 states, I’m just going to plot the range in life expectancy across the states for every year. And this is what it looks like. And this data runs from 1970 to 2014. Because the study that I’m using this from examine those years. But what I want you to see here is that until 1984, states were actually becoming more alike in terms of their life expectancy. The range was shrinking. And in 1984, something happens and the range and life expectancy just keeps getting bigger and bigger and bigger. And if I were to continue this chart out through present day, you would see that range just grow year after year after year. So, you know, there are a number of explanations, a number of hypotheses for what might be happening here.
Our team has been focusing on the possibility that this divergence in life expectancy across states might be partly explained by the divergence in policies across states. So let me give you a couple of visuals of how states have diverged in their policies. So, this chart, it’s a little messy at first. It has 50 arrows. There’s an arrow here for every state. It’s not very important to figure out which state is which arrow. What these arrows indicate is how each state overall policy context has changed between 1970 and 2014. So, Jake Greenbank is a wonderful political scientist, created this overall measure of state’s policy context. And so, what I’m showing you here is where each state started on that measure in 1970. That’s the beginning of every arrow. And then where each state ended up in 2014 on that measure. And that’s the arrowhead. And so, what I want you to see is that we’ve got most states moving away from the center in terms of their overall policy context. Okay. So, they’re diverging just like states life expectancies are diverging. And again, I picked out Connecticut and Oklahoma so that you can see, you know, in the 70s, these states weren’t that different in terms of their policy context, but they sure are today. So, you might be thinking, well, give me some examples of how are these policies changed over time. So, I’m going to give you just four examples. This summary measure you’re looking at here has over 120 policies all wrapped in it. I’m just going to pull out four of those, four that we know are important for population health. So, let’s take minimum wage and earned income tax credit. Again, two policies that have pretty good evidence that these are important for population health. You can see in 1990, there’s effectively no difference between these two states. In in 1999, neither state offered an ITC. So, there’s absolutely no difference between these two states in these two very important economic policies. But by 2019, you can see these two states are wildly different in these two core economic policies. Let me give you one more example. I’m going to show you how these states have differed in terms of two very important health behavior policies. So, in 1990, these two states had almost identical taxes on a pack of cigarettes and pretty similar number of laws meant to increase the safety of firearms. But by 2019, these states, again wildly different. And it’s not just that a state like Connecticut in blue is moving in one direction in states like Oklahoma or just stuck. But you can see as states like Oklahoma are actually rolling back some of these policies that we know are good for population health. And you can see this most clearly in the firearm safety laws here, where the number of those laws has been rolled back in Oklahoma. So, let’s go back to this chart then. Now what I want to do is give you one more view of how state policy context have changed during this time period. So, what I’m going to do is I’m going to again take this overall summary measure of states policy context, and I’m going to plot the range across the states for every year in that measure. And this is what it looks like. So again, in 1970 until 1981, states were becoming more alike in terms of their overall policy contexts. I mean, it’s almost unimaginable today. But then after 1981, they become increasingly different, increasingly polarized, increasingly divergent. Whatever term you want to use in terms of their overall policy context. And so, if you were here five minutes ago, you’re thinking, I have seen a pattern similar to this before, and you have in fact. So, what I have here is now overlaying the two charts that show how the range in states policy has changed over time.
And the range and states life expectancy has changed over time. So bottom line, as states policy contexts are becoming more similar so were states. Life expectancies three years after states becoming start becoming more dissimilar in their policy environment, states start becoming more dissimilar in their life expectancy. So, at this point in our team’s journey, we thought we had developed some pretty compelling descriptive evidence that there’s a relationship here now. Is it causal? That’s what we wanted to find out. So, I’m going to walk you through some pretty high-level summaries of what we have. Think we’ve learned so far about whether that relationship is more than just a correlation.
So, we’ve found that actually U.S. life expectancy trends would have been significantly steeper if state policies hadn’t changed the way that they did. And that if we were to change all state policy, so all 50 states, if we were to change them all, to have either a very liberal or a very conservative policy context, we could alter us life expectancy by about 2 to 3 years, which is huge. That would put the U.S. about average among its peer countries, as opposed to being very securely at the bottom right now.
Changing state policies in this way would also alter the number of working age deaths each year by about 220,000, again, a very substantial number. So, in more recent work, we’ve been trying to put a more a finer understanding of where are these effects taking place for which causes of death are these effects happening and can we better understand the time lags under which these policies might have an effect? Do we see that policies have an immediate effect on working age mortality? Do we see that it takes a year or two years? How many years does it take? And so, I’m just going to summarize a piece of those findings. So, what you’re looking at here is how much the mortality rate of working age women would change if a state policy changed. And this is specifically CVD mortality among working age women. So, a lot of dots here. So let me walk you through what’s going on. So, look at the far left under the criminal justice policies. So, our analysis suggests that if we were to examine what would happen to working age women, CVD mortality during the very same year that a state’s criminal justice policies went from very conservative to very liberal. That was a lot of words. Let me say it again. So again, this is what we estimate.
What happened to working age women’s CVD mortality, If a state changed its criminal justice policies from conservative to liberal. So, we find that if we were to examine that in the very same year that that that policy was made, we would get a non-significant change in women’s CVD mortality. A year later, we start to see an effect, and within three years later, we start to see a significant reduction in women’s CVD mortality.
So, what this is saying is that if you believe these counterfactual analyses that it takes a while to see the benefits, the mortality benefits of moving from a conservative to a liberal criminal justice policy environment in the States. I’ll just walk you through a couple of other policies, gun safety policy. We find that we see almost an immediate effect in the reduction of women, CVD mortality when gun policies go from conservative to liberal.
And that effect seems to be stronger with each passing year. But there are other policies like health and welfare where we see an immediate effect, but over time that effect attenuates. So, what we take away from an analysis like this is that. The timing matters in our studies. And we don’t often do a very good job of taking timing into account. But imagine the implications. If I were to have only done this study examining no lag or a one-year lag, I would have walked away saying some policies don’t matter when they actually do or saying some do when they actually don’t matter after a given period of time.
And the other thing to take away from this is that not only do we need to pay more attention to it these lag times, but the appropriate lag time might depend on the specific policy that some policies just may take a longer time period to see a population health effect than others.
Another high level finding from our work is that the policies that have changed and polarized the most since the 80s happened to be the same policies that have the strongest associations with life expectancy and working age mortality, and those policies are mainly around labor and firearms.
And then the last finding I want to highlight, and this is not from our group, but it’s important. And I and I’m anticipating some of your questions later on, is that the growing disparities in working age mortality across states do not appear to be due to the changing socio-economic composition of a state’s populations.
So that’s, again, a very high level, a very selective set of what we’ve learned so far. So, what I want to do now is talk about how did we get here. And I want to do this because I want to make sure you, you leave this session realizing that the changes in these state’s policies, these are not exogenous changes, right? There are forces behind the scenes turning the knobs. So, if we want to move our analysis, you know, up the causal chain we need to be looking at who’s changing the knobs and why are they changing them. So, I’m going to point out, maybe my thing. It’s not moving. Okay.
So, I’m going to point out four interlocking forces. And I’ve got several citations down here. Really great in-depth books that you can read on this by sociologists, political scientists and others, a historian. And if you want just the quick and dirty that the very last article in the Milbank Quarterly covers these, these four issues.
So how did we get here? Four things really come together. One is the devolution of federal authority to the states, where states have gained increasing policymaking authority, especially since the Reagan administration. The other thing that has been happening that has given states this increasing power is there has been a proliferation of states enacting preemption laws to take away local authority, to do any number of things from raise the minimum wage, to mandate paid leave, to banning fracking. And so not only have states been given this additional authority by the federal government, they’ve been taking away authority from the states at the same time. Now, those two trends are not in and of themselves problematic but as a result of that, states have made very different decisions about their policies’ environments.
Some of those decisions have been unduly influenced by corporations, their interest groups and wealthy donors and some of the influences coming from the nationalization of political parties. And what I mean by that is, you know, we used to have a Republican version of Oklahoma and a different Republican version of Texas. But now there’s increasingly a Republican version across the U.S., just like there is an increasing Democrat version of policy context across the U.S. And I’m just highlighting this very quickly and again, I’ve given you some citations if you’re interested in digging into that further.
So, I want to conclude with talking about where do we go from here? And some of these recommendations are going to echo what Tyson presented earlier. I think my mouse is acting up here and I’m just pulling these ten ideas from editorial in the Milbank Quarterly this year on ten ways to better understand how shifting state policy contexts affect Americans health.
I’m not going to go through all ten, but I’m going to talk about some that keep me up at night. One of the things that we have got to do a better job with is giving more attention to policy bundles or indices. There is a very strong correlation across policies within any given state. If you were to tell me a state’s minimum wage, I can tell you almost everything else about that state. I can tell you can give you a good idea of what its tobacco taxes are, or whether it has an earned income tax credit, whether they’re right to work laws. Policies are becoming increasingly bundled. And so, the tendency in a lot of our work is to create summary indices or other kinds of indices, which I think is the right direction to go. But at the same time, I think we need some general guidance on how to use these indices responsibly. And there was a really great commentary by Harper and Andy last year around their concerns of using these kinds of indices. I don’t want to persuade anyone not to use indices, particularly because there is no single policy that can explain the difference between states. We wouldn’t choose a single policy to try to describe why U.S. life expectancy is different than that in Sweden, for example, because they’re just two completely different policy context and the same is true across states.
The other thing that I want to draw attention to, and this is going to echo what Tyson said, is that going forward, we need to pay more attention to lag times. We need to understand how these state level exposures accumulate across the life course. You know, by the time people are, you know, in the 30s, 40s and 50s, they have likely experience multiple different state policy context. They might have moved and so they experienced different context, or they might have stayed in their own state of residence. But, you know, as you saw earlier, states policy contexts are very dynamic and they’re changing.
So how do we capture this cumulative exposure to different contexts over people’s life course? And at the same time, how do we understand how the health effects of those exposures also evolve over time? So, I think, you know, version 2.0 of this work is has got to get just into this messy detail about how these dynamics, how to capture the dynamic interplay across the life course. And then the last point I want to draw on here is that I think, you know, as a group of researchers interested in this topic.
We need to develop an easy to implement method for accounting for inter-state migration. It is the question that comes up any time that those of us who are doing this work present it, and there’s no agreed upon way to account for it, it’s very, very difficult to account for it. In most surveys. You just don’t have the information. But can we not come up with some sort of agreed upon way, you know, baseline way to take this into account so that we can better isolate the effects of state policies on people’s health.
That is all I have. I’m going to stop here and say thank you so much. And I look forward to your questions.
Mark Mather, PRB: Thank you so much, Jennifer. We are now going to move to the Q&A. And so, as I mentioned before, if you have a question, we have a Q&A box. You’re welcome to put your questions into the box at the bottom of the screen.
And I will start with you, Dr. Tyson. There’s a question that came in through the chat asking if you could say a bit more about why different types of structural injustice vary in their geographic distribution. This person would have expected them to align more than they do.
Dr. Tyson Brown, Duke University: Yeah, that’s a great question. So, I’ll start by just noting that, you know, in my research, I argue that because racism is dynamic, flexible and really adaptive to socio historical context, that there are likely distinct contemporary racialized regimes, and that these regimes are characterized by different manifestations and modalities of racism across place. And so, whereas contemporary discrimination, discriminatory, legal and cultural forms of racism are especially pronounced in states in Southern and Appalachian regions. Findings from my research really illustrates how contemporary structural racism that’s manifest in discriminatory institutional contexts and racial inequities, that this is particularly severe in states and Midwestern and Northeastern regions.
And so, although the historical and modern roots of place-based differences in social races have not fully understood, you know, scholars have posited that that really the extreme degrees of contemporary structural racism reflected by racial inequality and institutional contexts in many northern states, them in part from institutionalized policies and practices of social control, racialized social control through exclusion and subordination. So, you can think about examples of resource hoarding, of redlining, of racial covenants and discriminatory policing and that these white supremacist tactics were increasingly deployed after the Great Migration because northern whites perceived the increasing Black population as a threat. Right, and so, given the fluid, shapeshifting nature of structural racism, it’s really important that future research investigate the etiology and consequences of these distinct contemporary racialized regimes across time and place. But that’s a really astute observation and frankly, we don’t know and so this is a really exciting time to be doing this research and I think it’s a really important time as well.
Mark Mather, PRB: For you, Jennifer, there’s a question in the chat, to what extent do changes in interstate migration due to increasing political polarization?
I think they’re talking about people moving because of the policy context. Perhaps, would that lead to a select group of unhealthier people in more conservative states and conversely, healthier people in in liberal states? Thinking about the change in interstate migration over time.
Jennifer Karas Montez, Syracuse University: That is a great question. So, I will say that in the ways that we have tried to account for interstate migration and also the study that I mentioned in the talk, we’ve not found that it is a major contributor. So that being said, I am not sure that that will those kind of null findings will hold up post 2020 due to both increasing polarization and people potentially moving to places that are more aligned with their political values, and the fact that, you know, we’re seeing a lot of people moving to red states, to Texas, to Florida, I mean, even Oklahoma. So, I don’t know, you know, on the whole how that’s all going to play out. But my working hypothesis at this time is that what we know about who moves and who doesn’t move might be different pre versus post 2020.
Mark Mather, PRB: Thank you. This question is I guess mainly for you, Tyson. But Jennifer, you’re welcome to respond in your future directions. You mentioned digital trace data, Tyson, could you expand a little bit more on what that type of data looks like, why it may be a future direction?
Dr. Tyson Brown, Duke University: I’d be glad to. So just a level set. Digital trace data includes things like social media activity, web browsing histories, search engine queries, e-commerce transactions, text messages, emails all where we live our lives today, right? And digitally and so there’s a lot of data out there and in my work, I argue that harnessing the data revolution, which is the rapid, you know, growth in data generation and storage analysis that’s driven by technological advances big data and digitization and transforming how information is used in decision making you know in research and everyday life. Right.
So, I think this is a really important and, and it’s especially critical, to use digital trace data to really capture what we termed as backstage cultural dimensions of racism. Right. And so, you don’t have to rely upon what people responses that they give in surveys because there’s social desirability. There’s a number of reasons that we may be getting not we may not be getting the full picture from survey data, which is still really important and even administrative, that can be really important. But there’s something unique about how we live our lives online that you know, they’re basically receipts. You know your digital life doesn’t lie, right? and we have a lot of digital traces, and so I see it as really, a really valuable way to complement more traditional data sources that many of us as demographers have used.
Mark Mather, PRB: In place and again, for you at this person, notice that there’s not a lot of overlap in the map to measures of structural racism with high values in the Midwest and West, and cultural racism with high values in the southeast and on the state level similar, I guess, to the other question, but how do you envision these measures potentially capturing different pathways for racism to impact population health?
Dr. Tyson Brown, Duke University: Yeah. Well, I guess see my previous response. You know, again, getting back to these contemporary racializing regimes, I would refer to the person who asked the question to the recent study. So, there’s a 2024 article in the Journal of Health and Social Paper. Between this author by myself and Patricia Home and also a couple forthcoming in your articles and your view of sociology and review of public health will be really digging deep with some of these issues and so I think this is really important. You know, the latter part of the question was, you know, what do I see as there, you know, sort of unique or joint pathways in shaping health. Right? So, whether you have sort of the institutional manifestations and you’ve got the more ideological, cultural dimensions and that is an empirical question that we really don’t know, but many of us are working on that. And so, you know, I hope that in a year we’ll have better answer and especially five years from now. But I think that really is one of the frontiers for understanding population health in general and more broadly, and then more specifically thinking about racial inequities in health including at the state level.
Mark Mather, PRB: Your question for either or both of you, is there an agreed upon way to incorporate different races living under alternative government structure like Native Americans or tribal lands, into measures of structural racism and population health when they might not be present in our standard data resources.
Dr. Tyson Brown, Duke University: I didn’t fully understand the question, but I will just note that I think it began by is there an agreement? and I would say no. You know, these are debate, you know, like any fields of science, there are contested debates. There are new revelations, there’s discoveries, we’re always innovating and I think that we’re always learning more about these sorts of racialized practices and processes and certainly I would note that, you know, really there is no one size fits all and that there are real limitations to all the ways in which we measure these things and how folks are coded, whether it’s self-reported, whether it’s by the interviewer, whether it’s, you know, there are other ways of getting at sort of trying to triangulate to figure out someone’s racial identity or status. But, none of them are perfect. And so, this is part of the job of trying to advance the field and do so in responsible manner. So, I appreciate the question.
Mark Mather, PRB: Do you want to say anything to that, Jennifer?
Jennifer Karas Montez, Syracuse University: Sure. I’ll just add that, I mean what the question reminds me of is just, you know, the need to examine heterogeneity more carefully and, you know, the need to go below the state level to understand some of these processes. You know, there the states are just super interesting unit of analysis. I mean, you know, we call them institutional actors. And, you know, I mean, Tyson made a great pitch for why states are important, but they’re not the only thing that matters. And so, I think to get at the kinds of detailed analyses that that question would require going below the state level.
I would also say that what it seems like is that, you know, states and probably also local environments too, seem to matter most for the health of people who are marginalized. We have this term colleges of firewall, right? So that if you have a college degree or higher, it almost doesn’t matter where you live, you’re going to have good health. But with each, you know, lower level of education, that the place that you live matters more and more for shaping your health. And so, but again I mean that those kinds of analyses are going to benefit from going below the state level.
Mark Mather, PRB: Great. And I just had one question for you, Tyson. You had mentioned things like hate speech and racial animus. And I am curious about how do we measure those types of structures, partly because they might be reported differently in different local jurisdictions or not reported at all in certain places. So, I’m wondering, is that where the social media comes in to capture some of those things, or is it a combination of social media and some of the criminal justice data?
Dr. Tyson Brown, Duke University: Yeah. Great question. I think that it’s like you mentioned, you know, I think it is really important to triangulate and use a variety of data sources. They all have their strengths and limitations and certainly reporting on official Bureau of Justice statistics on hate crimes as well. It’s got its limitations, to say the least. And there’s certainly variation across place about how and when they report if they report and so that data you know, it’s got major limitations but I think that we can get at things by looking at the proportion of hate groups and indexing it to the population size. Right?
So, I think that’s really revealing, you know, when we map that data, I think that, as you mentioned also that using things like social media data really can get at some of these sorts of things by whether it’s Google searches or people’s activity on other social media platforms and there’s also experiments that folks have done, including things like the AIT that get at sort of underlying logics and subconscious biases as well as survey data. I think that, you know, there survey data on racial resentment. If you map it, it’s in a rather predictable way, it varies across states in a predictable way and it’s highly correlated with other measures of racial essentialism and norms and things along those lines. So, I think that all of the above, frankly, you know, they all have their relative advantages and disadvantages.
Mark Mather, PRB: Well, we are at time, so I think we need to close here. But Tyson and Jennifer, thank you so much for joining this discussion. It’s an important and timely topic and for those who stuck around, thanks for joining. As I mentioned, this is being recorded. We will send you a link to that recording in the next few days. So, thanks everyone.

Today’s Research on Aging, No. 44 (2024)
Contributing Senior Writer
Associate Vice President, U.S. Programs
Senior Vice President, Programs
This brief explores recent research probing the dynamics of social connection and health supported by the National Institute on Aging. The findings point to myriad ways in which social ties bolster health—from slowing aging and boosting cancer-fighting hormones to preventing depression and protecting memory. Health policymakers and program planners can use this evidence to inform a variety of interventions—particularly those aimed at reducing social isolation in vulnerable groups—to support longer and healthier lives for older Americans.
Studies have shown that both the quality and quantity of our social ties shape our mental and physical health, health behaviors, and mortality risk. Researchers are studying multiple aspects of our social lives—from the levels of social support we receive to our activities and the strength of our social networks—to understand how they link to health outcomes.
Healthy, supportive relationships with family and friends may slow aging, concluded a research team from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and the University of Southern California (USC).1 According to their DNA, older adults with the most supportive relationships with spouses, adult children, other family members, and friends were aging one to two years slower than those who lacked such ties, they found. The pace of such aging is important—rapid epigenetic aging at younger chronological ages can contribute to the early onset of chronic disease and disability and premature death.

The healthiest older adults had strong social connections and just a 4% risk of dying within five years.
The authors, led by Kelly E. Rentscher, based their analysis on aging-related molecular changes in DNA among older adults participating in the nationally representative Health and Retirement Study (HRS). Even after factoring in smoking, alcohol use, and other lifestyle factors known to accelerate aging, the protective role of strong social relationships persisted, they reported.
Supportive relationships with spouses and children helped slow the pace of aging by more than three weeks per year, they found. Having support from other family members and friends also helped slow the pace of aging, by about three weeks per year and more than two weeks per year, respectively.
Overall, the findings affirm that both the presence of relationships and their quality mattered for longevity. The new study may support interventions with the potential to “prevent, slow, or reverse accelerated aging and extend the healthspan and lifespan,” the authors wrote.
Other ongoing research underscores the important role of social factors in the overall health of older adults. Linda Waite and Yiang Li from the University of Chicago found that the healthiest older adults had strong social connections and just a 4% risk of dying within five years, while those with the poorest health had weaker social connections and a 57% risk of dying within five years.2 Key factors linked to longevity included robust social networks and partnered sexual activity, highlighting the importance of social integration in maintaining health in later life. Their preliminary findings are based on nationally representative data from the National Social Life, Health, and Aging Project (NSHAP).
More new research poses that social connections may also improve the well-being of cancer patients by boosting protective hormones.
A research team from six major universities found that in ovarian cancer patients, social support was associated with higher levels of oxytocin—a hormone linked to some protection against cancer.3 Specifically, having a more positive outlook, a sense of purpose, and a role in caring for others at the time of cancer surgery were associated with higher oxytocin levels. (However, a person’s perceived closeness with others was not related to higher oxytocin levels.)
“Nurturance is consistent with the oxytocin-focused ‘tend and befriend’ hypothesis of female coping and stress response,” wrote the team, led by Michaela G. Cuneo at the University of Iowa. Thus, even though this research is in the early stages, feeling needed by others could have protective health effects for women with ovarian cancer.
Similarly, another team of researchers at the National Cancer Institute and the University of Wisconsin–Madison found that strong, supportive relationships between cancer patients and their caregivers were associated with better self-reported health for both parties.4 This was especially the case for those dealing with lung cancer, where social support was linked to better self-reported health 12 months after diagnosis. Dannielle E. Kelley and coauthors speculate that there may be a beneficial “partner effect” for lung cancer that can counter internalized and social stigmas associated with the disease for former smokers.

Strong, supportive relationships between cancer patients and their caregivers were associated with better self-reported health for both parties.
Social connections might also help a patient adopt more healthful behaviors after diagnosis—but the benefits could depend on their education level. According to Won-tak Joo of the University of Florida, college graduates have more robust health conversations with people in their social networks at the time of diagnosis, which may help explain why they are more successful at improving their health behaviors and show a better prognosis than those with lower education levels.5
“The cultivation of health discussion may be more active in earlier stages of illness when patients require external support to adapt to new lives with diseases,” writes Joo. For older adults with lower levels of education, Joo finds that both social networks and health conversations decline with disease diagnosis, suggesting a need for interventions to help this group.
Researchers are also studying how social ties affect the health of older people with disabilities. Karen L. Fingerman of the University of Texas at Austin and colleagues find that those with limiting disabilities were more likely to attend medical appointments when spending time with friends and family.6 And Sophie Mitra of Fordham University and coauthors report that older adults with disabilities have as much close, regular contact with partners, family, and friends as those without disabilities.7 For those with disabilities and others with serious medical conditions, social connectedness may lead to help with activities that improve their health and well-being.
Connectedness also affects our health in ways that ultimately impact our sleep. A recent study from China’s Xi’an Jiaotong University, the University of Texas at Austin, and the University of Maryland found that socially isolated older adults—those with smaller and less intimate relationships—had more depressive symptoms, were lonelier, and had more chronic diseases and pain, all of which contributed to greater sleep difficulty.8 Dan Zhang and coauthors argue that improving older adults’ social connections could enhance their mental, physical, and sleep health.
Some groups of people are more likely to be socially isolated than others, report Debra Umberson of the University of Texas at Austin and Rachel Donnelly of Vanderbilt University.9 Older married women may become socially isolated when a spouse needs round-the-clock care, while men who either never marry or divorce may begin experiencing social isolation in young adulthood.
In addition, non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic older adults are more likely to experience social isolation than non-Hispanic older white adults, they found (see Figure 1). Black and Hispanic Americans’ social isolation could be related to the impact of lifetime discrimination and financial stress, the researchers suggest. Using HRS data, the study measured isolation among adults ages 50 and older based on whether they are married or cohabiting, participate in volunteer activities, and have contact with parents, children, and neighbors.
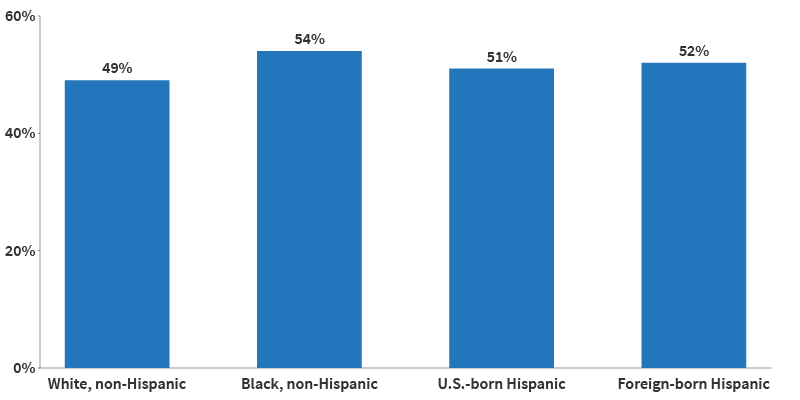
Source: Debra Umberson and Rachel Donnelly, “Social Isolation: An Unequally Distributed Health Hazard,” Annual Review of Sociology 49, no. 1 (2023): 379-99.
Another study out of Johns Hopkins University estimated that nearly one in four (24%) of older Americans living in the community are socially isolated, and one in 25 (4%) are severely isolated.10 To measure isolation, they examined participants’ living arrangements, religious attendance, social activities, and the number of people they spoke with about important matters. The study used data from the National Health and Aging Trends Study, which includes a nationally representative sample of Medicare beneficiaries ages 65 and older.
Being unmarried, male, and having low education and income levels increased the odds of being socially isolated, according to the analysis, led by Thomas Cudjoe. Specifically, men were four times as likely as women to be severely isolated, while people with annual incomes below $30,000 were twice as likely as people with incomes over $60,000 to be severely isolated. These findings offer “easily identifiable” factors to help program planners target those most at risk, the researchers wrote, noting that living arrangements, discussion networks, and social activities can all be modified to improve social connections.
Calling social isolation “an unequally distributed health hazard,” Umberson and Donnelly urge future researchers to undertake “a systematic assessment of social conditions that foster isolation over the life course” to better understand the root causes and identify ways to reduce isolation among those most at risk.
“We need to understand why people become more isolated over their lives, because social isolation is a public health issue,” Umberson said. “People became more concerned about isolation in the wake of Covid-19 because we were all more isolated for several years, but this is a problem that’s likely to become more serious, not less.”11
The stability of older adults’ lives may also contribute to richer social networks. While younger adults experienced turnover in social networks after a major life transition, such as getting married or having children, older adults maintained relatively stable social networks after such changes, including retirement, changes in marital status, or becoming empty nesters, found Jordan Weiss and team at the University of California, Berkeley.12 The authors suggest that for older adults, having stable, long-term (often decades-old) relationships make for more reliable networks.
A person’s temperament also may influence their lifelong social ties. Using NSHAP data, James Iveniuk at the University of Toronto finds that among older Americans, personality traits such as extraversion and agreeableness were associated with stronger social ties than openness, conscientiousness, or neuroticism.13 Thus, certain personality traits may strengthen the social connections linked to health benefits.
Older adults’ social networks may protect both their mental health and cognitive abilities. Getting help with daily activities may be an important reason why—since many older adults need assistance bathing, getting in and out of bed, and doing other tasks, some built-in social interaction can accompany aging. But feelings of closeness and companionship may also help stave off memory loss, loneliness, and depression—and may matter as much or more than geographic proximity or number of family or friends, new research shows.
To try to understand the importance of relationship quality, Sarah Patterson of the University of Michigan and Rachel Margolis of the University of Western Ontario looked at four groups of older adults with different types of family connections: those who were geographically and emotionally close with family; those who were kinless and without a partner or children; those who were distanced and lived far from family; and those who were disconnected and had no family members in their social network or did not know where they lived.14

The closeness of the relationships—especially with family—buffered loneliness.
“We were interested in understanding how much the presence of family ties matters for older adults’ well-being but also in measuring the quality of those relationship ties,” said Patterson.15
They found that older adults who lived near family members and discussed important concerns with them were less likely to report unmet need for help with daily activities than the other groups (see Figure 2). Meanwhile, those who reported no partner or family or disconnection had the poorest mental health and socialized less often—even less than those who lived far away from their family.
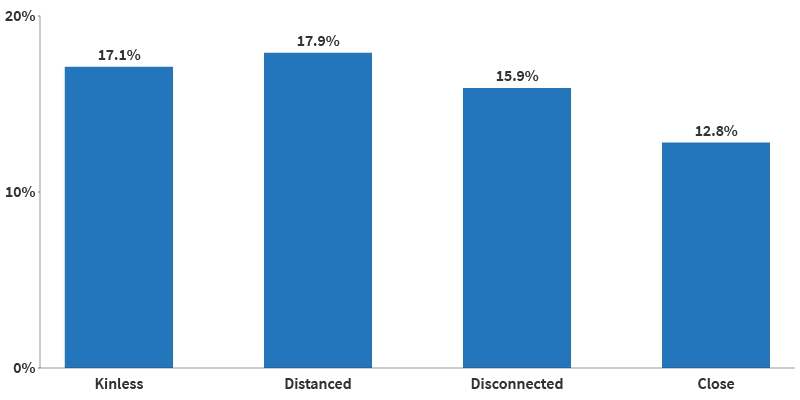
Source: Sarah E Patterson and Rachel Margolis, “Family Ties and Older Adult Well-Being: Incorporating Social Networks and Proximity,” The Journals of Gerontology: Series B, Volume 78, no. 12 (December 2023): 2080–89.
The findings suggest that the presence and strength of family ties matter for older adults’ mental health. “As families continue to evolve, researchers should strive to capture the size and shape of family networks, as well as the level of connection that older adults have with those kin,” the authors note.
In fact, social connections can also produce distress. Stephanie T. Child and Leora E. Lawton of UC Berkeley found that social companionship and emergency help mattered most to older adults, whereas having more people from whom they sought advice was related to more psychological distress.16 The findings suggest that mental well-being may be enhanced by enjoyable and helpful relationships, while those that are more demanding may detract from it. Data are from the UC Berkeley Social Networks Study (UCNets), which includes a locally representative sample from across the San Francisco Bay Area in California.
In a similar study, the Berkeley authors found that those who were more dissatisfied with their social networks also experienced more loneliness and isolation.17 Interestingly, it wasn’t the number of connections but the closeness of the relationships—especially with family—that buffered loneliness. Further, having a romantic partner helped older adults feel less isolated.
As Child and Lawton write, “evaluations about one’s own social network, including whether someone feels satisfied in the number or quality of connections they have to call on for social engagement or support, may be a more meaningful precursor of loneliness.”
Similarly, social engagement may be connected to cognitive benefits. Using Michigan Cognitive Aging Project data, Abbey M. Hamlin at the University of Michigan and colleagues find important differences by race in both social engagement and its connection to cognition.18 Older white, non-Hispanic adults engaged in more social activities than their Black peers, and those activities were linked to better episodic memory—or the recall of information from the past—and thus better cognitive health. The findings suggest that social isolation is not only more prevalent among older non-Hispanic Black adults, but also that it may be taking a toll on their cognitive well-being.
Several recent studies build on the well-established link between marriage and better physical and psychological health in old age, particularly for men. They examine some of the ways marriage may benefit health as well as the connections between marriage and other forms of social interaction.
New research finds that marriage can help men be less socially isolated throughout their lives. Umberson of University of Texas at Austin, Zhiyong Lin of University of Texas at San Antonio, and Hyungmin Cha of USC show that men tend to be more isolated in adolescence and young adulthood, while women tend to experience isolation in later life.19 Their analysis of HRS data shows that levels of social isolation increase with age for both men and women.
But gender patterns differ by marital history (see Figure 3). Among older adults in stable marriages, women are less isolated than men until age 60, but by age 68, men are slightly less isolated than women. This gender gap shrinks at older ages for those who have experienced marital disruptions, possibly because chronic health issues contribute more to social isolation among women, the authors note.
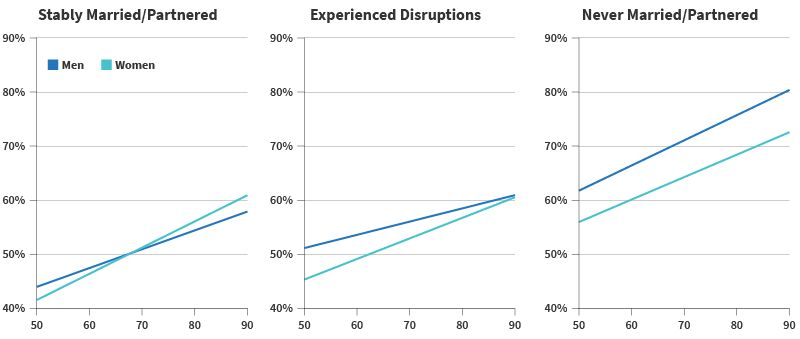
Source: Debra Umberson, Zhiyong Lin, and Hyungmin Cha, “Gender and Social Isolation Across the Life Course,” Journal of Health and Social Behavior 63, no. 3 (2022): 319-35.
There may be an unexpected physiological explanation for some of marriage’s health benefits. Drawing on lessons from primate research and using stool samples from a subset of participants in the long-running Wisconsin Longitudinal Study, researchers affiliated with the University of Wisconsin-Madison find that spouses in self-described close marriages tend to have more diverse and healthful gut microbiota compared with siblings, people without a partner, or married couples in less close relationships.20 Less diverse gut microbiota is related to obesity, cardiac disease, type 2 diabetes, and other inflammatory disorders, Kimberly Dill-McFarland and coauthors note.
Not all marriages are equal when it comes to social support and its potential health effects. Both men and women in same-sex marriages are more likely than those in different-sex marriages to offer concrete support to a spouse in distress, such as taking over chores or giving extra personal time, found Mieke Thomeer of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, Amanda Pollitt of Northern Arizona University, and Umberson.21 The team used a survey of 378 midlife couples ages 35 to 65.

Among older adults in stable marriages, men are less isolated than women.
Relationships can be a source of stress as well as support, and individuals in a marriage with a difficult or demanding partner experience a similar degree of loneliness as single people and more loneliness than other married people, another study finds.22 Shira Offer’s research at UC Berkeley draws on UCNets data to identify these differences and finds that the same is true for tough relationships with adult children.
Two other studies offer new insights into the mental health toll of the loss of a spouse due to death, separation, or divorce. People with less than a high school education face a higher risk of losing a spouse than people with more education, research using HRS data shows. But higher education levels do not lessen symptoms of depression when divorce, separation, or death does occur, find Claudia Recksiedler of the German Youth Institute and Robert S. Stawski of Oregon State University.23
People who lose a spouse often receive helpful support from social networks. Using NSHAP data, James Iveniuk of the Wellesley Institute and coauthors find that friends and family of older adults respond with social support after the death of a spouse, but less so when a close friend or other confidant dies.24
Multiple studies have shown that a neighborhood’s physical features—from broken sidewalks and high crime to plentiful parks and low air pollution—are related to older residents’ health and quality of life.25 Not surprisingly, the places older people call home also shape their social connections, thereby influencing both their physical and mental health.
Neighborhood social ties may promote sensory health, a study using NSHAP data shows. Older adults who have more social connections in their neighborhoods report better self-rated vision than those who have fewer connections, find Alyssa Goldman of Boston College and Jayant Pinto of the University of Chicago.26 More social ties may lead to more time spent engaging with people and places outside of the home, protecting visual abilities, the researchers suggest. Good vision is key to older adults’ ability to safely navigate their environment, they add.
For caregivers, social support can counteract the negative effects of living in less-connected neighborhoods. Researchers at the University of California, Davis and the University of Michigan show that neighborhoods with low social cohesion—lacking a sense of community and trust among neighbors—can take a toll on mental health in the absence of social support.27 This is particularly true for dementia caregivers, who face a high risk of depression related to the emotional and physical burden of their work. But dementia caregivers living in neighborhoods with low social cohesion had fewer symptoms of depression if they had family and friends to talk to and help with daily tasks, Oanh Meyer and team found.

Local opportunities for social connection may strengthen social ties.
Community-level interventions focused on increasing neighborhood connections—such as caregiver support groups in disadvantaged neighborhoods—could be important for maintaining caregiver health, the research team suggests.
The proximity of one’s close friends also makes a difference for mental health, reports Keunbok Lee of UCLA.28 Older adults with fewer confidants who live nearby show more severe depression symptoms when faced with traumatic events than those with more close friends in their neighborhood, according to Lee’s study of UCNets data.
Local opportunities for social connection may strengthen social ties and help prevent suicide. A new study finds that suicide rates are much lower among working-age adults, including people ages 51 to 64, in counties with more places for people to connect, such as public libraries, community centers, religious groups, coffee shops, diners, and entertainment and sports venues.29 These findings held true even when the researchers accounted for differences in health care availability, age, education, race/ethnicity, and proximity to metropolitan areas.
Gathering places, part of the social infrastructure, may buffer suicide risk and improve mental health by boosting social connections, reducing social isolation, and facilitating social support, trust, and information and resource sharing, report Xue Zhang and Danielle Rhubart of Penn State University and Shannon Monnat of Syracuse University. Local governments should consider partnering “with market-based services and social service agencies to increase the availability, access, and use of spaces that promote social interaction,” they write. In addition to helping to lower suicide rates, building more robust social infrastructure may also support overall health, they suggest.
Research has established that living alone at older ages raises the risk of poor health, early death, and dementia. New evidence demonstrates that living alone for extended periods increases the risk of dementia more strongly than previously thought.30 Every two years of living alone is linked to about a 10% increase in the risk of dementia, according to study authors Benjamin A. Shaw of the University of Illinois Chicago, Tse-Chuan Yang of the University of Albany, and Seulki Kim of the University of Nebraska.
Social isolation may explain this dynamic. Their analysis, based on HRS data that tracked more than 18,000 older Americans for 18 years (2000 to 2018), suggests that a lack of mental stimulation combined with limited day-to-day companionship may increase stress “that, over time, could accumulate and eventually lead to cognitive impairment.”
Another recent study shows that the impact of social isolation extends to diet and nutrition. Analysis of data from an HRS nutrition survey shows that older adults—particularly men—living alone with no adult children or friends in their neighborhood had the lowest fruit and vegetable intake.31 Lack of motivation to cook and eat healthy may explain this pattern, according to Yeon Jin Choi, Jennifer A. Ailshire, and Eileen M. Crimmins of USC.
Because fruits and vegetables provide key nutrients for maintaining health and protecting against age-related diseases, the researchers recommend local agencies consider ways to improve social engagement among older adults who live alone to boost health outcomes. They also suggest providing help with grocery shopping (such as transportation) and meal preparation (including home-delivered meals).
Phone calls and Zoom or FaceTime gatherings replaced in-person get-togethers for many people during the COVID-19 pandemic shutdowns, but a growing body of research suggests virtual interaction cannot fully replace face-to-face contact. Two recent studies, one led by Namkee Choi at the University of Texas at Austin and the other by Louise Hawkley at NORC at the University of Chicago, show that older adults who had less in-person time with family and friends and more phone calls during the first year of the pandemic were more likely to experience loneliness.32

Phone calls are an important source of social connection for older adults with impaired vision or hearing.
Older people with impaired hearing or vision may be an exception—phone and video chats appear to have protected them in 2020 from depressive symptoms, find Amanda Zhang and colleagues at the University of Chicago.33 One reason may be that phone calls are important for the mental health and mood of people with small social networks, replacing some of the day-to-day interactions that shrink with age and physical impairment, report Yijung K. Kim and Karen L. Fingerman of the University of Texas at Austin, based on another study.34
At the root of these mixed findings on digital versus in-person interaction may be the immune system. A team of researchers from Colorado State University and UCLA show that face-to-face interaction protects health-promoting immune functions in ways that digital contact does not.35 They examined the gene activity that stimulates inflammation and inhibits antiviral responses in the blood of adult study participants during the COVID-19 social distancing period. Participants who had mainly online social contact had higher levels of such unhealthy gene activity than those who had more in-person social contact.
“Digitally mediated social relations do not appear to substantially offset the absence of in-person/offline social connection,” the research team concluded.
As many as one in four older Americans are socially isolated and face an increased risk of poor health and early death. The research documented in this report underscores the links between strong social ties and longer, healthier lives. U.S. Surgeon General Vivek H. Murthy has called for making social connectedness a national priority, “the same way we have prioritized other critical public health issues such as tobacco, obesity, and substance use disorders.”36 His recent advisory, Our Epidemic of Loneliness and Isolation, identifies multiple actions based on growing research evidence, including:
Social Isolation and Loneliness Among Older Adults: Opportunities for the Health Care System, a recent report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, details ways health care organizations can address social isolation among older people by better educating their staff to intervene and aligning with other community agencies. Specific recommendations include:
“Our relationships are a source of healing and well-being hiding in plain sight,” Murthy said, “one that can help us live healthier, more fulfilled, and more productive lives.”37

Accessible public transportation can help improve older adults’ health by connecting them to both medial care and social activities.

October 29, 2024
Senior Program Director
U.S. society and policy disproportionately burden women with unpaid (or underpaid) caregiving responsibilities. In her new book “Holding It Together: How Women Became America’s Safety Net,” author Jessica Calarco (University of Wisconsin-Madison) draws on five years of research to show how thinly stretched American women are.
In June 2024, PRB convened an expert panel to discuss Calarco’s key findings and their implications for reproductive health care policy and explore additional research on abortion, contraception, fertility, gender, and motherhood. Calarco was joined by Tiffany Green (University of Wisconsin-Madison), Karen Benjamin Guzzo (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill), and Jocelyn Foye (The Womxn Project), and nearly 200 attendees.
Women in the United States are often the primary caregivers for children, older parents, and others, even when they have full-time jobs, and even when men could share in the care work. This gender gap in caregiving can have significant negative economic consequences for women, especially when that work is unpaid or underpaid. Coupled with complex and inaccessible social safety net programs, the caregiving burden can limit women’s career opportunities, reduce women’s earnings potential, and increase financial hardship for women and their families.
Systemic inequality and discrimination have taken a financial, physical, and emotional toll on marginalized groups, such as Black women, Indigenous women, Hispanic and Latina women, disabled women, and transgender women. For example, Dr. Green shared that the practice of birth cost recovery (also referred to as the “birth tax”) in Wisconsin disproportionately affects Black families and creates financial burdens for fathers, hindering their ability to participate in their children’s lives.
U.S. policies have historically burdened women with caregiving responsibilities and offered limited protections compared with other nations. When asked “What can be done?”, panelists offered suggestions based on their research:
By addressing the systemic challenges faced by caregivers, we can create a more economically vibrant, equitable, and healthy society.
The first PRB Book Talk webinar discusses the book, Holding It Together: How Women Became America’s Safety Net, with author and sociologist Jessica Calarco. In Holding It Together, Calarco (University of Wisconsin-Madison) draws on five years of research to show how U.S. society and policy disproportionately burden women with caregiving responsibilities. With an expert panel, we discuss Calarco’s key findings and their implications for reproductive health care policy and explore additional research on abortion, contraception, fertility, gender, and motherhood.

September 5, 2024
The United States is facing persistent labor shortages, limiting businesses both large and small and spanning all industries. What’s driving these shortages, and what can be done to address them? On Sept. 5, 2024, PRB and the Critical Labor Coalition discussed the latest data behind the shrinking workforce and explore potential policy solutions.
Panelists include:
Diana Elliott: Great. Thank you all so much for joining us today. My name is Diana Elliott, and I’m the vice president of programs at Population Reference Bureau, or PRB. PRB is a not for profit and nonpartisan research organization that uses population data to improve the health and well-being of people in the US and globally. We are delighted to be hosting this webinar today with the Critical Labor Coalition and our special guest, former Labor Secretary Alexander Acosta. On the heels of Labor Day, we are reflecting on the state of the labor force. Anyone who reads the news these days is presented with an array of data in the US that suggests that any one time that we don’t have enough workers or enough workers with the right skill sets, or we have too many workers in certain professions or sectors. This webinar is an attempt to cut through the noise to present who is in the workforce, why we have long term challenges ahead of us, and some possible solutions.
I am delighted that both former Labor Secretary Alexander Acosta and CEO of the Critical Labor Coalition, Misty Chally, are here with us today to discuss these issues. First, we’ll hear remarks from Alexander Acosta, former US Secretary of Labor. He will present background about the state of the US labor force, drawing upon his experiences as the former head of the US Department of Labor. Next, I will present how demographic trends matter for the labor force now and in the future. Then Misty Chally will present information about the Critical Labor Coalition and why they are working to find solutions to labor shortages and the legislation they are seeking to advance. We will conclude with a Q&A session with all panelists, where we welcome audience questions about the workforce now in the future, and ways we can work towards solutions.
Finally, a bit of housekeeping before we begin. If you have any questions during the presentations, please type them into the question box in your webinar control panel. Attendees will be muted. We will also share a recording of the webinar after the event on PRB’s YouTube channel. And now I am delighted to introduce Alexander Acosta, former US Secretary of Labor, for his remarks.
Alexander Acosta: Diana, thank you. I appreciate the invitation from from you and from Misty to be part of this webinar and in particular, I appreciate the opportunity to be, you know, to to go over the data because I think there is so much discussion and, and, frankly, noise in this space that it’s important to take a step back and just look at that data and say, where does the data lead us? there’s a PowerPoint that I think you have, and I want to start with the first slide if if we could.
So, the first slide is a slide going back to the year 2000. that’s very simple. This tells so much of the story. It starts out with this is the labor force participation rate. All my data, I should say is from either the Bureau of Labor Statistics or the OECD, which is an international organization. These are the aggregators of data that are sort of the gold standard, in my opinion, in labor data. And I think we often focus on the unemployment rate. But what really matters in the long term is the labor force participation rate. Put simply, the unemployment rate is of those who are working or looking for jobs, what percentage cannot find jobs? The labor force participation rate is much broader, it says of the population, of our adult population that is not institutionalized. That is by, you know, excluding individuals who are in the military, who are in jail or in other institutions. Of those who could work, what percentage are either working or looking for work? And as you see, in 2000, the number was pretty close to 68%. And then there’s a pretty dramatic and steady decrease until about 2016 where it levels off, goes up a little bit, and then Covid hits and we haven’t quite recovered to where it was.
The next slide sort of puts it all in numbers with a little bit more specificity. And so, you see that we started out at 67.3%. By ‘04 we dropped about 1.2. We sort of hovered through ‘08. By 2012, we dropped again, 2.5 by 2016. We dropped another point. Between 2016 and 2020, we actually managed to go up. We went counter trend, for a short period of time and and then not only have we dropped again, but if you look at the projections that come from the Labor Department, the, the drop in the labor force, participation is expected to continue, through 2028 and again to 2032. you know, what’s truly frightening about this is that by 2034, the labor force participation rate, in other words, the percentage of Americans that are working or looking for work is going to be about the same level as the worst month of Covid. So if you think back to the worst month of Covid, all those folks that said, we’re not going to be part of the labor market, by 2034, that is going to be the everyday state of play in America, not according to me, but according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. and the question is why it’s complicated, but it’s easier to say to some extent. Why not?
Moving to the next slide if we could. You know, I put this up here and this is from 20, from the year 2000 to to the year 2015. You know, it breaks different age cohorts down by race. And I put it up there because I think it’s important to recognize that the effect is, is quite comparable, regardless of race. You know, if anything, you see a larger percentage drop among Caucasians than among other racial or ethnic groups. But you see in this slide and the next slide, you see that, you know, race is not really, something that easily explains, you know, this massive, really, really substantial, massive drop in labor participation rate.
Moving to the next slide if we could. And again, the same issue. You know race is not the the explainer if anything. You know overall you see a larger drop in Caucasians than others. But race doesn’t explain, moving to the next slide. So, this is one of my, my favorite slides. Maybe favorite isn’t the right word. I think the most interesting slides here are the Bureau of Labor Statistics. They always do projections going out about ten years, and they break those projections down by age cohorts. And, and you see that they’re overall predicting a pretty substantial decrease in labor participation rate. in four years out, eight years out. And if you look on the website data, the trend continues, and you see that the trend is much stronger with men than women. the drop is much less for for women than it is for men. but you also see that the drop is greatest among the youngest age cohorts. And this matters because we often hear that part of the problem is that the baby boomers are retiring, that we’re- that our workforce is aging. And that is an issue because the baby boomers are a very hard-working generation. And as they age out, we lose a lot of, you know, both in terms of number but also in terms of workforce participation. We lose a generation that worked very hard, that was very large and that heavily participated in the workforce. But we also see that it doesn’t fully explain it because as new age cohorts enter the labor market, the younger you go, the larger the decrease in labor force participation rate. So, there is something about this decrease that is unrelated to the retirement of the baby boomers, or something about how we’re addressing, newer generations that either discourages or does not connect them to the labor force the way previous generations were connected.
Moving on to the next slide, if we could. So, this is, I think, something we don’t talk about enough and something that’s very important. This data comes from the OECD, which, as I said, is the gold standard for international data. They aggregate data from several countries. And this shows the United States when compared against, the G7 nations, and the eurozone nations. And as you see on the far right, this is in 2000 in red, you see the United States, we had the highest labor force participation rate compared to all the eurozone nations in the G7 nations. And I should say that this particular slide, pulls individuals from 25 to 64. And that’s important because we want to adjust different countries have different university systems, different points at which individuals stop being students and, and fully enter the labor force and different retirement ages. And so, the 25 to 64, is an important comparator when you’re looking internationally because you’re sort of cutting off the two age extremes to really prevent different retirement systems and different university systems from affecting the data. So, in 2000, we had the highest labor force participation rate compared to all our competitor countries.
Let’s look at the next slide though. So here we see by 2008 the United States the red bar was was pretty much right in the center compared to the eurozone countries. And let’s look at the next bar. The next slide I’m sorry. and so, this is 2016. And in 2016 you see that the United States now is one of the lowest rates of labor force participation rate compared to the eurozone countries, you know, and we’re far to the left. We’re, basically fourth from the bottom after as I look closer, after Italy, Greece and Belgium and all the other countries had a higher labor force participation rate. And I think this is important because much of what is happening here is not attributable to a broad global change but is really attributable to something happening within the United States compared to our competitor nations. Either we have done something to change our percentage and lower our percentage, or they have done more to correct the downward trend that I think we’re seeing globally. Because we have fallen behind quite substantially. You know, from being number one to being fourth from the bottom compared to the G7 and the Eurozone nations. And so, I put this out there because I think long term, you know, we can talk about solutions and there’s some solutions in the short term. Part of the issue here is that, you know, businesses want solutions now. They don’t want to talk about societal trends that might take 5 to 10 years to fix. And I understand that because businesses need workers now. And when you talk to Congress and when you talk to policymakers, sometimes it’s easier to present solutions that you can pass a law tomorrow and say, we’re going to have this influx of workers, but I don’t think we talk enough about this, this 20 year trend that, you know, that stopped for a little while, but has now restarted and and is going in the wrong direction because, you know, the United States should not be fourth or fifth from the bottom. We should be at the very top of this.
And so how do we change it? You know, and one final point. I’m not adverse to short term solutions. We need short term solutions, but we can’t implement short term solutions without paying attention to this long-term trend. If today we were to apply a labor force participation, the labor force participation rate that we had in the year 2000, right, we would have 16 million more workers. 16 million. And so, while we can talk about the unemployment rate being lower than it has been historically, for, you know, over the course of 20 years, it’s up a little bit now and it’s, you know, on the upper trend. But it’s you know, in the grand scheme, the real employment rate as a percentage of population is lower than it’s been in a long, long time, lower than it’s been in decades. And those 16 million individuals that are not engaged with the labor force really matter.
We are a different nation of seven out of ten people working to support the three out of ten that are not. Then if only six out of ten are working to support the four out of ten who aren’t. Not simply in terms of our population dynamics, but in terms of tax structures, distribution of tax burden, ability to repay debt, not to mention, you know, the impact that has on GDP. And so, I think this is an issue that we need to address in the long term, you know, with much more specificity. And with that, I’ll, I’ll yield the time. And I look forward to hearing from my fellow panelists.
Diana Elliott: All right. Thank you so much, Secretary Acosta. Really appreciate your remarks. Working at PRB, where we think a lot about demographics and population trends, it can be somewhat frustrating to see news stories that have such short-term focus. Right? Much as Secretary Acosta was suggesting so understanding point in time, employment is incredibly important for getting a pulse check on the economy. It tends to overshadow the bigger picture story.
Next slide. For example, the unemployment rate is followed very closely in the news cycle because it’s an important piece of evidence about whether or not, for example, we’re in a recession. But the larger context is not always presented fully in the news. As of July 2024, the unemployment rate was 4.3%. This is not as low as it was a year ago when it was 3.5%. But it’s still better than what economists consider to be full employment. And that detail isn’t always shared in the news stories. But the unemployment rate, again, doesn’t tell the full story. We’ve had a longer-term trend where there are more job openings than unemployed people, and even if some of these job openings are ghost jobs, something you’ll also hear about in the news or postings that employers don’t intend to fill. We can safely assume this 1.4 million gap between jobs and workers is not all ghost jobs. So actually, back to the previous slide, please. So, the unemployment rate is also a lagging indicator and is not terribly future looking. It all misses the nuance and context around who isn’t working and why, but demographics can fill in some of this information as I’ll walk through. The U.S. has had a rapidly changing age structure and changes in mortality and illness that may be contributing to long term challenges in the labor force. Further, policy decisions in the U.S. may contribute to reasons why not everyone who wants to work is actually working.
Next slide. So, as was hinted previously in the in the prior prior remarks, one of the biggest shifts in the U.S. and one that is changing the labor force right now is how we are aging. Between 2000 and 2023 and the 21st century alone, the U.S. median age has increased by 3.8 years. If you lined up every person in the U.S. from youngest to oldest in 2023, the person in the middle would be 39.1 years old. In part, this is because baby boomers, the large cohort born after World War II between 1946 and 1964 are aging. This is affected and is currently affecting the labor force because baby boomers are retiring. To put this into perspective, as of 2022, 57% of baby boomers were over the age of 65. And we know that by age 65, 90% of Americans are. Previous slide, please. 90% of Americans are already collecting Social Security. We also know that most retirees report having retired at age 62. This means that most baby boomers are retired. The youngest of baby boomers turns 60 this year, meaning all are eligible to access their retirement savings without penalty. And by 2030, most will be over the age of 65 and will have exited the labor force. One of the themes you may hear about in the news is the prediction that older people will live longer and work longer, but the evidence so far suggests that hasn’t come to pass for the majority of older Americans. While Warren Buffett may be hard at work at 94, the data suggests this isn’t the future for most people.
Next slide. So, another way to look at this is through the age dependency ratio, which looks at the share of those aged 65 and older relative to those of working age, ages 15 to 64. Since mid-2000, the age dependency ratio has reliably gone up every year. In short, we have a growing number of retirees, which has implications for Social Security and public pensions, for example.
Next slide. An important reason why this ratio is shifting is because our birthrate has declined in the U.S. since 2000, the total fertility rate has been well below the replacement rate. Why is 2007 a significant year for thinking about the labor force? Because those born in 2007 are now 17 years old and entering the labor force, the provisional fertility rate and 2023 total fertility rate was 1.6 births per women, down 2% from the previous year. As context, the replacement rate is generally considered to be 2.1. Put simply, there are too few young Americans and future workers being born to replace retirees. In the news, you may hear complaints about how young people aren’t working. I would argue that’s an incomplete statement. In fact, there just aren’t as many young people to fill roles, which makes workforce training programs all the more important in the larger U.S. context.
Next slide. And the U.S. is not alone in confronting these challenges. Our peer countries are also facing a shrinking share of the working age population. The share of the working age population in Japan has dipped below 60% through a combination of factors increased longevity, fewer births, and tight immigration policies. And there are adaptations to that new reality underway. The U.S. and Canada have both seen a decline since the mid 2000, and Canada remains slightly above the U.S., in part because they’ve implemented various policies to try to change that trajectory.
Next slide. Unfortunately, we also need to confront that deaths among working age adults have risen in the U.S. in recent years. Since 2010, as a result of various conditions, there have been a decrease, a decline in the number of working age adults in the U.S. Covid-19 certainly exacerbated this. In 2020, it’s estimated there were 58 excess deaths per 100,000 people ages 15 to 64. So excess deaths are not just from Covid-19, but from other illnesses that went untreated because of pandemic lockdowns. Further, long Covid symptoms may be depressing labor force participation, similar to general trends with Americans with disabilities. Workplaces may not be accommodating people with long Covid optimally, and others with long Covid may be leaving the workforce to handle their symptoms. One study estimated that 1.6 million workers were missing from the workforce in 2021 because of long Covid symptoms. So, because so little is known about the trajectory and treatment of long Covid symptoms, it’s unclear how permanently this will affect the labor force in the long run.
Next slide. This graphic from Paris 2022 publication “Dying Young,” authored by Richard Rogers of the University of Colorado at Boulder and coauthors, shows that the U.S. really stands apart from other peer countries for the probability of death among teenagers and young adults in the U.S. This suggests that there are health and safety policy challenges in the U.S. that are contributing to these sad and tragic outcomes. And other countries have done a better job creating safer environments for their young adults and accordingly, their future workforce.
Next slide. Demographers also think about immigration and how it matters for our labor force. Immigrants and U.S.-born children are a significant share of the overall labor force. but in recent years, immigration policies have contributed to backlogs, which made things worse during the pandemic. While things have mostly returned to pre-pandemic levels, there remain persistent problems with issuing work permits and visas to immigrants who have entered the country legally. For context, in 2023, the overall population added 1.6 million people. This is despite a falling birth rate. The census attributes this increase to the resumption of post-pandemic norms around immigration, as well as fewer deaths following the pandemic uptick.
Next slide. Beth Jarosz at PBB analyzed the most recent Census Bureau projections in a blog published in 20th November of 2023, and describes how the most likely scenario for the future population of the U.S. is for us to reach a high point in our population around 2080, and then to begin slowly losing population with us reaching the year 2100 with about 366 million people. For perspective, a baby born today would be 76 years old in 2100. And these numbers in part reflect our slowing fertility in the U.S. However, if immigration were to slow or to be halted in the U.S., we reached these inflection points sooner, potentially within the next 1 to 2 decades.
Next slide. In fact, she shows that within 20 years the main series or the most likely scenario for the future shows that within 20 years, deaths will outnumber births. This is all accelerated with the curtailment of immigration from current levels. Next slide. But let’s move away from a doom and gloom scenario, because policy matters tremendously in terms of how we confront these demographic challenges, we’ll think about that with respect to the U.S. labor force.
Next slide. So one way to confront the demographic challenges is to think about who in the working age population would likely be more engaged with work and how we can address those barriers. One group is women, particularly those with young children. The U.S. is notable among our peer countries for a lack of family friendly policies. This limits women’s full labor force participation. That said, women’s labor force participation is now above pre-pandemic levels at 77.6%, but it is still lowest among those with young children. For perspective, Canada’s labor force participation rate for women is 84.9% and is notable for women with young children. The Canadian government has invested billions in recent years to cut childcare costs for working parents. One of the stories you may hear about in the news is that men’s labor force participation rate is also down. That is true from a historical perspective, but it remains higher than women’s rates. men, for example, have a labor force participation rate at 89.1%. Missing from these news stories is why there’s even a gap at all between men’s and women’s labor force participation rates, when women are now outpacing men in their educational training, and the U.S. states are often policy laboratories for what could be. One example to elevate here is New Mexico and its shift to prioritize early childhood education and care. They created a state level department, increased investments in early childhood education, and expanded subsidies for families. This could be a state to watch in coming years for policy examples that help working families and improve parents’ engagement in work.
Next slide. Another group that could be better engaged with the labor force are people with disabilities. In fact, this group of workers saw improved employment during the pandemic, in part because remote work enhance their abilities to engage with work. Between 2021 and 2022. There was a notable increase in their employment and a notable decline in their unemployment. That said, for people with disabilities, their unemployment rate is still two times higher than those without them. Studies have shown that accommodations matter for the employment of people with disabilities. Nearly half of needed accommodations are free, and for those with a one-time cost, the expense is typically $300. So again, states offer examples for policy ideas to engage people with disabilities who are eager to join and be a part of the labor force. For example, Ohio established the state’s vocational apprentice program in 2019, which are paid apprenticeship opportunities within state government. This not only helps people with disabilities enhance their resume and potentially find a permanent state government job, but it also helps to fill gaps within state government offices.
Next slide. So, let’s reflect on what we know about the state of the U.S. labor force. Births have slowed in the U.S., and there is neither a growing cohort of young people nor older Americans who will be tomorrow’s workers. Challenges such as mortality and morbidity present uniquely American challenges in our labor force. As we look to the future, we’re confronting a demographic future where there are fewer workers amidst an increasingly aging population. But policy can intervene to better engage workers who have been sidelined and want to be more engaged in work. There are examples happening in other countries, and even within the U.S., that suggest ways to attract, retain and train the workforce amidst overarching demographic shifts in the labor force.
Next slide. So, thank you. And now at this point, I’m going to turn it over to Misty Chally of the Critical Labor Coalition to additionally share how her group is working on legislative solutions to these issues.
Misty Chally: Thank you, Diana, and thank you for everyone who took the time to join our webinar today. Just waiting for the slides in a moment. And while we wait, I would just like to mention an add-on to the Secretary and Diana’s comments about the workforce. I think also what we’re seeing is the workforce, the nature of the workforce has changed, with a lot of people working from home and, you know, having flexibility as an Uber driver and setting their own schedules. We’re seeing a lot of people leaving places of employment where you need in-person attendance, if you will, a set schedule, somebody to be in a restaurant or a hotel or a retail location, where you actually need people physically there. And so that’s why when you go to a restaurant and you know, there’s a long wait, but you see a lot of empty tables, it’s because of the labor shortage, because there simply are not enough workers in those in person needed areas, to fill those spots. So, want to just to add that to the conversation and yes, AI does help in some ways, and definitely contributes, but you cannot replace all workers with I although it does help the employers and the workers in many ways. So, it looks like we’re we’re back up. So, thank you for letting me give my little personal opinion on that.
My name is Misty Chally, executive director of the Critical Labor Coalition. My background is in representing franchisees and franchisee associations. And so, this issue came up when I was talking to a number of different franchisee associations. called the Critical Labor Coalition, and they represent everybody from Planet Fitness and Domino’s to Burger King and Meineke. So, all different industries. And we were talking about, you know, what are our key issues, regardless of industry. And the issue was the labor shortage. Everybody was and continues to have an issue with the labor shortage. and that’s really where the Critical Labor Coalition was formed.
So next slide please. So, I formed a Critical Labor Coalition in July of 2022. It’s a nonprofit 501(c)(4) to address the issues of the labor shortage. We seek legislative solutions to address labor shortage, understanding that there is no silver bullet here. I mean, there are different ways to approach it. and that’s what we do. Our members are trade associations, corporations, individual business owners. And I should note that we advocate for bipartisan policies, that incentivize individuals to return to work and that grow the workforce. And how we do that is by focusing on different communities of workers. How do we get them into the workforce? Everybody from guest workers to seniors to, entry level workers to veterans, to those in the Second Chance community, the disability community and caregivers. We look at them individually and collectively to determine how do we get them to return or enter the workforce.
Next slide. These are our members right now, as I mentioned, trade associations, individual employers like Chipotle, the Restaurant Association, hoteliers, um staffing services, the um Amusement Park Association, food distributors. I mean, everybody of every industry is still having this problem. SHRM, representing the human resource community of everybody continues to have this issue. And so, I am honored to have them as members of our coalition.
Next slide. So how do we get something done? How do we address this labor shortage? Well, the Critical Labor coalition focuses on two issue areas. One: How do we grow our workforce? And two: How do we promote tax incentives to get those in the country already in the country, incentivized to enter or reenter the workforce? And I’ll go into these, individually.
So next slide please. So, when we’re talking about what are the tax incentives, CLC uh supports a number of different tax incentives. one being a bill that would expand the work opportunity tax credit or WOTC, and that is a tax credit for employers to hire from, certain communities that face roadblocks to entry. That bill was initially or WOTC was initially passed in 1997 and hasn’t been updated since. So, this bill would increase the percentage of the credit from 40 to 50% of up to $6,000. Again, these are not silver bullets. These are not significant amounts of money, but they help get people back to work. And then it has a provision that would provide additional support if those workers work at least 400 hours or stay in their employment. EITC for Older Workers Act. EITC stands for the Earned Income Tax Credit, and this is a tax credit that would expand to include seniors over 65 without an eligible dependent. Right now, to qualify for the Earned Income Tax Credit, you have to be part of a specific community similar to WOTC and earn under a specific amount. But right now, if you are older than 65, you can’t get the earned income tax credit. And so, what this bill does is it eliminates the top age restriction for EitC eligibility. And the third one, the credit for Caring Act is bipartisan bicameral bill. And it gives a tax credit to people that are family caregivers, those that go to work, come home and have caregiving expenses that they then have to go and take care of a loved one, which is very broadly defined. and so again, it helps those people that have to go to work and then come home and take care of a loved one. And I should mention, our Coalition works with what we call strange bedfellows. So, while we represent the business community, we’re working with AARP, on these issues, as well as nonprofits, antipoverty centers like Golden State opportunity, out of California and where we want to show Congress that this is not a partisan issue. Businesses support this. AARP supports this, antipoverty group supports this. This is just a workforce issue.
Next slide please. And then when we focus on workforce growth how do we get more people here? Again, we are working with groups like Refugees International, the Asylum Seekers Advocacy Project and other groups to promote these pieces of legislation that will help get more workers here, one being the Essential Workers for Economic Advancement Act. Right now, there is no real visa program for those that are in nonagricultural less skilled positions. There are seasonal workers, but our members like restaurants and hoteliers and others, they need people year-round. So, this bill would introduce an H-2C visa program, that would allow for individuals to come over. It’s a nonimmigrant visa program, and work in the country, get some experience based on need. and there are economic triggers to make sure that those workers are needed, that there is low unemployment in the areas, and that the employers have been looking for somebody to fill that position for a certain period of time as well. The Asylum Seekers Work Authorization Act, is a great solution, I believe, to get people back into the workforce that are already here. Again, a bipartisan, bicameral bill, that would shorten the waiting period for asylum seekers to receive work authorizations. as many of you know, when asylum seekers come here, they have to wait 180 days to even apply for a for work authorization. This bill would reduce that deadline to 30 days and then they could apply and start working. and so, this bill would get the people who are staying in hotels and being subsidized by the government to actually work in those hotels who actually need the workers, and they want to work, we want them to work. So, it’s common sense, a bill that we really would love to pass Congress. The Senate and the House bills are, are two different versions of the same bill, but we support both of them because we just want people to get back to work.
Next slide. And just some ways in how we do that. We do congressional briefings quite frequently. That right there is the future of the workforce caucus briefing. On your left and on your right. We did a briefing for the New Democrat Coalition. talking to them about workforce issues. And we do many of these every year.
Next slide. Just a couple other things. We had the pleasure of having Diana speak to our group and provide, data and information, really, really interesting data. To our group, we do many, many hill visits to House and Senate offices. and we do briefings with groups like the Problem Solvers, and other coalitions. whose goal is to pass bipartisan legislation. We do webinars like this. We did a webinar on fair chance hiring, second chance hiring, with, the American Probation and Parole Association, which was, great to have them on board.
Next slide. Finally, we do digital ads in Politico and Bloomberg. And this on the top is an ad that we put in a number of different electronic media. And it’s just an astounding number, as Diana mentioned, if every unemployed person had a job, we would still have over a million unfilled jobs. And that’s kind of a startling number for some people and really kind of hits home to what the problem is.
Next slide. And just as an opportunity, I was on a podcast that will be available tomorrow, but wanted to give you guys a sneak peak. The Friday Reporter is a great podcast that goes into some of the issues that are going on. in DC, a lot of reporters, and congressional staff, are subscribed. So if you scan that QR code, you can get a sneak peek of what we were talking about on this podcast, which is more in depth discussion of the labor shortage.
Next slide. And I would just conclude by saying, you know, we welcome everyone to the conversation. So please feel free. We would love for you to follow us and check out our website. talk to us more. That’s my email address. and and get involved in the conversation. We certainly need the help. And again, thank you all for joining. And I’m going to send it back to Diana, and Secretary Acosta to answer some questions.
Diana Elliott: Great. Thank you. and just a reminder to put questions in the Q&A. I also have a few questions where I’m going to use, you know, sort of moderator’s privilege and ask a question of my co-panelists. So first off, I think I’d love to hear from both of you. You know, we’ve heard a lot about challenges right now. are there bright spots that you see on the horizon for our labor force? in the wake of demographic change in the wake of structural changes that we’re seeing?
Alexander Acosta: So, let me take it. Take it first. if I could. I do think there’s a bright spot in that. I think this is, you know, the first time that I sort of addressed the issue and I focused my personal view is that a lot of this has to do with our education system. I saw a lot of heads nodding, and I’m seeing more and more heads nodding. You know, I, I had early on as secretary and meeting with, community members from a city in Texas and a businessperson said, we need more welders and I’m willing to start a welder out at 60,000 right now. And the president of a community college said, that’s great. We’ll start a bachelor’s degree in welding. And I’m thinking, excuse me. The answer to more welders is we’re going to start a bachelor’s degree in welding. Is that really the case? You know, I think starting in the ‘70s, for all the right reasons. we started subsidizing education, particularly college education, in the matter of trillions. But along the way, we forgot that there are all these folks out there that aren’t going to college.
And if you were to break down, I showed a lot of data. If you were to break down the the data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics by college, whether you’ve attained a college degree, whether it’s, more than high school or high school, only you see that the biggest drop in labor force participation rate isn’t among the college students. It’s among those that don’t have college. And it’s really among what we’ll call the service workers, the construction workers, folks that work with their hands. And along the way, we’ve done three things. One, we say that college education is education at the Department of Labor. And if you don’t go to college, you get workforce training, I’m sorry, call it education at the Department of Education. And if you don’t go to college, it’s workforce training at the Department of Labor. Why is learning to be a welder any less an educational experience than going to college and learning to be a nurse’s aide? It is not. And language matters. It’s all education.
Two, we subsidize college education to the trillions of dollars, but if you want to learn to be a welder, you have to pay for it yourself. All these college loans are not available. All the Pell Grants are not available. And that matters. And so, we are biasing folks in favor of jobs that may not be their first line of preference. I gave this talk in Boston once, and the person running the audiovisual came up to me afterward and said, you know, I went to, I forget if it was Boston College or Boston University, I’m still paying off the loans. And then afterwards I had to go and get educated to run audio-visual equipment, because I make more running audio-visual equipment than I do from my college degree. And not only do we subsidize them, but now we’re forgiving all those college loans. But what are we doing for all those folks that that are working with their hands?
And then finally, I’d say even the way we talk about this. Right. You know, how often in our communities have we heard we have a health care crisis? We need to expand our nursing schools or medical schools. and we do, and I have no issue with that. But then how often have you heard we don’t have enough folks to build those hospitals to, you know, to work inside those hospitals as service workers. Do we then say we need to go out and create job educations for them, or do we talk about immigration as a solution? Do we really treat all tracks equally and say, is the goal a family sustaining wage, or have we started biasing the conversation in favor of those that have our backgrounds? All of us on this talk on this panel went to college is our tendency. Just think about this from the perspective of the college graduate. And, and if you look at the labor force data, you see that the biggest declines are not among the college graduates, but among those that didn’t go to college. And what are we doing to address them?
Final point, and this is where I think the business community and I disagree a little bit. I have no issue with short term solutions, but if short term solutions bring in more workers from abroad, you’re driving down wages. And that’s discouraging a lot of Americans from joining the labor force. And so think back 20 years ago, how many neighborhood kids would go and, let’s say, mow lawns and and are they doing that now? And if they’re not, why are they not doing that? Is it that the wages have not kept pace and that therefore what what economists would call the reservation price of labor and a lot of these service industries, are really to some extent reduced because of the immigration flows? Because, you know, according to, to the data that we saw, if we have low immigration, we’ll have 12 million fewer workers. But if we return to the 2000 labor force participation numbers we’ll have 16 million more workers. And so, to some extent, the short-term solutions undermine the long-term policy shifts that sort of my perspective.
Diana Elliott: I think I can piggyback off of that with a bright spot I see which prior to coming to PRB, I worked on apprenticeship programs, and I feel like apprenticeships are a bright spot for helping people who, perhaps cannot afford to do not want to go to college right away, or that’s not something that they’re planning to do to have that training program sort of with the employer, have that combination of employer based learning and learning in the classroom is really a tremendous benefit. And I’ve been really encouraged by an uptick in apprenticeship programs, for example, to that welder who or that, you know, the welder who needed more welders? I would say. Have you considered, have you considered an apprenticeship program or sponsoring apprentices yourself? In, in the past, right, post-World War II, we had more employers who took an active role in training, and that kind of faded away. And there is a role for employers to be more involved in training. Misty, do you have a bright spot? Before I go to some of these great questions coming in from from, participants?
Misty Chally: Yes, and I would like to respond to some of the, the income and wage questions, but I will say that, bright spot, I think whether because there are many expiring tax credits at the end of next year or because Congress wants to get something done, I do think we are going to see legislation that will help address the workforce shortage pass next session. Because it, honestly, it has to. A lot of the provisions passed in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act expire at the end of next year. And so, you are seeing a lot, even now, of members organizing themselves and discussing how to help, and the Critical Labor Coalition is certainly part of that discussion.
Alexander Acosta: If I could, Diana, I know that there are a lot of questions, but to respond a little bit to, to your, I think, point about apprenticeships, which is absolutely correct. And it’s a bright spot. You know, one of the weaknesses is that we’re asking employers to step up and fund these apprenticeship programs. Yet we fund college education, right? We don’t ask hospitals to fund the cost of educating nurses. So why should we ask welding companies to fund the cost of educating welders and one substantial difference between us and a lot of Europe is Europe is much better than we are at treating all types of education horizontally equally. And so, you know, community colleges, you know, aren’t what they once were. They’re focusing much more on college, you know, on full college degrees rather than vocational.
There’s a fascinating school in San Antonio. It’s called the Construction Career Academy. It’s a public school, and it’s a magnet program, just like we have high achieving Stem magnet programs. and they have more students and more families applying that they can fill. And every student graduates with the focus on either pipe-fitting, on carpentry, on construction management. And I forget the fourth and the, the fascinating part about it is they then teach math in the context of, how do you keep your books in English in the context of how do you write a business proposal? And you have students that might not otherwise be engaged in high school, fully engaged in high school. And those students have amazing success. And when I visited, the principal said, every year we have X number of students that graduate with scholarships and go on to college, and Y number of students that graduate with job certifications that have a job. And I thought that that equating of the two career paths, the two tracks, the family sustaining wages was wonderful. But why am I only aware of one public school district that has that?
Diana Elliott: Excellent. Um, fair point. Misty, there is a question that feels designed for you to address based on your experience with the coalition. So, it says, what is your opinion on the role of wages to incentivize people to enter the labor force?
Misty Chally: Right. And thank you for that. And I think Secretary Acosta and I will disagree on this, but, you know, coming from the franchisee small business world, I will tell you that the average starting wage, and don’t quote me on this, is about $20 an hour to work in a Burger King. And there’s a reason for that because there are not enough workers. So, they will, their income has increased, their salary has increased, their wages have increased. They’re getting a lot of our members to provide benefits like savings plans, college tuition plans, all of those. And I will say that, you know, the service industry, honestly, I think gets a bad rap for, for being kind of a starting job. I will tell you that many of these jobs, if you have no experience, need to put something on your resume. Want to get started? You can start. And I know many franchisees have started as a dishwasher and if you are a hard worker, I will tell you you will move up in that, in that business, in that restaurant, in that hotel, very quickly. And they have their own training programs for individuals that want to do that. So, they do provide many opportunities that people don’t often see to people that need jobs.
And I’ll, I’ll further say, that the wages issue, and I know it’s been front and center. It, there are, there are resulting effects from an increase in wages that I honestly didn’t understand until I spoke to franchisees that were suffering from this. So, let’s say you are a McDonald’s franchisee, and you raise the wages of your workers, your entry level workers, which means you then have to raise the wages of those managers and the like. And as a franchisee, you are, what you take home is the bottom line, right? What the franchisor takes is the top line. So, if you are paying individuals more, then you’re taking home less. And honestly, if you earn one franchise, this is not, you’re not buying yachts and sailing along the Riviera. And then you’re talking about raising the price of a Big Mac. So, when we’re seeing people complaining about a Happy, or not a Happy Meal, you know, an extra value meal being $15, $20, that’s, that’s a reason why. And so, what do they do? They can go get a kiosk that will be cheaper than paying for somebody to stand and take your order. So, there are a lot of different effects of raising wages. And while I understand that argument, you know, there are, that may actually decrease the number of available jobs in the U.S. So, that is my two cents and you’re seeing it in California where, you know, there’s a law that requires, I think it’s $20 an hour for quick service, and all the franchisees I know are switching to kiosks because they need to make a living as well.
Alexander Acosta: So let me let me just respond, Misty, because, because you said that we might disagree, and I don’t disagree with your, your specific point. You know, national franchises pay very well and and one of the results that you saw with the minimum wage in California, where a number of restaurants are closing down, switching to kiosks, I agree with all of that. My point was a broader one. And, and I think it applies less in the franchise area than other industries that, simply, if we believe in the free market, we need to be equal opportunity free market, you know, folks. And if we believe in the free market for goods, we also have to believe in the free market for labor. And at the end of the day, you know, while legal immigration is necessary and brings incredible, incredible people and, and knowledge to the U.S. – and this is not an anti-immigration statement because I think legal immigration is critical. The reality is that if we focus immigration on just, we need to fill the service sector. So, let’s bring in folks to fill that in.
To some extent, supply-demand means we are intervening in the free market for labor. I don’t think, you know, personally, I think one of the key drivers for franchises is not just wages, but all the regulations and the benefit costs, you know, around hiring a person that can, you know, almost increase the cost of a hire by 50, 60, 70%. And there’s so many other issues around hires, particularly, you know, in franchised as the franchise or to get liability for their franchisee that it makes hiring the franchise world very expensive. So, I don’t think we disagree with respect to, let’s say, the McDonald’s, which is the example that you used.
Misty Chally: No, I agree with that. And I think what you have to look at, what we used as a tool is look at the profit per employee, look at the industries that are not making a lot of profit per employee and see if they can handle, you know, any type of additional regulation, legislation, price increases and the like. So, thank you for that question, Diana.
Diana Elliott: Yeah. Thank you. I want to note that we are actually over time, but looking through the questions that people sent in, although we may not have asked your exact question, I think we touched upon a host of issues raised from vocational school apprenticeships, the wage challenges, to even robotics or kiosks being used. So absolutely, I encourage everyone to keep the conversation going via social media. Um, stay tuned. I think there’s a lot of material here for us to think about a post-event blog as well.
Keep asking your questions. We would love to think more about this and respond to you on social media. And if you haven’t already, go to prb.org. Consider making a donation so we can keep fantastic panels like this going. We’d love to do more of this. So, thank you so much for tuning in and joining us. And I want to thank Misty and Secretary Acosta for participating and really kicking off our Labor Day week in the best way I could imagine. So, thank you to everyone for joining and for asking great questions, and we hope to see you soon. Enjoy your afternoon.
Alexander Acosta: Thank you.

A conversation with author Jessica Calarco on her new book, Holding It Together
June 27, 2024
On June 27, our first PRB Book Talk focused on Holding It Together: How Women Became America’s Safety Net with author and sociologist Jessica Calarco.
In Holding It Together, Calarco (University of Wisconsin-Madison) draws on five years of research to show how U.S. society and policy disproportionately burden women with caregiving responsibilities. With an expert panel, we discussed Calarco’s key findings and their implications for reproductive health care policy and explore additional research on abortion, contraception, fertility, gender, and motherhood.
Panelists include:
Beth Jarosz, PRB: Welcome, everyone. I’m Beth Jarosz, Senior Program Director at the Population Reference Bureau, and I want to welcome you all to today’s discussion.
As we were preparing for this webinar, I started to write a really formal introduction to this talk. But as I was writing, I kept thinking about my grandmother, Alice. Her story began almost a century before the examples gathered in Dr. Calarco’s research but mirrors many of them so closely: pressure to get married, poverty, violence, and very few resources to teach out there.
It’s been generations. The same patterns still play out today. And it’s not like we don’t know these things. Researchers have been working for years to understand how policies can uplift people or leave them behind. We know that policies in the U.S. have a history of burdening women with caregiving responsibilities and offering them limited protections relative to peers and many other nations.
To be clear, we’re using the word women today in a gender-expansive way that encompasses cis women, trans women, people with a uterus, people who’ve had hysterectomies but identify as women, people who are parents, and those who are child-free. Under that umbrella, we find a group of people who tend to be marginalized by U.S. policy, with marginalization that cuts much deeper for Black women, Indigenous women, Hispanic and Latino women, disabled women, and trans women, to name just a few.
Today, we’re going to unpack some of the ways in which women are asked to hold it together. For the discussion, I’m joined by an all-star cast: Dr. Jessica Calarco of the University of Wisconsin–Madison; Dr. Tiffany Green, also of the University of Wisconsin–Madison; Dr. Karen Benjamin Guzzo of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; and Jocelyn Foye of the Womxn Project. We’ll hear from all four panelists and will round out the hour with Q&A.
If you have questions, please type them into the Q&A box. I’ll ask as many of your questions as we can during that Q&A portion. Without further ado, I’m going to invite Jess to begin.
Jessica Calarco, author of Holding It Together: Thank you so much to the PRB team for inviting me. Thank you all for being here today.
And thank you also to the, uh, you know, um, the panelists who are helping to flesh out this topic with more details and insights from their expertise of Karen and Tiffany and Jocelyn. It’s a pleasure to be here with all of you, and I’m so grateful for your work, um, engaging with this material and being part of this conversation.
Um, and thanks, a note of thanks also to the research team that contributed to the work that I’ll talk about today, which included, um, a very large number of graduate and undergraduate students and staff members who helped me produce the research that I’ll be sharing in my talk today.
So I’ll start off here by alluding to or kind of building on what Beth mentioned, this idea that other countries—other, especially high-income countries—have invested in social safety nets to help people manage risk. They use taxes and regulations, especially on wealthy people and corporations, to protect people from poverty, give them a leg up in reaching economic opportunities, and give them the time and energy and incentive to participate and contribute to a shared project of care.
In the U.S., we have instead tried to DIY society. We’ve kept taxes low, we’ve slashed huge holes in the social safety net that we do have, and we’ve told people that if they just make good choices, they won’t actually need government support at all.
Now, the problem with this model is that you can’t actually DIY society. Essentially forcing people to manage all that risk on their own has left many American families and communities teetering on the edge of collapse. And yet, as I’ll talk about today, we haven’t collapsed in part because we have disproportionately women being the ones who are holding it together, filling in the gaps in our economy and the gaps in our threadbare social safety net.
So to illustrate what I’m getting at here, let me tell you the story of a mom that I’ll call Brooke. Brooke was raised in a conservative, white, working-class family in rural Indiana, and her parents had a volatile relationship when she was growing up, and given that upbringing, Brooke never wanted to have kids of her own. But then, like many young women, she ended up accidentally getting pregnant in college.
Brooke and her boyfriend Brendon initially planned to get an abortion, and Brendon’s parents even offered to pay. But then Brooke’s parents found out, and Brooke’s mom persuaded Brooke to keep the baby, promising that she would help both with raising the baby and also with helping Brooke finish college.
Once Brooke’s son Carter was born, though, Brooke’s parents told her they couldn’t afford to pay or help her pay for both child care and for college, and in the wake of that decision, Brooke ended up dropping out of college, moving herself and Carter into a women’s shelter and enrolling in welfare. And because welfare came with work requirements, Brooke also took the first job that she could find, which was a part-time minimum wage job in retail that she hated. And she eventually found a full-time job at a child-care center, but that job also paid only around minimum wage. That said, it did come with free child care, and so this was appealing because at the time she was paying almost as much for child care as she was for rent.
And so at the same time, even when she got promoted to assistant director of the center a few years later, Brooke’s salary was still only $25,000 a year. And given the precarity of that situation, Brooke thought about trying to go back to college to, to get a nursing degree. But Brooke just couldn’t figure out a way to make it work. She didn’t trust her parents to watch Carter, so night classes weren’t an option, and quitting her job, even with how little it paid, seemed too risky. So Brooke just kept working at the child-care center, and she was still working there five years later and still hadn’t finished her college degree.
So Brooke is one of the hundreds of mothers that my team and I interviewed for this book between 2019 and 2022. We conducted more than 400 hours of in-depth interviews with moms and their partners from across the socioeconomic and racial, ethnic, and political spectrum. Most of those families were initially recruited through prenatal clinics in Indiana, so I also conducted two national surveys, each with more than 2,000 parents of kids under 18 from across the U.S.
And what I find in the data, and what Brooke’s story illustrates, is that women’s unpaid and underpaid labor helps to maintain this illusion of a DIY society. It makes it seem as though we can get by without a sturdy social safety net. Brooke’s story also illustrates a second piece of the equation here, which is that to facilitate this kind of exploitation, the U.S. has tried to trap women in motherhood and leave them with nowhere to turn for support in holding it together for their children and nowhere to hide when others ask them to hold even more.
And I talk in the book about how this system of exploitation is, is particularly damaging for low-income and middle-income women and disproportionately for Black and Latino women and women from other racially marginalized groups. In the absence of a decent social safety net, women in these groups can be easily forced into having or raising children or more children than they planned. And once they’re caught in that kind of motherhood trap, they can be easily forced to fill in the other gaps in our economy and also in our social safety net.
So to that end, to give you another story, I’ll talk about a mom I call Patricia. Before the pandemic, Patricia, who’s a Black mom, was still married to her husband, Rodney, and they had three kids, a toddler and two in elementary school. At that point, Patricia was working full time from home as a customer service rep, and Rodney was working full time in construction, and they were earning less than $30,000 a year combined.
Patricia, unlike Rodney, had some college education and she might have been able to find a higher-paying job, but she’d taken her customer service job, even though she found it repetitive and demoralizing, because it was the best remote work job that she could get before the pandemic. And being able to work remotely meant that Patricia didn’t have to pay for afterschool care or make alternate arrangements if the kids got sick.
When the pandemic hit, though, that arrangement ultimately meant that Patricia and Rodney never even talked about who would care for the kids when, you know, schools and child-care centers closed. That responsibility just fell to Patricia, and Rodney kept leaving the house every day for work.
Now, this kind of pandemic parenting took a huge toll on Patricia. The kids were constantly interrupting during her work time, leaving her frustrated and overwhelmed. She talked about the guilt that she felt, saying, “When it’s time to clock out, I need to not clock out mentally as a mother too.” And given that guilt, Patricia decided in the fall of 2020 to cut back to just four days a week of paid work. She figured it would give her more time and energy to focus on the kids, and she also hoped it would give her more time to rest because she had recently and unexpectedly become pregnant with twins.
What ended up happening, though, was that Patricia’s extended family saw her extra day off as an opening to ask for her help with car rides. Patricia was one of the only people in her extended family who had a reliable vehicle at the time, and she and her family were living in Indianapolis, which has been rated as the worst major city for public transit in the U.S. And so Patricia said yes, even when she explained that, she said, “your whole day that you had to yourself ends up being dedicated to running errands for someone else.” And she told me, she said yes because she had, you know, she knew her family had nowhere else to turn. The buck sort of stopped with her. And she also worried that she might need help herself someday.
And unfortunately, that someday came when Patricia and Rodney ended up divorcing just before the kids, the twins, were born in 2021. At that point, Patricia had to lean on those same people who leaned on her, and after her C-section, for example, she needed someone to drive her to doctor’s appointments, and she was grateful that she hadn’t pushed them away before.
And so Patricia’s story gets at this idea that, you know, our attempts to DIY society have, have decimated families, and particularly families that have been systematically marginalized in our society. And in that context, it’s often impossible for women not to get stuck filling in the gaps in our economy and in our social safety net, because we’ve really left them with nowhere to turn for support and nowhere to hide when others ask them to hold even more.
Now, within this system, it’s important to acknowledge that, that more privileged women have it easier because they can afford to offload some of their responsibility they’ve been handed by dumping it onto others who are more vulnerable than they are.
And in the book, I talk about a couple that I call Holly and Kathleen. They’re a white, same-sex married couple, and when their daughter Willa was born in 2019, they planned to split paid work and care work evenly. But the child-care crisis kept getting in the way. Without family nearby to help and with huge wait lists for care, their best option, child-care wise, was a part-time spot that wouldn’t be available until Willa was 9 months old.
And so to make it work in the meantime, Holly and Kathleen decided Holly would work for pay part time from home, while Kathleen worked for pay full time, in part because Holly’s job as a data analyst didn’t pay as much and was able to be done remotely, while Kathleen’s job in law enforcement, you know, had to be done outside the home and paid a whole lot more.
So that arrangement, though, got increasingly difficult as Willa got older, and Holly couldn’t wait for Willa to start child care. But then almost as soon as that spot opened, COVID closed the center, and they’re just right back where they were before.
And, you know, this caused deep frustration for Holly. And she actually went in and complained to her, tried to go in and complain to the center director. But what she learned in the process was that the center couldn’t afford to recruit and keep staff, as she learned, for example, that, you know, her child’s previous teacher didn’t have health care benefits and was still struggling to pay off medical debt that she had accrued, you know, years before the pandemic started.
And hearing those stories left Holly feeling guilty. She told me, “Kathleen and I just feel really guilty about being complicit in this thing where it’s like we have all these women of color watching our kids, and we’re not really taking good care of them.”
And, you know, that guilt of complicity weighed heavily on Holly, but she also recognized that, that she and Holly needed reliable, affordable care if they were going to be working full time and especially if they wanted to pay for IVF to have another kid. And so she talked about how, you know, “we have more than we need right now, but it could change at any moment without that social safety net. So you’re like, I guess I should just hoard it in a giant pile and sleep on top.”
And so as we see in Holly’s story, some women benefit from this kind of exploitation of women who are more vulnerable because that exploitation makes it possible for them to afford to outsource help with care. And yet, at the same time, and as we also see here, even relatively privileged women are drowning because our DIY model has left all but the wealthiest families with more responsibility than they can manage and because what’s left over disproportionately falls to women, even when men could do more to fill in the gaps.
And on that front, and I’ll quickly tell the story of a mom I’ll call Virginia, who’s a tenure-track professor at a research university who makes $75,000 a year, and her husband is a middle school math teacher who makes $45,000 a year. And despite being the primary breadwinner, Virginia is still the default parent for the kids. She’s also the default caregiver for her aging parents, even though her brother could be stepping up to do more, and it makes it tremendously difficult for Virginia to be able to feel as though she can concentrate enough to do her work, her research. She said, “I do actually have a brain. I love thinking, and I’d love to be able to do that again sometime.”
Um, at the same time, she also balked at the suggestion from her employer that she should just be taking more time for self-care. She said self-care is just a way that institutions have offloaded their responsibility of enacting humane work. Um, and she said that what she really needed was institutional support. She said, “I need the child tax credit back. I need a financial cushion. I need time and reliable care for my kids. I need consistency, I need institutions to step up and be humane.”
And essentially, I mean, Patricia, or Virginia’s lament here makes clear that we already know what the problem is, and we already know the solution. And so the solution is to build the kind of safety net that would actually protect us all.
But we haven’t built it, and I, and I argue in the book that we haven’t built it because, you know, billionaires and big corporations and their cronies, or who I talk about in the book as sort of the engineers and profiteers of our DIY society, have us right where they want us. And because they’ve promoted a series of myths that help to dissuade us, to help, to delude us into believing that we don’t need a social safety net, and to, to divide us by race and class and gender and politics and religion in ways that prevent us from coming together to demand the kind of social safety net that would better protect us all.
So I’ll leave things there for now, just to ensure that we have lots of time for other discussion. But I’m looking forward to the, to the questions and also to the, to the discussion with the whole group. So thank you.
Beth Jarosz: Thank you so much. Um, and I’m going to invite Tiffany now to speak a bit about her research.
Tiffany Green, University of Wisconsin–Madison: Thank you so much for having me here today. Congratulations, Jess, on your new book.
Um, I’m going to talk a little bit today about, um, some work that my team and I have been doing on a policy called birth cost recovery, or the birth tax, and just really thinking about its implications for caregiving. Um, a special thanks to the people that have funded this research, including the Wisconsin Partnership Program, uh, the Wisconsin Department of Children and Families, and the Centennial Scholars Program. So many people on my team to thank, um, including, uh, Klaira Lerma, who’s not pictured here, my research director; Frank Lewis, Obi Anaya, and Mikaela Miller, who are RAs as well; and also the many community partners that have been involved in this work.
So, what is birth cost recovery and what does it have to do with what we’re talking about today? Um, birth cost recovery is a policy primarily practiced in Wisconsin, where states draw upon a certain interpretation of federal Medicaid law that allows them to pursue, um, the Medicaid birthing costs, um, that, that people pursue. So if I have a baby and I’m on Medicaid, uh, the father, um, the non-custodial father would be asked to pay part of that cost.
And, how does this work? Um, basically, a person discovers that they are pregnant. Uh, they may or may not decide to enroll in prenatal Badger Care or Medicaid is what we call it here in the Badger State. Um, a person gives birth. Now, the state cannot withhold, uh, birthing coverage if the father is not declared. However, there is an automatic referral system in the state where if someone has a Medicaid for part of their birth, labor, and delivery costs, it automatically gets referred to child support.
Um, after that, the courts determined, um, one within the context of that child support order, if birth cost recovery or the birth tax should be incurred. Um, and that can be, that can be used to garnish a person’s wages, etc. And this is very much separate from child support, and it does not go towards the maintenance of the child. Um, if the birthing parent refuses to declare who the father is, the state can take away Badger Care or Medicaid after the 60-day period is over and they are otherwise eligible.
And so why does this matter? Well, for someone like me who studies structural inequality, this matters a lot. Because of structural racism, Black people and Indigenous people are far more likely to have their births covered by Medicaid, both in Wisconsin and the rest of the United States.
Um, I first learned about this policy from Rachel Azanleko, who was a former MPH student here who really focused on thinking about the impacts of birth cost recovery on outcomes. And she told me that, and as an economist I got excited, that there was a huge policy change in Wisconsin, which I’ll talk about in a minute.
But this is something that’s also coming up in the context of discussions with communities. This idea, particularly among Black communities, that this is a policy that magnifies financial instability for families. It penalizes birthing parents with health care coverage loss if they don’t declare the father. And it deepens many men’s struggles to financially support their children and strains family dynamics. So, you know, if there are strained family dynamics that that caregiving work almost certainly is going to go towards the birthing parents or mothers.
So in January 2020, Dane County stopped collecting new birth cost recovery funds. And we did some work to think about what the impacts might be on families. We found that there was an increase in child support that went to the birthing parent, and this was particularly true among Black families.
But one thing we found is that we weren’t hearing a lot about the Black families that were actually affected. And so in this, in this work through the Wisconsin Partnership Program, we decided to really try to document the experiences of the team and eventually create a quantitative survey where we could kind of assess how people’s experiences with birth cost recovery were affecting their mental and physical health.
Um, we started with birthing parents, and I’ll talk just a little bit about what we found. Um, and we also will be interviewing fathers as well, or non-birthing parents. Um, how do these birthing parents think that birth cost recovery has affected their lives? It’s dads not having money for necessities or extras. Negative impacts on bonding and, and these inequitable effects, particularly among Black Wisconsinites.
And so what this boils down to, again, is that it makes sure it helps to ensure that fathers are not able to fully participate in their children’s lives because of this extra cost that’s incurred. Um, here’s one quote from some of the qualitative interviewing that we’ve been doing. We interviewed, uh, I think 24, uh, birthing parents at this point.
“Yeah. I mean, that could be challenging for the 5-year-old.” So, so they’re talking specifically about birth cost recovery.
“I can’t give you extra money for school clothing because I got to help pay the birth expenses. Hey, I don’t have—let’s say I was to run into a gym where I needed $25 for gas. The funds is so tight that they’re not even leaving room for the fathers to do anything extra or curriculum activities, because they’re getting this money, taking out of their checks every two weeks or every week for child support.”
A second quote from a respondent: “If men didn’t have this birthing fee right off top, that would make it a better relationship bonding for the mother, the father, the child. Men would be able to do more, provide more, and it’d just be a healthy family overall.” So again, these quotes really embody the fact that this, this particular policy, far from being sort of these individual-level choices, has the capacity to frame what can be offered, fathers are able to offer children, and the stability of family units.
Um, just so you know, there have been some more recent policy changes. I feel like it’s a moving target for us. Um, Milwaukee County has stopped taking fathers to court for birth cost recovery. And Dane County also is, is working on forgiving back pay, as is Milwaukee. So there’s been a lot of change just since we started studying this policy. And we’re working to try to understand how this shapes family dynamics and caregiving within families.
Um, now we are focused on interviewing Black fathers now to understand their perceptions of the policy and understanding how this affects how they see fatherhood and their ability to support, uh, child, child experiences in their growth, and really trying to understand the short- and learn long-term effects of these policy changes on all Wisconsinites, but specifically Black Wisconsinites.
And I’ll end there and kick it over to the next person. Thank you so much.
Beth Jarosz: Thank you. And Karen, I will invite you to share about your research next.
Karen Benjamin Guzzo, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill: Great, great. Thank you so much, and I’m really pleased to be here. And thank you to PRB for putting this together. Uh, and thank you Jess for writing this book.
And so I’m a demographer, and so I study population-level changes in behavior. And my particular area of research, uh, is childbearing, uh, looking at birth rates and trends over time, differences across different groups, um, the factors that predict whether people have children.
And so what’s important to me and some of my takeaways from this book or that related it back to a larger issue some of you may have heard of, which is that the U.S. is at record low fertility rates. Uh, this has caused considerable alarm and for all sorts of reasons, and maybe we can get into this later. Um, but different groups are alarmed for different reasons.
Uh, and so the question has become, geez, why aren’t women having births? And this is, I get this question a lot from journalists. And really, it’s tightly tied to how we think about women and birthing people. And you know, what we expect from them, how we judge them, and what we do or do not owe them and provide them as a society. And so when we’re talking about birth rates declining, um, to me, this is very much a story of damned if you do, damned if you don’t.
So for years the U.S. has had higher fertility rates than other countries, many of its pure nations. We, so we kind of aim for what’s called replacement level, which is about two births per woman. This allows women basically to replace themselves and their partners, and, uh, absent immigration, this keeps the population stable. And so with the U.S. was above this rate for, for quite a while when many of its pure nations were not.
And, as such, the U.S. was kind of able to ignore the social safety net, the kind of things Jessica talks about in her book: things like affordable care, affordable and accessible child care, lack of paid parental and family leave, um, having a functional health care system that everyone could access regardless of income or employment status.
And so low fertility, low birth rates, was really not on our national radar. Um, any woman can probably tell you it’s certainly on the individual people’s radar. So lots of women were, “So when are we going to start having kids? When are you going to start having kids?” Um, but this wasn’t a national conversation because what we are, the conversation we’re actually having as a country was who shouldn’t be having children.
And so the U.S. has generally had very high teen birth rates and high unintended pregnancy rates relative to our peer nations. Uh, and as it turns out, those teen birth rates and unintended pregnancy rates were actually propping up our overall fertility rate.
And so, since the 1990s, under the Clinton administration, um, we had the emergence of, um, different efforts to reduce teen and unintended pregnancy. Uh, so in 1996, we saw the emergence of the National Campaign to Prevent Teen Pregnancy, um, come out. And then later expanded to include, um, teenage and unintended or unplanned pregnancy. Uh, it since changed its name again.
Um, and so in the 1990s, teen pregnancy rates were at, um, sort of record highs, but only in terms of recent memory. Because if you go back to the 1950s, during the baby boom, teenage birth rates were much, much higher. But they were the right kind of birth. They were births to people who were married, and we weren’t worried about those.
So what happened in the 80s and 90s is that birth rates were increasingly teen birth rates were to low-income women who were unmarried, women from racially minoritized populations. And these were the wrong kinds of births. And so we were very worried about those.
Um, and so, um, we had all sorts of campaign ads to reduce teen and unintended childbearing. So you might remember from just a decade ago, New York City ran these fairly horrific ads, um, targeting teen moms and trying to shame them into not having, um, children.
Um, and then even at the federal government level, we have official policies. Uh, every 10 years, the federal government publishes something called the Healthy People objectives or Healthy People initiatives. And, and these are kind of health, public health goals they’d like to reach over the next decade. And for a long time, those have included, uh, reducing teen and unintended pregnancy rates.
And so I say all this to say, over the past 10 years, basically since the Great Recession, it actually happened. We’ve seen this long-term decline in teen pregnancy rates, but now we’re also seeing a pretty sizable decline in births to unintended births that would be characterized by people themselves as happening maybe later in earlier than they would have wanted. So now that people aren’t having those births, this is essentially good news.
So when reporters ask me, you know, “What’s happening with birth rates? Why aren’t people having kids?” I’m like, this is a success story. This is a story in which young people, those are, those are the people who typically, if they had a birth, would consider it sort of earlier than they would have wanted. This is a good news story that people are able to better control their reproductive lives so that they can have children when they want them, under the context in which they want them, and to have as many children as they feel personally able to have.
Um, and so this is a good news story, but part of this good news story, the background to this is that we have been preaching for years that it is irresponsible for people, but really for women, for young women, to have a child when you’re not ready: you don’t have a good job, you haven’t finished school, you don’t have a good partnership, you know, you can’t afford to live on your own, you live in an unsafe neighborhood.
So we’ve been preaching this for years that you shouldn’t have a child if it’s, if you’re not in the right circumstances. And so the decline in unintended fertility in some way it’s very good. And the decline in birth rate is because of sort of declining teen and unintended birth rates. But we need to think about the other side of the story.
Um, since the Great Recession, our society, and that of other societies, I’ll be honest too, who also have more of a social safety net, um, a lot of these societies are not providing people, young people, a sense of security and optimism for the future. I mean, all for all intents and purposes, having a child is a future-oriented decision. And so people need to look to the future and think, “Okay, I can do this, and I’m going to have a good life, and I can provide my children with things.”
And so to me, it’s, it’s baffling that people are baffled that we’re not having, young people aren’t having kids today, that they are waiting. And because they’re holding up their end of the bargain, the bargain that we’ve been preaching for, you know, 15, 20, 30, 40 years really: don’t have kids, don’t have kids if you do not have, you know, essentially all your proverbial ducks in a row.
But the other half of the bargain is that society needs to create a set of conditions in which you can reasonably predict for the future that you’ll have enough money, you’ll have a good job, you can afford health care, you can afford to find a safe place to live. You can have a good partnership. And so people aren’t having kids because those things don’t look like they’re happening for them in the future. Um, and, of course, without an adequate social safety net otherwise, it’s just simply too risky to have children in some ways.
So most of my research really shows that it’s not that people are saying, “I don’t want kids.” They’re saying “I want kids, but not now. I want kids if—.” And they really are thinking quite rationally about what they want in the future, what they think childbearing for them should look like.
Um, and so if you’re a woman, childbearing is incredibly risky. So it starts in pregnancy. We monitor what you eat, what you drink, how little or how much weight you gain. If you have a substance use disorder, uh, and you’re pregnant, you could go to jail or risk losing your child rather than getting help. Um, if you’re sick during pregnancy, you know, God bless you. Um, because we don’t know what meds might work for you because we actually don’t study, um, women, pregnant women have typically been excluded from medical trials.
If you have a condition that threatens your pregnancy, um, or threatens your life and you live in certain states, uh, again, you might literally be risking death because health care professionals cannot or don’t feel as if they’re allowed to treat you. Um, even before some of these recent changes we’ve seen in abortion law, uh, your chance of dying during pregnancy, during childbirth, or thereafter was much higher in the United States than elsewhere.
And then, of course, if you make it all through that, and you have a child, and you’re on your own to figure out if you can take time off. We do not have paid family leave in the United States. So people go back to work much sooner than they would like. Um, but if you’d like to stay home and recover from childbirth, you know, bond with your baby, you’re going to have to figure out how to do that on your own. You’re going to have to fund that on your own.
If you do go back to work, um, you’re going to have to find someone to care for your child. Um, and we have such a huge problem with child care affordability and accessibility, and this has really been accelerated and magnified during the, um, the pandemic and post-pandemic years, uh, where we’ve seen a real decline in child-care slots.
So you have to go back and try to figure out who’s going to watch your kid for you, and can you afford it? Um, if you do have a financial setback of some sort, you know, you’ll have to navigate our patchwork safety net programs. Um, and those, there’s a lot of sort of administrative burden there, and it often seems like they’re designed to turn you down and humiliate you in the process of getting them.
Um, even for advantaged women, you have these sort of do-it-all norms, uh, and you’re going to be struggling to find child care during summers if your kids are school age or before and after school. Um, you are worried about social mobility, so parents feel like they have to do everything right and get their kids into all the right programs. Um, if you can afford not to work as a mom and you choose to work, you’ll be judged for that, and you’ll face this constant feeling of neither being good enough at work or at home. And these are all just really gendered things.
And so when, when people ask me, “Why aren’t people having kids?” I’m like, well, they’re making really rational choices about what’s available to them. What’s the safety net look like? What does my own future look like? Does it look safe? Secure? And mostly they’re saying no, it doesn’t. It doesn’t look like that right now. And so people are waiting longer and longer to have kids. And sometimes that might mean they end up with fewer kids or not having kids at all.
And so this is not a story of individual women saying, “Oh, I just don’t like kids.” I mean, of course, some people probably say that, but really it’s a story about young people as a whole looking around and saying, “There’s— the conditions in which you’ve told me I’m supposed to have kids don’t exist for me, and I’m not sure they will.” And so this is very much a story about what is our social safety net look like for people and families, but particularly for women who are making these decisions.
So I think I’ll stop there, so we have chances for someone else to weigh in.
Beth Jarosz: Thank you so much, Karen. And last but certainly not least, um, we want to, we’re talking about all of these challenges, the social safety net and sort of policy changes that could be helpful. So we’re going to wrap up with a little bit of discussion about, uh, how policy can change. So Jocelyn, turn it over to you.
Jocelyn Foye, Womxn Project: Thanks. Hi, everyone. How do you do? My name is Jocelyn Foye, she/her.
I am located in, um, Providence, Rhode Island, um, which I relocated from Southern California. But to give any of you a sense who aren’t from these parts, um, Rhode Island is the smallest state in the nation with only 1.1 million people living within our borders at this time. Our census says that we are a 77% white-identifying population, which if anyone studies census work, they’d understand that that’s not the right number for minority spaces. But, um, it’s an important one to name. And then also, we’re the third most Catholic state in the nation, which means we have an incredibly powerful, um, bully pulpit for the, for the bishops here.
And so when I moved here from Southern California, um, what I found really quickly was how restrictive the policy was for a state that people often say is a blue state when you see it on the map. And when we’re looking at presidential elections, it always goes blue. Well, we’re very purple, and it’s important to name that as I talk about this work, because, um, my organization came out of a place of recognizing that with Trump coming in as his first presidency, we had concerns.
A number of us who were doing policy, and I come from a background of being an artist, a spectacle-based artist and a design professor, and we wondered if we could put together policy strategies and inclusive installations that were spectacle based and activating of community to be welcomed into the process of how to do art and activism with us. So these are some images of ways we did the work. Um, and it’s, there’s a lot of pictures on our website. So we, we welcome you to take a look at it.
But the reason I think I was invited here was because the Womxn Project. Um, and I want to say to woman with an X when we originally named ourselves, was to be an inclusive organization to include all folks, of all folks who wanted to get active with us, to join it. Language has recently changed, and so we constantly are in a mutative form of how do we rebrand to be in alignment with inclusive, inclusive work?
Um, so, um, we came on the scene after 24 years of essentially what was the Roe bill in Rhode Island. It was, um, fought for, for 24 years and had no success. And so with our style of activism, what we did is we created this community quilt. And we wondered if by going into different areas across the state, and we had conversations with people about, were they aware of their rights? Were they aware that after, um, if Roe should be overturned—and mind you, we started this in 2017—um, that based on the constitution of our state, we would see that, um, providers would be tried as murderers.
And I went to an event in Washington, D.C., where I sat with some women from Alabama, and they said, you know, “Rhode Island and Alabama aren’t very different, are they?” And I was like, oh, tell me more like, what are you thinking? And what they said was, is that we both are run by the mob, which is true, and we both are, um, are going to have abortion providers tried as murderers based on our states’ constitutions.
So our group was like, okay, how do we bring more people to the table? Let’s look at the way marriage equality was done nationally. And we started doing one-on-one conversations, house parties. We started going into spaces where women were collecting, book clubs, sewing groups, you name it, and we started asking people if they wanted to make a quilt square with us. And the quilt square became essentially their own signature of a petition.
And as a lot of us may know, the history of quilts says a lot about, um, memor— like memorandums or histories of passage of people’s lives. But it also is a, is a, um, history or a path of understanding of where to go.
So what we did is we ended up building this giant quilt, and we had master quilters across the state helping us build these sections that we carabinered onto one another, and we moved around and we would display in our state house. And for anyone who’s a visual interests learner, installation art, this thing kept getting bigger and bigger, and we had security guards really angry that we had this mass thing.
But what happened was a ton of people across the state felt really this was their thing. They all were working on it. It was a very collaborative effort. And what really happened was, is we got to have 2,500 small conversations with people who made those squares with us that were part of those quilts, and that had the networking effect that women do do so well, or small communities that are unique and tight with one another.
So it became an intersectional project in a lot of different ways because of where we were invited. And we intentionally designed it so that different spaces made it their own. People built different methods of this, this style of work together.
And we were able, after three years, to pass the bill, which was turned into, they named it the Reproductive Privacy Act. Um, and we did it because we built community momentum, and we got people to a point where they not only understood what was at risk through conversations and networking, but also they learned about the education of how a bill becomes a law. And they learned that they wanted to get involved and they wanted to see this bill through.
People felt a level of ownership. And so when I talk about us as an organization, the part that’s hard for people to wrap their heads around it is, is that we stemmed from grassroots organizing. We still are. Um, but we also shift policy. And we do that by way of, of basically the people power.
And often when you talk to organizational leaders who say, well, what is your piece? What makes you different here? Um, unfortunately or fortunately, it is the fact that I’ll walk into a room with legislators or the governor, often not comfortably, they’ll see me and they’ll be like, oh no, she’s here, because I bring sort of this level of question of what is the action or the behavior that I’m representing, but also how many people are, are coming with me.
And so what it’s done is, is in this movement, this intersectional movement of “women’s work” or organizational, um, like, uh, patriarchally like suppressed spaces. What we’re doing is, is we’ve pivoted from not just working in the abortion space, but we’ve also been invited and have board members who are identifying in the space of the LGBTQIA space.
So after two years of passing the Reproductive Privacy Act through, excuse me, because of COVID, we passed essentially the Hyde Amendment in Rhode Island to be overturned. And so that meant that Medicaid recipients and state workers then had that included in their insurance policy, which, when we think about it, if you pull back on a lens, um, a lot of people will say abortion is been taken over by white women, second-generation feminists. And I can’t argue against that. But we looked for ways to make it everyone’s work. And with the second bill, it was an equity piece. It was like every, if one person has access to this, then everyone should.
And so now we’ve gone into the same sort of work in a similar way. But we’re not talking about abortion because it’s never really been about abortion. Roe was not about abortion being overturned. It was about taking away our rights. And so, in a medical way, and so we’re now looking at we just passed a bill this year, which is incredible because there’s really no good news in this horizon, but a provider shield bill.
And so we now have we just today, I just came from the signing of our governor where providers who are giving, doing abortions or who are doing gender-affirming care will be protected from any out-of-state attacks that they may receive from states so that those providers can be taken care of, as can the patients, which is not something we always get to talk about. So our work is this like modeling of policy mixed with community action.
And I think that, um, there’s a lot to say further, but I’ll stop. Um, we are, I will say this too, in, in just full disclosure, we’re an organization that started as a C4, not-for-profit, which is unusual. It’s not a C3. A C3 is tax exempt, so it’s not allowed to talk about policy as a lobbying thing. Well, we started as the opposite, which is a lot harder in America. People don’t like to fund this type of work.
But what it allowed us to do was it was tool, we had tools in our toolboxes that were different, so we were able to drive billboard trucks around our state with faces of General Assembly members on it that said, this person doesn’t believe in the right to abortion in your district. Here’s their phone number. Call and ask them why. Because it became an accountability process.
And, um, and we built massive coalitions around this work because people saw the value in it and for their communities as well. And so we’re growing while trying to figure out how to, you know, keep pushing the envelope. So I’ll stop there.
Beth Jarosz: I feel like I, we could continue this conversation for two more hours. Um, but we’ve got, we’ve got about 20 minutes now for questions, and we’ve had a lot of really fantastic questions, um, come in through the chat. So, um, I think I, I had prepared some questions, but I think the one theme that sort of has come across several of the questions that have come in is, what would an improved social safety net look like? And I’m thinking each one of you probably has a perspective on that. And we’ll go kind of in the same order we did. So Jess, Tiffany, Karen, and Jocelyn for that one.
Jessica Calarco: So I mean, I think that’s a great question. And I think the kind of social safety net that we need, in my view, is one that helps to essentially take care out of the for-profit market. That’s one piece of it, in the sense that so much of the unpaid, underpaid labor that women end up doing, women hold almost 70% of the lowest wage jobs in our economy. And often those are jobs where women, especially women of color, especially women from more marginalized groups in our society, are pushed into doing these kinds of low-wage jobs because someone, they’re not, they don’t work within our profit-driven model.
And so ensuring that that taking that work out of the market, whether that’s child care, home health care, the, you know, health care in general, that removing that from the profit pressures can help to then pave the way for the second step, which is about ensuring that the care, the care work is equitable and funded to the level where it can be both equitable and sustainable, essentially taking care of the people who care. And that includes both paid work and unpaid care work in the sense of things like unpaid, or things like paid family leave, things like paid vacation time, things like limits on paid work hours like they have in places like France, to ensure that everyone has the time and energy to contribute to this shared project of care.
So those are sort of, you know, two key components, um, kind of ways to think about the social safety net as opposed to, you know, specific programs. Um, so it’s about sort of, you know, giving people a backstop and also making sure that people have the time and energy to, uh, you know, take care of each other and take care of themselves because we can’t outsource everything, even with a sturdy social safety net.
Beth Jarosz: Tiffany, do you want to add to that? What’s, what would the safety net look for you?
Tiffany Green: I don’t have much else to add. I think high-quality child care is, is a key thing where, where child-care workers are paid well. We know that child-care workers were at the front lines during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, and many quit, um, during, during that time. So making sure we have high-quality child care where the people taking care of our kids can actually afford, um, that high-quality child care is really key. Having, um, paid parental leave is really important.
But I would say even within the context of our institutions, many of us are at universities—I’m tenured now, so I will say this—um, a lot of the care work is put on, um, you know, faculty assigned female at birth. Let’s, let’s be really clear. So we have a pervasive, um, um, the thing where we put care work upon women and other people assigned female at birth within all of our institutions. So I think we need a full-sale overhaul, uh, a wholesale overhaul of what that looks like.
And the other thing I would say, I always think about the non-sexy things, and so one of those things is our tax system. I’m not an expert in that. But I’ve, I’ve been very convinced by my colleagues who are experts in the tax system in thinking about how we can use that to, to reduce poverty, because, again, many of the most impoverished households are headed by women. So things like the Child Tax Credit were very effective at, uh, at improving things, making sure we have, um, an equitable system so that people, people that, households that are headed by women, um, will not be as poor, I think is really important, other than, you know, burning down the patriarchy.
Beth Jarosz: Yeah. How about you, Karen? Anything to add?
Karen Benjamin Guzzo: Yeah, so I want to comment on something that I think I showed up in the Q&A a bit, which is that people sometimes say, oh, well, other countries have some of the social safety net things you’re talking about. You know, some of the Scandinavian countries have great leave or great child care, and their birth rates are also falling, or what’s happening, um, in East Asia, where the birth rates are extremely low and they have some generous policies.
Part of the problem, though, is that you need all the things, but you also need social change. Um, and it’s not enough to, especially for some of the East Asian societies, to say they have a generous maternity leave policy, um, if women are actually still expected to come home and do all the work, uh, and their husbands are not doing anything, or you still have a culture in where, um, working all the hours is how you actually get ahead in your job. So it’s not enough to have just any one of these things.
Um, but I would also say even if birth rates don’t go up, they are the right thing to do to have, you know, a strong maternity and parental leave policy, to have adequate child care. Um, it is, I think it’s important to have these things because it does improve the well-being of, of our families. And I think that is really where we all want to end up, where people feel like they can live the kind of meaningful lives without this level of stress.
But going back to the culture thing, and one of the things I find is a sticking point sometimes in conversations I’ve had in research I’ve done, which is that women feel as if they’re doing everything and their husbands are like, “But I’m doing so much more than my dad. I’m doing so much more than the earlier generations did.” And the women that they’re partnered with are saying, “But you’re not doing as much as me.” And so people are sort of talking across each other within relationships, but we don’t recognize this sort of care work and value this.
So there’s been this movement. Um, I think Richard Reeves is sort of the kind of most proponent, biggest proponent of this is, how do we get men, how do we help men out? But one argument he’s making is we’ve got to get men to understand that care work is important and meaningful. Um, and help them make, you know, firm relationships with their children, with their friends so that they can engage in this care work that makes everybody better.
And so we need a social safety net, but we need the cultural change that supports using a social safety net and that a social safety net is an investment and not some sort of extra expense that we’re doing because women aren’t doing their jobs.
Beth Jarosz: Thank you. And I actually think that answers one of the other questions that have come in. So the person who asked the question about how are men being called in, if that’s, if you want to continue on, repost that question in the chat. And then Jocelyn, do you have anything you want to add about the safety net?
Jocelyn Foye: The only, yeah, I mean from my lens as it would make sense then is, is that from a social safety net too, we need to be supporting not-for-profit organizations that are doing a lot of this work. Um, it’s the second largest industry in the United States, which is not-for-profit work, but how, um, those organizations struggle and actually exist within spaces where they’re in competition with each other is really difficult.
Um, and so I would just say for those with the means, it’s not always about money. It’s also sometimes, which we often talk a lot about, what it’s about, um, finding your superpower and what can you contribute to the work. Um, often for people who have the means, yes, money is a really helpful tool. But for people who time is of the essence, you have children, you, there are organizations that invite you to do some of the work with, um, them with your children, and more and more not-for-profits are making that a part of the process. Um, but also organizations are looking for people who can do work in ways that are very creative.
And so I’m just putting out there I think that, again, I come back to I’m not thinking of the folks who were trying to just get by, but I’m thinking of the spaces that are places where people can add a little something. Um, I think it’s important to name, and I, I don’t have a stat that’s as, as recent as I’d like, but Ms. magazine has been putting out research about what kind of not-for-profit funding exists in the United States. And in 2020, it was only 1.6% of not-for-profits were being funded that supported women and girls, specific not-for-profits. And so when we look at how support is existing out there, I think we could all do better. Um, and I think we make assumptions about that.
But I go back to I’m a designer. I always offer my resources as a designer. I can’t offer my resources as a, as someone who makes money. And so I try to fit it in when my kids go to bed before I go to bed, if I can. And I think that that’s a way to think about certain models. Again, a privileged model nonetheless. But if you had the time, what could you offer?
Beth Jarosz: Thank you. Um, and taking it in a slightly different direction and sort of a question that I had prepared, um, but then Tiffany sort of spoke to in the chat just now is that, you know, the underpinning this assumption is the idea that, um, that people should be having more children. Um, and is that really even a, is that really even the right assumption?
I know, um, Karen and I have been chatting about this a little bit too, that, and Karen, maybe you want to kick that off, that, that just that underlying assumption of is that even the right question, like is, is the question how to, how do we increase birth rates? Or is the question about making sure we have a safety net because that’s the right thing whether the birth rates get there or not? But also how do we push back against this idea that like people having kids is the way to solve our economic problems?
Karen Benjamin Guzzo: Sure, sure. So, um, I’ll just sort of lay my, my, my position clear, which is I’m not worried about our fertility rates. Uh, I worry about fertility in the sense of we have people who say they’d like to have kids and feel like they can’t have the kids that they’d like to have under the conditions they would like to have them. That is a societal failure to me that we have people who want to have children and feel like they can’t. That is a problem we need to fix. Um, but birth rates in themselves don’t concern me.
Uh, you know, if we’re worried about, you know, we talk about Social Security or, um, the labor force or something like that, or even worse, you know, nation-states. I can tell you how little I care about nation-states. Um, but, you know, things like Social Security, we have other means. We could, we could, we have other policy-level levers, um, but expecting people to say, oh, I should have children so that, um, future generations can, so that my kids 20 years from now can pay into Social Security to help fund retirees at that point is sort of nonsensical to me when we have levers like, we could raise the Social Security cap, um, you know, we can change our policies in terms of immigration. We, uh, we can, there are things we can do. And as automation changes and jobs change, do we need as many workers?
Um, and so we need to we need a wholesale sort of reimagining. And do I think it’s going to happen? I don’t know about that, but, um, but this idea that birth rates are going to be the thing that save us as a future just does not resonate with me, because it’s not just about birth rates. Let’s be really honest. It’s about the right people having births. Um, it’s not just we don’t want more immigrant births, so we don’t want births from poor people. We want a very specific group of people to have births. Um, and ideally, they should stay at home with their kids and get out of the labor force.
And I mean, it’s, there’s a whole level of things that, you know, probably aren’t worth getting into right now.
Beth Jarosz: And, Tiffany, since you were the one who put that comment in the chat, is there anything you want to add to how we think about the sort of social structures about who’s the right person, or, you know, that it should be going up?
Tiffany Green: Yeah, I mean, I think it’s very much grounded in the eugenics of, of, of earlier and I guess present times that the people that need to be having births are white cisgender women and other people should not be giving birth. Um, so I teach a lot about that in my classes, and I think it’s really important to sort of question our underpinning ideas of why we, we think people should be giving birth.
Like Karen, I don’t care about birth rates. I care about people that, you know, from a reproductive justice standpoint, the right to get pregnant and stay pregnant is really critical. And we know that social structures, uh, are very much against, for example, Black people, uh, getting pregnant, whereas during enslavement, um, the idea was for Black women to get pregnant and to, to perpetuate the institution of slavery. So there is no neutral way of thinking about birth rates, uh, in, in that context.
So in total agreement with Karen and just adding that extra historical context.
Beth Jarosz: Thank you. Um, and then there are, there are so many good questions. Um, and I have to pick, we probably have time for one, maybe two more. So I am going to go with one, um, that, uh, Jess, throughout the book, there’s this theme that good choices aren’t enough to save people, um, that, that there is this sort of social belief that, oh, well, you know, if that person had just done x differently, then y wouldn’t have happened. And you lay out a really clear case that that is not really how things work. Could you expand on that just a little bit?
Jessica Calarco: Sure. I mean, this is basically the idea that correlation is not causation in the sense that certainly there are, um, choices that people can make in our society or some people can make in our society, things like getting married, you know, delaying childbirth, uh, going to college, finishing a college degree. You know, these kinds of choices correlate with better outcomes. You know, more economic stability, lower risks of poverty, better health outcomes.
But that doesn’t necessarily mean that it’s those choices themselves that lead to those better outcomes. And it ignores the role of privilege in facilitating people making those kinds of choices. As Karen was talking about before, we’ve set people up to understand that you should really only be bringing a child into the world, or you won’t be, the only real way to not be judged for doing so is if you’re doing so in the right kind of context.
And the same is very much true for marriage. The same is very much true, I mean, for college. I talk in the book about how just going to college, especially for women given gender pay gaps and given the way that we, you know, differentially value gendered work, it doesn’t necessarily pay off in those kinds of ways.
And so we have to be very careful about that kind of messaging that just tells people to make good choices. And that’s really the whole, um, the basis of this DIY myth that I talk about.
Beth Jarosz: Does anyone else want to speak to that question?
Karen Benjamin Guzzo: I would just chime in to say some of the stuff that was in the book that I’ve seen in other places, which is you make the right choices and something catastrophic goes wrong and there’s no safety net for you. You have a sudden illness, uh, your spouse dies. All your good choices don’t mean anything, you know, because you’re on your own again, because there’s no safety net.
So, again, making these right choices, it’s no guarantee that things will work out. And so the amount of luck people have, um, in their lives is sort of underplayed because the people who’ve done well don’t like to think of themselves as being lucky or fortunate, but they are just one sort of bad mistake or bad, you know, car accident away from something catastrophic happening. But we don’t think about it that way. And we tend to say, oh, you must you must have made bad choices to have ended up this way.
Beth Jarosz: Um, I don’t think we have time to address this one, but I just want to note that a couple of people have mentioned in the Q&A that there’s also, we’ve talked a lot about child care, but similar patterns play out with elder care and with other family caregiving responsibilities. So I think it’s sort of just a resounding acknowledgment that that is true, and that when we talk about these roles that society plays on women, we’re talking about all of those, um, even if we’re focused on the child care piece today.
So the last question I want to leave with, um, is we’ve talked about a lot of what’s wrong. Um, we’ve talked about a lot of the challenges and the holes in the safety net. I want to just ask, is there anything that makes you optimistic about the future? And we’ll, we’ll go in reverse order this time. So we’ll do Jocelyn and wrap up. Jocelyn, what makes you optimistic?
Jocelyn Foye: Sure. Um. So, uh, the Womxn Project lately has been doing a lot of organizing at school board and town council levels, because that is a space where a majority of women are taking in, taking on the roles of those leadership positions, at least in school committees. But typically they get kicked. They decide not to continue in government because, frankly, it beats them down.
Um, what I will tell you is, is, well, we’re fighting against a lot of the hate group organizing ourselves in terms of how it’s impacting bodily autonomy and freedoms. Um, I will tell you that when people in their communities find out, so in Rhode Island, people don’t think it’s as present here. And so I would say that representation of the different states that is here in this panel, that’s a very different type of thing. But for this particular state, when people find out that there is things, there are certain things happening in certain areas close to them, people aren’t shying away from it as much as we expected. They’re actually asking, how can I help?
And so my talks have been very much around maybe it’s not direct because that puts you in direct conflict with people or vulnerable with people who are in your community directly, maybe at the supermarket. But there are different ways to engage. And I’m seeing a lot of innovative thinking and a lot of, of hopeful thinking, and that gives me hope that whatever happens on the other side of this, um, presidential election, that the network we’re building within our state, within these different communities to defend, um, their school boards and town councils that we’ll have a network of people that are working together to do something as simple as, how do you support people if Medicaid goes away?
And so there are different methods of behaviors that people are analyzing and turning to for their community health centers to do that. So again, I think hope is coming in like, who are the heroes? And it’s everyday heroes that we’re seeing, and it is moms, and it’s birthing people who are just like, you know, not, not on my watch. And so I think that that’s an important place to be and to hold on to is hope.
Beth Jarosz: All right. How about you, Karen? What gives you hope?
01:00:18
Karen Benjamin Guzzo: Young people. Um, they are very, they, they’re very clear that they, like, they think about parenthood a lot and what we owe kids. And they’re not willing to, to take it for granted that things will work out okay. They’re like, well, what do I need to do? And so they’re very conscious about, about having kids and about what their futures look like and how what they need to do to make it to, to, to make a better future for themselves and the, and the kids they’d like to have.
And so I’m always impressed by the young people I talk to. And I say, I sound so old when I say that. But, you know, my students in college, like they are really deliberate about thinking about their futures and what they want, and they want to make sure that they have those. So, so it’s not people aren’t taking childbearing too seriously, it’s that they’re taking it very seriously and they’re not willing to do things under, you know, less unsuitable conditions. And I think they’re going to work for those.
Beth Jarosz: Thank you. How about you, Tiffany? What, what gives you hope?
Tiffany Green: You know, um, so prison abolitionist Mariame Kaba always talks about hope being a discipline. And I think that is what I try to do.
You know, I work in reproductive health and equity and justice, and there’s a lot to be depressed about. But I think for me, it’s staying in the work and seeing that no matter how, how, you know, we despair, there have been people that have been working in reproductive justice for a long time. There have been people that have been working to, to expand access to child care for a long time. There have been people that have been fighting for all of the things that we’re talking about, and that progress is never, was never going to be linear.
So I think really for me, it’s staying in the work and working to uplift those people who are doing that work that keeps me hopeful.
Beth Jarosz: Thank you. And last but certainly not least, Jess, what gives you hope?
Jessica Calarco: Yeah, I mean, I think one thing that gives me hope, in addition to what’s already been mentioned, is that we got really close with Build Back Better, and we actually learned some really important lessons from the policies that we put in place during the pandemic: things like the Child Tax Credit, things like universal free lunch, you know, from the Medicaid expansion. We learned from these policies that we can do large-scale social programs in the U.S. despite our size, despite our political variations and all of the other challenges that we’re up against.
And the other thing that gives me hope is that, at least for now, we still live in a democracy, which means that we have the chance to, that we don’t actually need to persuade everyone, that we, if we can convince enough people to reject the kinds of myths that are designed to delude and divide us, then we actually have a shot at electing the kinds of policymakers who have the potential, at least, to fight for a stronger social safety net.
And so I think it’s those are the kinds of pieces that give me hope that we got very close and that this is possible if we just have enough people who are willing to reject some of these ideas that help us stay stuck in the status quo. Thank you.
Beth Jarosz: And thank you all so much. This has been—I don’t know if you can tell from the reactions that are coming in through the chat here with the hearts and the clapping—this has been an absolutely fantastic conversation. And thank you all for your time today. I truly, truly appreciate it, and we will post the recording soon.

Expert data users from PRB, the U.S. Census Bureau, and the Southern California Association of Governments review shortcuts, resources, and tools to help data users maximize their experience analyzing American Community Survey data.
An array of resources and tools can be used with American Community Survey (ACS) data to enhance the efficiency and proficiency of data users. However, given the volume of information available from the U.S. Census Bureau and elsewhere, learning about these resources and tools may be challenging for some users.
In this 90-minute workshop, expert data users from PRB, the Census Bureau, and the Southern California Association of Governments (SCAG) walked through some of their favorite shortcuts, resources, and tools to help data users maximize their experience analyzing ACS data.
Attendees were first introduced to the ACS data users group, an online community that provides help to members seeking to better understand ACS data and methods. The second presentation focused on accessing Census data via the API and MDAT, including basics such as how to create a call for an estimate in the API and access data through the public microdata sets (MDAT) on data.census.gov.
The third panelist provided a high-level overview of how to use R and the tidycensus package to execute commands such as switching between spatial scales, outputting a map, and looping through a query to assemble a longitudinal series from the ACS.
Mark Mather, PRB: Okay, well, I think we should go ahead and get started. Hi, everyone. Thanks for joining today’s webinar on ACS resources, shortcuts, and tools. I’m Mark Mather, and for those who don’t know me, I help manage the ACS Online Community website and other activities in partnership with the U.S. Census Bureau.
I am very excited to introduce the three speakers in today’s webinar. Lillian Kilduff is a Research Analyst at PRB and will provide a brief overview of the ACS Data Users Group and Online Community. Following Lillian, we’ll have Mary McKay, who’s a survey statistician in the American Community Survey Office. Mary is going to show you how to access the ACS through the Census Bureau’s API and microdata extraction tool, also known as the MDAT. And then we have Kevin Kane, who’s a program manager with the Southern California Association of Governments. Kevin is going to describe how he uses R and the tidycensus package to access and output ACS data.
A few housekeeping notes. We’re going to save the Q&A until the end. We do have a large number of participants. We encourage you to use the raise hand feature in Zoom, and then we’ll try to unmute you to ask your question, but you can also feel free to use the question box at the bottom of your panel there, and you can type in your questions at any time during the webinar.
Closed captioning is also available as an option at the bottom of your screen. And in addition to our three panelists, we also have several other Census Bureau staff members on standby to answer your questions today. And finally, this webinar is being recorded, and we will send you a link to the recording after the event. And with that, I’m going to turn it over to Lillian.
Lillian Kilduff, PRB: Thanks, Mark. I’m going to be talking about the ACS Online Community today and also showing the new upgrades. If you haven’t already seen to the look and feel of the website, I’m going to go ahead and share my screen real quick. Right here. Okay. Sorry about that. Okay. Um, so I’m going to provide the brief introduction to the ACS Online Community.
So here’s an overview of the presentation today. First we’re going to do a quick recap of the American Community Survey itself. Then we’re going to talk about the ACS Data Users Group and Online Community. Then we can go over the tabs of the ACS Online Community, and that includes the discussion forum, the ACS resources, webinars, and conferences tabs.
After that, we’re going to talk about the ACS Online Community itself. So behind the scenes, how many members do we have, threads and replies, page views, response rates, and then also talk about the discussion forum topics that often get viewed. We’ll go over the site upgrade if you haven’t already seen the changes and talk about how to join the ACS Online Community.
So just to review, if you’re new to the American Community Survey, people use the American Community Survey to get, uh, data on the demographic characteristics. So that would include social characteristics, economic, housing, and demographic. And you can see some of the examples in those parentheses there. The data products include one-year estimates, one-year supplemental estimates, five-year estimates, and you can access those through many tools including tables, the summary file, and PUMS.
Here is a quick hierarchy of the geographies available. So we have from the nation down to block groups.
When it comes to the ACS Online Community, this is a partnership between us at PRB and the American Community Survey Office at the Census Bureau. The ACS Online Community’s purpose is so that ACS data users can share tips and tricks, questions, materials, and then also we post announcements about things like today, the webinar. Membership is free and open to all ACS data users and new ACS data users. The group is led by our steering committee, and we try to pick a steering committee that represents all different data users, local governments’ data users, geography, geography data users. And we just had a new steering committee this this year.
So I’m going to show you the home page. Okay. This is fine. Here is the home screen of the new ACS Online Community. Here is just what I talked about, the purpose of it. Here’s some quick facts about it. And we also have the most frequently asked questions. That’s based on questions from data user surveys and also from the most viewed and interacted discussion forum post. You can view more FAQs on the FAQs page from there. We also have latest discussions, people who are posting in the ACS Online Community. We have a link to the Census Bureau website.
The discussion forum is the main part of the ACS Online Community. Here is an example of a discussion forum post. So a data user is asking a question, and then we get a reply from another data user. You can upvote replies, and if you become a member of the ACS Online Community, you can do things like uploading, replying, and adding to the discussion forum. Here you can see the views, replies. You can also add tags to new discussion forum posts. And then we have more information over here.
Next is the ACS resources page. Here you can see a lot of different links to ACS resources under these helpful headings. If you aren’t already familiar, the ACS handbooks are a great place to start, and we also have handbooks that are catered to certain data users.
Here is our webinar page. So this is the webinar we’re having today. And then we also have links to past webinars with recordings, information, and even the slide decks.
We hold a biannual conference every year. The latest conference was the 2023 ACS Data Users Conference. We have the agenda from that. That includes the recordings of the presentations and also the slides as well. We have the previous conferences, and those include that information as well.
I’m going to go back to my PowerPoint now.
Again, this is the discussion forum. Here is an example of a notification of a Federal Register Notice. That’s one of the examples of a discussion forum post that’s helpful to ACS data users.
Okay, so behind the scenes we can talk about the membership. We have over 5,600 members as of the end of May. Here you can see the fiscal year 2022 and 2023, and membership can vary over that time. And usually when we, when we have events like conferences or a new series of events called ACS on the road—we just went to the Texas Demographic Conference—we can see an increase in membership.
There’s a lot of discussion forum posts, and they get a lot of replies. Here again we have, uh, the total number of the threads and replies across the two last, last fiscal years.
And here are the number of page views that the ACS Online Community gets. If you’ve ever googled a question about the American Community Survey and its data, a lot of times the first Google result is the ACS Online Community itself. And you can see that overall, uh, with the last fiscal year, the page views and the ACS Online Community have increased.
The great thing about the ACS Online Community is that we do have a great response rate. So you can see that just within one day, if you post a question or an announcement or a comment, you get a pretty good, uh, you know, response rate.
And here are the top 10 discussion topics. We get a lot of questions about calculating margin of error, especially, uh, zip code–level geographic questions.
So onto our site upgrade. This is how the ACS Online Community used to look. You may remember it this way, but now live on the site, we have this new upgrade that’s, uh, more intuitive and more modern in the look and feel. This is how the discussion forum used to look. And now here is the upgraded website.
So finally, how do you get involved with this site? You don’t need to be a member of the ACS Online Community to view the posts, but you do need to be a member to post in the Online Community, comment, uh, and also upvote. You can tailor the email notifications that you get, so, uh, to new threads and comments. And these are all optional. So if you’re hesitant about joining the ACS Online Community because you’re worried about a lot of email notifications, you can cater those. You can also bookmark discussion forum threads so you can reference those whenever you have questions about a certain topic.
And again membership is free and signing up is very simple. First, you click on the sign up button in the top right and then just answer a few questions. We use this information so that we can better cater to different data user groups.
Finally, there is a picture of one of the ACS data users conferences, and please give us your feedback or suggestions.
Thank you so much. Here is my contact information if you ever have any questions. And I can either answer the questions or direct you to someone who will know your, the answer to it.
Mark Mather: Great. Thank you, Lillian. Next up we have Mary.
Mary Ana McKay, American Community Survey Office: Hello? Hello. Okay. All right, I can share my screen once Lillian is done sharing hers.
Lillian Kilduff: Yep. Um. Stop there.
Mary Ana McKay: Perfect. Knock on wood. Awesome.
Okay, so hello, everyone. My name is Mary Ana McKay. I’m a survey statistician with the Census Bureau’s American Community Survey Office. I’m here to highlight two data products and tools that you may be familiar with or you’ve never heard of before. And just a little bit of housekeeping, I’m going to apologize in advance if I speak quickly. I just have a ton of information that I want to share with you all, and I’m very excited to be here. I’m excited that you’re all here.
So without further ado, let me get started. I want to give a broad roadmap of what I’m going to be presenting during this workshop. So to start, I’m going to dive into the ACS Public Use Microdata Sample, or PUMS. This portion is going to cover basics. Then I’m going to run through the Census Bureau’s tool to access these data, and then I’ll wrap up that section with some resources for you as you dive in on your own.
And then immediately following the PUMS, I’m going to jump over and give a very brief introduction to the application programming interface, the API. We won’t go too much into details, but you will learn the basics, so you’re hopefully able to build off what we do today as you go off onto your own data journey. And we’ll go through an example API call, and then I’ll share just a sample of the many, many resources available to you as an API data user before I turn it over to Kevin for the last leg of this workshop.
So before I dive into the PUMS and API, I want to remind everybody about data.census.gov. It’s a really powerful tool for you as you grow your ACS data accessing skills. So many of you here today are probably familiar with data.census.gov, which is the primary way to access data from the American Community Survey, 2020 Census, and more. And I’ll be sprinkling my use of it throughout my two demonstrations, but it’s not the star of the show, so I’m kind of going to run through them a little bit more quickly than I would otherwise. But in an effort to be brief, I will let you know that there are a variety of how-to materials, video tutorials, webinars, and FAQs to help you use data.census.gov.
And I’m going to step aside again and just mention there are links at the bottoms of a lot of my slides. I have a colleague who will be sharing some of them in the chat, but also the PDF version of this presentation is going to have clickable links too.
So the ACS Public Use Microdata Sample can be overwhelming, but we’re going to briefly cover basics to start to get you familiar and hopefully comfortable with this powerful data set.
And I want you to think about these questions: What are your main goals when accessing ACS data? Are you primarily accessing pretabulated estimates? Are you finding that the data you need are not published in these estimates? And what about when you’re looking at cross tabulated estimates? How do you primarily access ACS data? Are you using data.census.gov or a third-party tool such as Social Explorer? What do the data look like on a daily basis? And finally, with the tool or tools you are using, what limitations do you face accessing ACS data?
So these questions might have different answers depending on the day or the data you need. So in some cases, the tool that we are going to explore will be the best option, but other times another method will work better. It’s all about the best way to address your needs. And I always check data.census.gov—I’m going to say this constantly throughout my portion—just to see if there’s pretabulated estimates for the data product and the geography of interest. But in cases that I need something a little bit more specific, I’ll hop over to PUMS.
So, for example, today I’m curious about poverty among veterans by age, and I know I can find tables in data.census.gov that might get close to what I need but not quite exact. And luckily, PUMS is going to be able to step in and get us the table that I want.
So I want to introduce a few PUMS basics before we work on an example. And finally I will share some resources that you can access on our website.
So again, when I say PUMS, I am referring to the Public Use Microdata Sample. ACS data products are released about one year after the data are collected, and the PUMS is a publicly available subsample of ACS records. The one-year PUMS estimates are a subsample of data collected over a calendar year, 12 months, and they constitute approximately 1% of U.S. households. Whereas the five-year PUMS combines data collected over 60 months, or five years, and they constitute approximately 5% of all U.S. households.
Additional restrictions are added to protect data confidentiality, such as including broader categories of data or grouping together extreme values in the form of top and bottom coding. And you’re going to see a couple examples of this top coding in my demonstration.
PUMS files allow data users to calculate their own estimates and margins of errors that may not be available on data.census.gov. Statistical software is recommended when working with PUMS data unless you are working with our microdata access tool on data.census.gov, and this is the tool that I’m going to be demonstrating today.
So here are some examples of why you might want to use the PUMS. These data come in handy when you are looking for cross tabulations that might not be part of the standard table packages released in the ACS. For example, you could be looking for specific poverty thresholds or income levels for veterans at a specific age ranges like I am today. Again, always check data.census.gov and the pretabulated estimates. They may have exactly what you need.
This information is going to be a little bit heavy, but I want to mention it before we continue. So PUMS data provide individual records that data users must aggregate to form estimates. Unlike in data.census.gov, there are no pretabulated data. Weights are included on the PUMS files so that data users may create weighted population estimates. If you are working with housing records, you will use the housing weights. And if you’re working with person records, you’re going to use person weights.
When working with a merged file that includes both housing and person records, person weights should be used to produce estimates for person characteristics. Housing characteristics cannot be tallied from this merged file without taking extra steps to ensure that each housing weight is only counted once per household. In today’s example, I am using all person records.
And then replicate weights, those numbered one through 80 are used for calculating replica estimates needed to calculate standard errors. These standard errors are necessary in order to calculate the associated margins of error or MOEs, and we won’t be going this in-depth for this presentation, but there are guided examples that I can direct you to for more.
The five-year PUMS is the equivalent of five one-year files, so again includes about 5% of all U.S. households. So people often ask, and you may be wondering, what is the benefit of the five-year PUMS? So there’s some nice standardization for the five-year PUMS that you can’t necessarily get by merging five- to one-year files. For example, there are new weights that are produced for these records so that the weighted population matches the latest population estimate. Dollar amounts have an adjustment factor to standardize them to the latest year, so that no one is comparing varying levels of inflation. Other coding schemes are updated, such as ancestry and occupation, so you don’t have to recode those yourself.
I’m going to focus on a limitation data users might experience someone accessing PUMS, and that’s geography. To ensure the confidentiality of ACS respondents, the Census Bureau has to balance geographic detail with detail in the data. There are more than 250 variables on a single PUMS person record. This means that we cannot identify as many small geographies in the PUMS as users might hope. We can put the region, division, and state on the file, but the only other geography is something called a Public Use Microdata Area, a PUMA. PUMS is not designed for statistical analysis of small geographic areas, but the PUMAs can still be used for focus analysis in counties and cities of about 100,000 people or more as well as many metro areas.
So I want to spend a little bit more time here on PUMAs. PUMAs are areas with a population of, again, at least 100,000, which is large enough to meet disclosure avoidance requirements. PUMAs are identified by a five-digit code that is unique within each state. These geographies are redefined after each decennial census and are defined by either the state data center or, in some cases, the Census Bureau’s regional geography staff. For example, the 2020 PUMA definitions were introduced with the 2022 PUMS files.
As with many geographic concepts, seeing PUMAs on a map may help you understand them better. So as you can see, some PUMAs are small and others are large, because, again, PUMAs are built on population and not geography. The smaller PUMAs here on this map are mainly concentrated in the Buffalo and Rochester regions of this map, and some counties in this region that have smaller populations are combined together as part of a multi-county PUMA.
So I use data.census.gov here to visualize geographies. This is a screenshot that shows, um, the PUMAs that make up Marin County, California. So as you can see, there are two that make up the county. So you can combine data from both to approximate estimates for the county. The primary difficulties occur when we get further away from urban centers to counties with smaller populations, which are then again combined with other counties to make PUMAs. And in these cases it becomes less feasible to infer data about the individual county. Furthermore, while I am showing you an example here of PUMAs that adhere to county boundaries, it is not actually a requirement that PUMAs be designed that way, although it is recommended.
And I want to acknowledge really quickly that some of you might know that data.census.gov now has an address lookup option in the search bar. I just want to let you know that right now, PUMA geographies do not pop up when you use that option. I just tried it before, but hopefully someday you’ll be able to put in an address and see what PUMA that falls into.
All right, let’s get our hands dirty with PUMS data. And to start, I’m going to heed my own advice and go directly to data.census.gov. I’m going to first see what tables I might find. And again, I’m going to zip through this because I want to focus more on the microdata access tool. I’m going to use the advanced search feature.
And again, today I’m interested in poverty among veterans by age. I’m going to apply two filters: “veterans” and then I’m going to select “poverty” to see what tables come up. I’m going to click the search bar. And I see here there’s actually a table age by veteran status by poverty status. And it’s a little bit more detailed; it also has disability status. But it does have generally what I’m looking for. So again I said poverty among veterans by age.
But as I’m looking through this table, the age ranges are not quite what I’m looking for, and I’m actually interested at below, at, and above poverty. So this just has two thresholds; I want to add a third. So in any other day but today this table might actually serve the exact purpose I’m looking for, but now I’m going to use the PUMS data to get what I really want.
I’m going to click on the logo to go back to data.census.gov home page, and on the top right, you probably can’t see it, there’s a little button that says apps. I’m going to click on that. And it’s this first option here that says microdata. So this is what you’re going to see. The default data set is the ACS one-year PUMS. And the select vintage is 2022. And perfect, that is exactly what I want. I’ll click next so I can select my variables.
So before I select my variables, I want to search for what they might be called. I know I want poverty, I want veteran status, and I want age. So I like to use the label option here—and I’m going to zoom in, I might have to zoom in and out—I like to use the label here to use keywords to see what pops up. And we also have PUMS documentation with data dictionaries, so you can do the same thing before you get into this tool.
So for the first one I’m going to type in “poverty,” and I see this income-to-poverty ratio recode; I selected this for, uh, today’s demonstration because this is the poverty variable in PUMS, so I want to show people how to use it. It does give me a little bit of a warning here that the variable is continuous, but we’re going to make a custom group with this variable to be able to put on our table, so we don’t have to worry about that quite yet.
And so for my veteran’s variable I’m going to type in “veterans” or “veteran.” And I’m going to open the detail of the three variables that show up. And this isn’t quite what I’m looking for. This veteran period of service is a little bit more detailed. I just want to know if a person has ever served in the military or not.
So now I’m going to try typing another keyword. So I’ll do “military.” And luckily for me I have this military service. Let’s cross our fingers. And yes, okay, this is exactly what we want. We have a value 2 that says “On active duty in the past, but not now.” So that’s how I’m operationalizing veterans. I’m going to select this variable. So now I have two. And my final one is age. So it’s right here at the top. It’s going to give me that same warning that the variable is continuous, but that’s totally fine.
So from here we have our three in the data cart. We’re going to click on View Table and see what we have to start with. So for most situations simply selecting the variables is not going to be the last step for you, for your table, unless by some chance it’s laid out exactly how you want it and the categories are exactly what you want.
So at first glance, there is a lot going on, and I’m going to rename the table just to keep myself organized up here. You can go in and change that title as much as you want, but I’m just going to do “Poverty x Age for Veterans,” so that’s just going to keep it organized in my head as to what we’re doing.
So we see that the default table has military, that military variable on the columns. We have nothing on rows. And then we have two variables here in the values in table cells. Then in this drop-down this is the first thing I’m going to change. I’m going to click on this and select Count. So this is going to give us a value for how many fall in each category.
So I’m going to organize to make variables, and then I’m going to put them so we have our universe limited to just veterans. And then I’m going to create grouped categories for age. And then income-to-poverty ratios on the columns will be three thresholds. Or I’ll make a threshold of three.
So to put in simple terms, our universe is going to be just veterans. My columns are going to be the recode of that income-to-poverty ratio. And then finally the rows are going to be simplified categories of age. And what’s great about this tool is you can organize and flip-flop your rows and columns super easily, so if you don’t like what we have planned, we can change it when we’re done.
So we’re going to start first with making our universe what we want, which is just veterans. So I’m clicking on the variable. I’m going to deselect everything that says Include in Universe. And I’m only interested in Value 2: “On active duty in the past, but not now.” I’m going to select that option, and I like to click into View Table just to see kind of what we’re working with with every change that I make. So now I see my universe is only limited to my definition of veterans.
So now let’s move on and make the age category. So I’m going to click on the Age variable. I’m going to click on Create Custom Group. From here we’re going to use the Auto Group feature. I’m going to change the start age to 17 because that’s generally the cutoff date to join the military. And then for this, this is an example of a top-coded variable, we have 99. So anybody who’s 99 years or older is going to be in this category. And then I want groups of 10 years. It’s not going to be perfect with the values that I have, but for what I need, this is going to be fine. And I’m going to click Auto Group, and you see that it makes those groups for you.
The last thing I’m going to do is there’s a Not Elsewhere Classified category. I’m going to click on Edit Group. These are all the values that aren’t in the groups that I just designated. I’m going to toggle to show off the table. So I’m going to toggle that on, and you have to click Save Group. So now this isn’t going to show in my table. Let’s view the table and see what we have. It doesn’t show up, but we’re just going to click and drag, and to keep myself organized, we have the rows is what we’re going to have for age. So I just clicked it and dragged it over to On Rows. And we’ll see. Now we have account for the people who are veterans in these different age groups.
And the last thing we have is to make the poverty variable. So again I’m clicking on the POVPIT variable. And just to look at this, it is continuous. And I want to explain a little bit more about what the numbers mean before I go in and make my custom group. So for this variable, less than 1 or 100%, because this is a percentage, is below poverty; 1 or 100% is at poverty; and above 1 or 100% is above poverty.
So these are the actually the three categories I’m going to create. But this is an instance where you can really go where your research question or your need takes you. For example, I know that 200% poverty is a threshold a lot of data users need, and there are limited options on data.census.gov. So using PUMS here is, you’re going to be able to get that.
So the calculation for this specific variable is simply to divide income by poverty thresholds, which are determined by number of children, sze of family, and inflation. So for this I’m going to click on Create Custom Group. I am not going to use the Auto Group feature. I’m going to dig in right here where it says Group Label. I’m going to start with Below Poverty. And again you can go in and change these group labels. Um, as you’re going through, if you want to relabel it, you’re able to do that.
So I’m going to click on below 501%. The bottom value I want is zero. And then the top value I want for this one is 99. I’ll click Save Group. So it makes that for me I’m going to click back into Not Elsewhere Classified. Let’s do at poverty. And this is going to be a single value. You can do that. So just when we’re looking at estimates, note that this only has one single value in it. So we have 100 to 100, Save Group.
And then finally we’re going to have above poverty. We’re going to select the remaining of the between 101 and 500. And then since this is another top-coded variable, I want this 500% or more because that’s above poverty. I’ll click Save Group. The last step similar to that Auto Group you’re going to click into, Not Elsewhere Classified. I don’t want this on my table so I’m going to toggle it off, Save Group. And now we’ll view table.
So again right now POVPIT doesn’t show, that Recode doesn’t show. But I’m going to click hold and drag on to columns. I can actually take the military variable off the table because it is my universe. I don’t need to have it on there. It’s included. And here is the example of the table. So now I have the poverty thresholds for different age ranges among veterans.
So I didn’t dive into this. But I want to mention that you can click Change Geography up here at the top. And you see that we have the geographies that we talked about. And the default is going to be the United States. And since PUMAs, the Public Use Microdata Areas, have populations of 100,000 or more, all of them and all of these geographies are going to be included in both the one-year and the five-year PUMS. So from here you can click, download, and share what you’ve made. And remember that you can calculate the error with resources available on the ACS website.
So now I want to go briefly and share some few links with valuable resources for you. So I do my best learning when I am practicing. So if you’re like me, I like to follow along with webinars that have some activities to check, and I put together a list of videos to see step-by-step directions for various aspects of the MDAT tool. So the data gems are going to be shorter, more brief videos, whereas the webinars go into a little bit more detail.
And I’m going to make a plug for the PUMS documentation page. I did mention it, but we didn’t go into it. It has all the resources you’re going to need for every data release. You can explore user guides, data dictionaries, and more. And this is also where you’re going to find directions for calculating variances.
And finally, I think a really great resource that we spent a lot of time perfecting, and Lillian talked about it briefly, are the data users handbooks. We do have one for PUMS users, and I also don’t want to spoil the next part of my presentation too much, but you can find the PUMS on the API.
Um, and with that, that’s the worst segue I’ve ever had, so again, I apologize, but now we’re going to jump immediately into talking about the Census Bureau’s application programming interface. So let’s take a deep breath and move on to the next part of the workshop.
So I want you to think again about the same questions we, we had when we were exploring PUMS data. So what are your main goals when accessing ACS data? Are you primarily accessing pretabulated estimates? Are there a few variables within a single table that you find yourself going to more and more? And what about variables across different geographies or across years? How do you primarily access ACS data? Are you using data.census.gov or third-party tools such as Social Explorer? And what do the data look like on a daily basis? With the tool or tools you are using, what limitations do you face accessing ACS data? Being able to answer these questions can determine if the API is a good option for your needs.
Now on to the basics. When you use the API, imagine that you are in a strawberry field since it is summer. The strawberries are data points you seek, and in order to go get them, you are going to be running calls or going around the field and picking the ripe strawberries. Data.census.gov itself is a fellow strawberry picker. What we are doing today is just a smaller example of what data.census.gov does through its website. We are trying to directly access the data in a very simple way.
So some of you may be creating dashboards on your websites that users will access to get different data to display, given certain criteria. Others might be trying to make data visualizations, and there may be some of you who are using R to run analysis. It’s also okay if you are none of these types of users. The API can still be a very simple process to get the estimates that you want.
As I was just describing what uses the Census API might be for, here are some more specific examples. What if you simply need just one variable, let’s say percent below poverty level for individuals under 18 and nothing else within the table? What if you wanted to grab all the census tracts within a county in Delaware? How about an estimate for an individual below poverty level at the census tract, county, state, and national level? It could just be that you have a data point that you’re trying to easily access year after year. I’m going to show you some ways to simplify that process for you using the API. And I will say this, and I’ve said it several times before using the API, consider checking out data.census.gov.
So with that let’s run through an API call. These are the ACS data tables that you can find on the API. In data.census.gov, the second column here is what the table ID starts with. For our example today we’re going to be using subject tables from the five-year estimates. So we’re going to be using this here. So after you put the beginning of the call, you’re going to put in the variables the tables and the geographies you want, but we’re going to get there in a second.
We’re going to start with data.census.gov, like I’ve said a million times already. And just for the purposes of time, I have screenshots here. So I typed in “poverty” because that’s what I’m interested in for this example. I found Table S1701. And then I limited my geography to Wyoming County, New York. That’s my hometown is there. And this is a smaller county, so it’s going to be the five-year estimates. It has a population of fewer than 65,000 residents, so we’re going to be using the ACS five-year estimates.
Now on this table I see, and I’m sorry if it’s hard to read, we have below poverty levels. So we have the estimate and the margin of error. That’s what I’m interested in. Just those two pieces of the entire table. This table also has percent below poverty level, which is a measure I would prefer, especially if I’m going to be comparing with other counties of varying sizes, but for this example, I’m just going to stick with the estimate and its margin of error.
I’ll mention one cool thing about data.census.gov, there are many, but if you look along the top of your table, there’s actually an API button now that you can click and it’ll create the call for the table that you’re looking at. So this can be really helpful if you’re using the filter options to select geographies, and you might just want that entire table you’re looking at. You can also use it as a starting point to build off. If you want a little bit more detail with your call. And I highly recommend always working off an example when you’re working on calls; it makes it a lot easier than building from the ground up.
So we only want two variables: the estimate and then the margin of error. And what I’m showing here is the entire call. But we’re going to dissect it before running and seeing what happens. I use the slide a few back to figure out what table type I had. And then I did a few additional steps, using some web pages to figure out (1) the variables that I need and (2) the geography.
So to start to break it down, this is the base for all Census API queries. This second set pulls out the data product year, 2022; the program, ACS; the date, the data set, ACS five-year, so this is the 2018–2022 ACS five-year; and then, finally, the table type, which is subject. And again you can refer back a few slides to see the base of all the table types. That slide will get you the portions up until this point. So once we get to this after ?get, that’s where the customization gets started.
So this pulls out, this is where I’m picking the variables. And how did I get here? We’re going to hop over to the website, and just for transparency, I’m using Google Chrome because that’s what I prefer to use when I’m doing API. So I’m going to census.gov/api, the main website, and I’m going to scroll down to latest available available APIs and view all available APIs. From here you see what’s available. I’m going to click on American Community Survey, in theory. And we divide it by the different data products, um, which I find they’re all pretty similar for all of them. So it’s easy once you know how to use one, you can jump around and use the other ones.
So we’re selecting the five-year data. We release this for every data release. So we’re here in 2022. I’m going to scroll down, and I find Subject Tables. So this is again the same for all table types, what I’m doing; you just have to make sure that you’re following along with your table type.
So the first thing I’m going to start with is the second bullet down: the 2022 ACS Subject Table Variables. I’m going to click on the HTML. So for API, Ctrl+F is going to be your best friend, if it’s not already. So I’m going to click Ctrl+F on my keyboard. And we’re going to type in “poverty” because I want to overwhelm you briefly with what shows up.
So as it’s loading, in theory, we’re going to have thousands of options. So it’s loading, um, there’s so many of it that now it doesn’t want to do it. So there’s actually over 3,700 results on this page for poverty. And that’s a lot to go through. So I’m going to show you a little bit of an insider secret, or at least that’s what I like to call it.
Um, I’m back on S1701. I’ve magically loaded it for us here, and I’m going to talk about the different columns. So this is a column set 1. We have the total. And then for this table, there’s a column set 2. Now what does that mean? We’re going to go back to this table, the variable lists. And if I start to scroll down, you hopefully can see that there’s a table ID, then there’s an underscore, and a CO1 that corresponds with column 1. So I can use this as my base to Ctrl+F again. And since I’m looking at S1701, I’m going to type that in. It’s going to jump me to the first time that that shows up. When I do the underscore, it’s going to jump me to the section for this table.
And I know I’m looking for the second set of columns, so I’m just going to write in CO2. And luckily for me it’s this first estimate in column set 2. So we have below poverty level population for whom poverty status is determined. Then the one that ends in E is going to be my estimate, and I want that margin of error, and you should too. That’s going to be the one that just ends in N.
So let’s hop back over to the slides to see what I did here. So I have the two variables that I found and I put them in here. I also put Name here. So to make sure that I get the geography names when I run the call. But this is not a necessary component of your call. I tend to use it just to confirm that I have the right geography, so I can run it with that, confirm I have the right geography, and then you can run it again without if you don’t need it for the larger purposes of your call.
One thing I will note, you separate the variable names with just a comma. if you add a space or an additional character, you are going to get an error when you run your call. So working backwards, if you get an error, double-check your call and make sure that there’s no spaces in between the commas. You can pull up to 50 variables with this method, and if you want more than 50, it’s likely that you just have to pull the entire table and then work from there.
I also want to mention one more thing. You can pull variables from different tables of the same type. Say, for instance, you want to pull all of the same variable in a table series for different race iterations. So we have detailed tables for the different race and ethnicity iterations that end in A through I. You can pull the same variable from those different tables.
I also want to jump back to this name variable and give you a little bit of a warning. So it does cause a shift in Excel, especially if it’s a geography within a geography. And you’re going to see this when we open the file from our example here. And I’m not sure if this happens with every table type, but just keep that in mind that I know for a fact that we do not recommend using it for group calls, particularly with data profiles. So just keep that in mind that it can get a little bit messy. But again, I like to have it as a little check for me.
So before I move on, what happens if you want all variables in the table? What if you want the entire S1701? You can use a group call. So I have that down here. Um, you can also use data.census.gov if you have the geographies you selected already. That API button is going to do exactly what this is going to do for us.
So now we have the last part, which is the geography. And in many instances you will want to limit to a specific geography. And in this example I want one county. And you may be wondering how I got these numbers. And I did not, in fact, memorize every county code for every state to figure this out. I’m going to share another secret, and I think this one’s a little bit more exciting, but who knows? You’ll have to tell me.
So we’re back on the ACS five-year API page, and we’re still in the subject table section. I’m going to click on the fourth bullet down that says Examples. So this breaks it up by geographies. And since I’m looking at state and county, I’m going to look at the example API calls that I have here. And fortunately for me I’ve used this so much that it’s already, um, calling itself out.
There’s one here that has a wild called, wild card or the asterisks for county and state. So if I click on this, it’s going to actually give me, um, and hopefully let’s, that we’ve zoomed in, it’s giving me all counties in all states. It does have a random variable. Um, just to call it out again, as an example, you can leave that in there, or you can delete it with the comma and just have name. So now you have the call to get all of the counties in all of the states.
And again, your best friend, at least for now, is Ctrl+F. You’re going to start to type in your geography of interest. And luckily for me, the first Wyoming on this list is actually Wyoming County. So I can use context clues here and see 36 for all of the New York counties that shows up. So I know that’s my state code. And then the second three digit code, 121, is going to be my county code.
So now we have all the pieces we need. I’m going to jump back. And we have the &for county 121 and &in state is 36. So the nice thing here is that you don’t have to remember the little syntax components, the codes. If you follow an example, you’re going to be able to always have access to what you want, and then you can customize from there.
So much like getting the full table, that group call, you can get full geographies. So what if you wanted all counties within a state? You can use that wildcard in your calls like we just did. For some geographies, as we just did to get our geocodes, you can do the wild cards for both components. It’s really trial and error.
So let’s take this call. I’m going to copy it from my document, and I’m going to run it in the browser. So I copy paste it, and now I’m going to run, and this is what we have. So we are getting the number the estimate of those in Wyoming County in New York who live below poverty with the corresponding margin of error. And we see we have the name here, we have the estimate, the margin of error, and then the state and the county codes.
So I want to just show you back on this slide that your output might look different than what you see here. Sometimes it’s the browser you’re using or the settings. But it’s okay, because when you download it, it’s all the same.
So jumping back over to the browser, if all you needed was the estimate, you can stop here, but you can also download it. And what you’re going to do is you’re going to right click. You’re going to click Save As. You’re going to name your file. And this is important, you’re going to type in the file name .csv. The last step for the Save As type you’re going to select All Files. So you’re going to click Save. And it’s going to download that CSV. And I’ll open it up just to show you what we have.
So like I mentioned briefly, or maybe not briefly, I think briefly, name does cause a shift, especially when you have a geography within a geography. So I had a county within a state. So here it shifted my variables, and all I’m going to do is highlight these. I’m going to cut and paste to move them over. Um, so that is just what you’re going to look like, what it’s going to look like when you download your file.
So hopefully that was not too overwhelming. Um, and that was just a little bit of a breakdown of what the API is. So really quick, I now want to share some resources as you go on your own. But don’t worry, I do have contact information so you can always be connected with our team if you get stuck.
So when you’re on your own, start with checking the example calls to get yourself started. I sound like a broken record when I say that. That’s what we did today. So I want to emphasize how useful they can be and how much time you can save. You can always edit them to fit your needs, but having the base like we walked through can be really helpful.
Unfortunately, some variable names change with every data release, so variables are added and subtracted from tables, so it’s important that you check the variable names if you’re looking at data year after year, to make sure you are extracting the same data variable. It’s super easy when you use that variable list, so I always just open that HTML as soon as I get started, as you saw in the walkthrough. And then the other one is that Examples page. So these are the two that I use when I’m customizing the components of my call.
And one thing I want to mention is keys. Um, some of you may be wondering what or why, and a key is essentially just that: a way to open the door to more calls. Without a key, you are maxed at 500 calls a day, and if it’s just you and your organization running calls here, there, a key isn’t necessary. But if you are creating a dashboard that’s going to get a lot of traffic, you might consider a key. It’s completely free, and it takes mere moments.
Um, and I will mention that if you’re going to use the R package tidycensus, you need a key. And Kevin’s probably going to repeat that as well. Can’t do it without a key.
Um, this is just a start regarding the resources. Again, this PDF is going to be able to be clickable if you can’t get access, um, in the chat to the links. So there’s a lot on here. And if you’re lost I can always connect you. The last two in this webinar list, um, are going to be a good run-through of an example similar to what we did today with a little bit more detail. And I also included some resources for using open-source data and programs, which is really helpful if you’re using the API.
One really unique and valuable tool we have to offer is the Slack channel. There are Census staff that engage on their every day to help with data user questions, especially if you’re accessing data through different ways such as R or Python. And finally, as I mentioned, tidycensus, it’s a great R package to use with the Census API. It is not maintained by us, but it has great resources to guide you.
Um, and I finally want to mention a few final things before turning it over to Kevin to wow us with his expertise with tidycensus. There is a team at Census that has live workshops to go over that MDAT tool and the Census API. I highly recommend you sign up if you’re curious to learn more about either. These are great for both beginners and advanced users. Please consider joining the ACS Data Users Group that Lillian highlighted at the beginning of this workshop if you aren’t members already.
And I know these were very quick demonstrations of the PUMS and API, but you can email our team at acso.users.support@census.gov if you have any questions in the future. Thank you so much. And Kevin, the floor is yours.
Kevin Kane, Southern California Association of Governments: Well, goodness, Mary, thanks for such a thorough and comprehensive, uh, you know, overview of both PUMS and, uh, Census API calls. Hopefully I can build on it. Um, doing these is kind of your job, for the most part, I just kind of, uh, do this as somewhat of a service to a degree.
I’m Kevin Kane. I’m the Program Manager for demographics and growth visioning here at the Southern California Association of Governments. Uh, why do I do this, uh, type of, this type of a webinar? Just, you know, um, I find it extremely useful to kind of have effective workflows, certainly in my field, which is regional planning and demographics. But, uh, I also teach this material to a course at the University of Southern California.
So, um, you know, bottom line, uh, I find, Mary’s API call workflow, uh, to be really useful, but you are a little bit limited in terms of the replicability of it, um, by putting calls into a URL. And, uh, she gives me a hard time every time I follow her after a webinar, um, because of what I’ve titled this, uh, “R tidycensus: Your graceful exit from data.census.gov.” And what I’ll share with you here is basically the workflow that I kind of developed once data.census.gov, um, started a few years back in order to just kind of help, uh, you know, be a little bit more replicable.
Uh, Southern California Association of Governments has 191 cities under its purview across six counties in Southern California. So we’re working with a lot of county-, place-, uh, and tract-level data longitudinally, uh, and kind of that’s buried within either PUMS or other detailed tables. I’m sure that’s the workflow for a lot of folks here.
So, um, I’ll be very brief in terms of, uh, slides here, but, uh, really, what I want to mostly show to you is a demonstration. Um, because frankly, it’s not possible in 20 or so minutes to actually get into R or RStudio or a coding environment. But basically what I’m going to pick up where Mary left off, uh, and wrap that within an R, or a code-based workflow.
So R is an open-source, uh, programming language. RStudio is a freeware wrapper of it that just makes it a little bit easier to use. Um, I’ve included here some very easy installation instructions, uh, for you, uh, like teaching in this because, uh, it’s not a commercial product. You can take it to wherever you work, uh, and not have to worry about a license.
The second thing that I’ll say is I’ve posted a lot of training materials here on this GitHub, uh, website here. I’m not sure who, uh, you know, the level of folks are GitHub users or not. I frankly just use this for file transfer. I am going to have to confess, I’m more of an intermediate-level user of this and frankly of some of the R packages. But like all of us, you know, hey, we’re, we’re doing this to do our jobs better.
Um, so what I’ve done here is included a package which I call the kind of a half-day R introduction. There’s also a video where I did the full webinar for this, uh, if you like the workflow. Um, I would say it probably would take you about a half a day, roughly, to get through it and to actually learn R to a point where you can use the Census API usefully. Um, if you hit this code here, you can download a ZIP file containing all of this. The key file is one that has a dot R at the end of it. And that’s what we’re going to be kind of going through mostly today.
Um, switching back here to kind of all the information you’ll need. Um, Mary already gave you a lot of the Census API information, so I won’t repeat that. Um, uh, there’s a full recording, uh, of, of the webinar that takes you through how to actually get up and running in our studio so that you can get to the point where we’ll start here today. Um, and also the details on Kyle Walker is amazing, tidycensus package, uh, which, although not maintained by the Census Bureau, uh, clearly is good enough to make a make a guest appearance in a Census Bureau closing slide. So, uh, certainly has kind of revolutionized how I interact with American Community Survey material.
So, um, how to get up and running here. Basically, uh, I’m going to open up this particular dot R file for you in our studio. If you’ve gone to the GitHub page that I shared with you before, uh, and I’m sure perhaps, uh, if you do want to follow along, maybe I could task Lillian, who has this slide deck to toss it into the chat for folks. Um, but if you’re, uh, I’ll just go through a couple of ways to, uh, to kind of access and use code here.
But, um, at the, at the bottom bullet here, uh, is what’s in this, Rbootcamp file. I basically have 10 modules here. Module sections 1 through 6 are just basic data usage skills and visualization skills using R. I’m not going to go over those today. I’m going to skip them and start with section 7, which is how to use the Census API. Um, and then I’m going to provide you with section 8, which is basically a replicable code block for doing those API calls. Uh, once you’re, uh, kind of up and running in R, you can use that to basically declare whatever variables you want, geographies, etc., um, and get them in, in a nice tabular format, in Excel format, even a shapefile format, if you like to do that.
Um, and, uh, new since last time we’ve done this, I’ve added a little bit of a code block to get longitudinal ACS data if you want the full series from 2005 or 2009, uh, when when ACS one and five years started respectively until now on the same thing. Uh, and then a new little section here at the end on, um, doing a tract-level map of something in your census place or in your city, uh, as, uh, Lillian shared in one of her earlier slides. I’m going to nab it here, um, you know, a lot of kind of how you interact with this, the API is, as Mary also said, uh, it follows the Census Bureau’s geographic hierarchy. Um, you know, and there’s, there’s a difference whether you’re on kind of this main vertical or if you’re off the main vertical.
Um, you know what I tend to focus on, uh, are counties or, you know, as kind of a reflection of the overall trend or census tracts to kind of be reflective of neighborhood-type dynamics. ACS oftentimes does go down to block group as well, but you tend to get those high margin of errors, which, uh, you know, well, I’ll leave it to you to decide the level of importance of the margin of error for your for your, uh, for your workflow.
But one of the challenges is that, um, cognitively, uh, and electorally and everything like that, places are pretty important census places, uh, which are basically cities, towns, CDPs, etc., are really, uh, you know, how people interact with information. So if you’re looking to get an understanding of how a phenomenon, uh, is dispersed across the neighborhoods of a city, you really need this tract-to-place relationship. So I’ll go into that a little bit, um, as I do the demo.
Um, apologies. I’m not really able to see the chat right now, but, uh, please, please holler if any issues. And thanks, Lillian, uh, for putting those, uh, those links up there.
So I’m going to, uh, go over now to RStudio, where I’ve just opened up Rbootcamp, uh, 2024.R. So really basic two ways, two main ways to enter code. On the righthand side here I’ve got a script file, which is, um, I prepared this, this one for you here. It’s about 500 lines or so and goes through those 10 modules. You can update it, change it, change things, um, and using this nice hashtag here could kind of comment something out. So, for example, line 22 here, um, the command is Print; I’m gonna print something, and then I made myself a little note behind the hashtag here.
On the left side is actually where you’re executing code. It’s got this little triangle called a chevron and a blinking cursive. So if I want to use the Print command to say “hello world,” which is sometimes what folks do when they start a new programming language, it’s going to return to me a line that says “hello world” back, because that’s what I asked it to do. Um, certainly when we get a little bit more sophisticated with our calls and things that we want to put into the console here, uh, typing it is not going to be efficient. So that’s why we have the script file up on the righthand side here.
So long as your cursor is on a line or has highlighted a portion of code, there are a lot of easier ways to run that code. The first one is to go up here to the top right and hit run. It’s going to do the same thing. Or if your cursor is just on it and you hit Ctrl+R if on a PC, Command-R on a Mac, or in some instances it’s Ctrl+Enter. I’m not sure exactly why people’s computers all have slightly different setups. That’s going to be the other way that you can run this line of code.
The second thing that I’ll mention about kind of RStudio in general, um, in terms of this workflow, is to just be really careful what you’re working directory is. What that means is a file path on your computer somewhere where you’re saving data, where you’re saving images, where you’re saving your output, or sometimes reading in data as well.
Um, there are a few ways to do this. Um, you can, uh, if I type “getwd,” it’s going to get my working directory. Goodness. The default is, uh, what appears to be somewhat something of a My Documents on a C drive. Um, I can go up here to Session, Set Working Directory, and choose, uh, where I want to pull information from. Or I can declare it in the code here. I’ve already written it down here is “setwd.” So if I “setwd,” um, something I’d like to do kind of early in the workflow, uh, I’m going to be working with this folder. Um, and you can see it’s in Dropbox, Rbootcamp as, as the folder.
So, um, that’s just the absolute basics again. Um, if you want more information, you know, certainly I would suggest downloading, uh, the package from GitHub, including this dot R file following along yourself or following it along in the video link there. And right now I’m going to scroll down to the fun step to actually the, uh, using Census API here in R, which is, uh, what I have as section 7 here.
So, um, the way that, uh, R is, is useful is that it kind of has a lot of base functionality kind of built into it. And then it’s very customizable. Folks have built, um, tons of different packages in it. And the one that’s really helpful is called tidycensus. I’m also going to be using a few other packages here to be able to work with spatial data and to do some other data manipulation.
Um, when you install it, you have to do two things to use a package in R, first you have to install it, and you just have to do that once. But then every time you open R or RStudio, you do have to kind of invoke the package or activate the package. So you install it with this line here, Install Packages. And I’m not going to run that because it’s installed already on my machine. But I am going to highlight all of these and activate these four packages here by running this line of code. So this is basically telling our studio, hey, add this new functionality to this instance of the program that you’re working on.
Mary already mentioned getting a Census API key, which you will need. Uh, it takes, she said, mere moments to sign up. I think it takes probably like 2.5 seconds perhaps. Uh, and that, that is an alphanumeric code that’s a little bit ugly here, but, um, it allows you to actually use this because you are going to be iterating and pulling a lot of things. Um, it’s nice not to overwhelm the, uh, the, you know, our, our federal government’s, uh, servers, uh, the Census Bureau.
So they’re, uh, the first thing that you’ll have to do is to enter your Census API key here. And tidycensus has a command called, you know, what do you know, Census API key. So you put it in here like this and hit Run. Here’s my Census API key and boom, you’re done. Um, it gives you a new flashing chevron. Uh, so that means it’s taking the line of code, uh, effectively.
So, um, really we’re just working with a couple of key commands here. Um, as Mary had mentioned earlier, there are a lot of things available through the Census API, the Economic Census, the decennial, various other programs that the Bureau has, and ACS being the key one.
In tidycensus, you’ve got decennial and you’ve got ACS. So “get_decennial” is the command here for how to how to get something from the decennial census. And this gets decennial census command takes a few different arguments. And you can see what I’ve set up here in line 405 is, well let’s see, I want state-level geography. So I want state-level data. I want this variable. We’ll get to how you search for variables in a little bit. You know a little bit already.
Um, I want the census summary file, and I want from the year 2000. So I’m going to run this “get_decennial” command. And then what this equal sign does is it puts it in an object or thing or a, you know, something that you can call back called medrent00. I’ve just called it medrent00. I could call it whatever I want. So I’m going to run this line here, and what it’s doing there, uh, for that a quarter second is it’s actually getting the data. And now if I just type that run, oh, um, it’s going to show me the median rent across all the 50 states.
Uh, I can make it a little bit easier by using the view command and view medrent00. What that will do is pop it up into something that looks a little bit more like Excel or tabular data and see that, um, goodness, in Alabama in 2000, rent is probably a heck of a lot less than it is today. Um, quite a bit higher in Alaska. So, you know, this passes the smell test. Always a good check. Uh, when you’re, when you’re doing a new data extraction process.
Um, so that’s useful. Um, you know, you can certainly there’s, there’s commands, right dot CSV commands to save this in Excel. You know, if you really want to, you can just grab and copy or what have you, uh, from here. But R has a lot of really nice visualization capabilities, so it’s nice to be able to take advantage of them.
I’ve left you with a few examples in this code here that you can, you know, certainly, uh, you know, modify the name of the, the variable, the data set you’ve extracted or the variable or change some of the other parameters. But if I run this line here, it’s going to make a nice little bar plot, um, of states by rent. And you can see here. Oh, Hawaii is quite, by quite a bit the highest. And this is alphabetized, um, well, not quite alphabetized by FIPS code, but, you know, thereabouts.
I’m going to close this here, and, and I’ve made a slightly fancier bar plot here with some bells and whistles by sorting the data, adding some color, adding a label, adding some guidelines. And I can highlight all of this and hit Run or Ctrl+R or what have you. And it gives me a really nice little bar plot here of state median rents in the year 2000. Again, seeing how it varies from a high of Hawaii to a low of North Dakota. Um, did not expect that to be lower than in Puerto Rico even, but goodness.
So, uh, here. So that’s, that’s just the way to kind of get a little bit of a visualization. And I haven’t uploaded any data into my program, which you usually have to do. Um, as long as you have the internet and a Census API key and tidycensus, uh, as a package installed, uh, you’re able to just extract it in one clean flow.
Now, in order to find good variables to use, uh, Mary already gave a little bit of a tutorial to that, but, um, you can do that within tidycensus if you want to. So, um, load variables is a, is a command here. And I’ve just asked it to look at 2022, five-year ACS, um, and put it into an object that I’ll call “acsvars” and, um, oh goodness, I have 28,152 entries for, for, uh, you know, explicit ACS variables that are coming in through what I imagine, uh, Mary can correct me if I’m wrong, what I imagine are the detailed tables rather than the summary tables.
Um, in any case, uh, this is a little bit cumbersome, you know, certainly. Um, and Ctrl+F is one of your friends. You can write this to a CSV here as comma-separated values file and, and open it up if you want to. But in the GitHub site I’ve included, um, my little cheat sheet. Um, if it’s useful to you, happy to share. But these are my top one, top most commonly used 125 ACS variables with their code and a somewhat intuitive abbreviation, um, that I’ve, that I’ve, uh, renamed it, “totpop,” for example, or median age. Um, this includes just some of the, the age structure, basics, race, race, ethnicity, commuting, educational attainment, income, and housing. Just to give kind of a smattering. Um, so if you want to start there, um, that’s, that’s not a bad way, at least, at least in my view.
So, um. Right. Uh, so, so now that we’ve found some good census variables to use, and we’ll scroll down just a little bit here and try to assemble, um, some tract-level variables for a county. Um, now this is the kind of the main command here. It’s get underscore ACS and you pass it a lot of information. I want tract-level data. I want the state of California, Orange County, and this variable here, 25035, which is the median age of the housing stock in each tract. You’ll notice that I’ve also added this argument called geometry equals true. This will also extract the data as spatial data so that you can visualize it right here in R. Or you can export it as a shapefile if you’re a GIS user.
So, um, it just takes maybe two or three seconds or so to get all the tracks, uh, in Orange County, California. Um, if I look at what this is, “head” just gives me the first five rows of any given data set. Uh, let’s see, I’ve got a GEOID. This looks like my FIPS code. I’ve got estimate, which is actually the value I’m looking for. So this tracks median housing home year, built year was 1971, 1959. All right. So this passes the smell test. Certainly these are reasonable values especially in the western United States.
Um, so I can do just a little bit of manipulation, renaming it old age. Um, you know, getting rid of the old one. And if I want to see how many rows there are, take a quick look and see that there are 614 tracts in Orange County, California. So now I have a good understanding of, of the rows and columns, which at the end of the day, that’s all data are.
What if you need more than one variable? Um, tidycensus will extract it for you, but it’s a little bit trickier because it does it long. Um, to show you what I mean, I’m going to, um, make a list of three variables: population; housing stock age, which we already did; uh, and median household income. And I can extract those in one single call by, uh, declaring this list that I made as the variables that I want. So I’m going to call this one TR underscore plus. Again, it just took a second.
And if I want to see how many rows are in underscore plus, oh goodness, it’s 1,842. Well I know there are 614 tracts. So, um, I can take a look at it and see that, hmm, this is not stacked in a terribly intuitive way. I’ve got three records for each tract, and each one’s for a different variable. Kind of a pain in the butt when you want to do math, compare it, put things as a rate, uh, put them on a map, uh, or anything like that. So, um, you know, if you really want to use it, you can use something called the match command, which is described in the earlier sections that I totally glossed over. Uh, and, and do a subset of this lengthy file and then and then bind it to your original text file. So now I have 614 entries here and eight total columns. I’ve got one for home age, total population, median income. My apologies to the Bureau for omitting the margins of error here, but you can grab those as well, especially for tracts. Mea culpa.
Um, some of the other nice features within R is that you can actually just plot this as a map using one of the, using what’s called the SF package. So if I hit line 450 here, sorry, um, uh, goodness, I can get a nice little map already of the tracks in Orange County. And again, uh, let’s see, we’ve got 1940s, 1950s here, kind of in the North Side. This is downtown Santa Ana, the older neighborhoods of city of Anaheim. Those look a little bit older, uh, then used to get to the south, to Irvine, to Laguna, Niguel, Coto de Caza. These are the newish developments up in the hills. You can see that reflected in the more curvilinear boundaries but also in the, the newer home ages there.
So, um, neat little trick there. And if you are a GIS user, you can use this “st_write” command here. Um, whoops. To write an entire shapefile. Um, now this is, uh. Let’s see. What did I call it? I called it orange underscore merge. So if I go back to here now, I have four files here I’ve seen if you’re a GIS user, you know, you’ve got somewhere between three and eight files typically together in a shapefile format. But now I can use this in GIS. I have orange underscore merge. All right.
So, uh, racing along right here. Um, hope folks are getting a little bit out of this at least. But what I’ve built here in section 8, um, is a way to group a lot of variables together. Uh, like I said, it’s a little bit clunky to extract variables one by one because they’re stacked long. So you want to make a loop and, uh, loops are, you know, a little bit more advanced coding skill. Uh, but I’ve built this to hopefully make it so that you can just enter your parameters here, um, and, uh, and then run this big block of code in section 8 and then get a good data set.
So I’m going to ask the audience here for somebody to put in the chat a state and a county, like not a tiny county, at least the medium-sized one. You know, five more seconds before I use Tampa. Okay. Sacramento. Let’s do, let’s do Sacramento okay. Thank you.
So Sacramento County, California, my state equals CA. My county equals Sacramento. Let’s see. Let’s I’ll run the first chunk of this. And the first chunk. The way I’ve set this up is it’s just grabbing total population B01001 underscore 001. And then what I’m doing is taking this whole big list of 125 variables that I’ve shared with you earlier in this spreadsheet here. Uh, and then I’m renaming them to something that’s a little bit intuitive. Um, not perfect, of course, but, uh, you know, if you follow a logic, uh, you know, commute, walk, uh, median household income, you know, female aged 5 to 9, etc. Uh, you know, should be logical. Select all of this, even do a little bit of math on the end of it. And it’s really only going to take probably a few seconds to extract this for, um, 125 different variables for, um, the tracts in Sacramento County.
All right. There we go. I can view this. I just called it D to keep it a little bit easier. Uh, and now you can see all the tracts, uh, total households, median age of 29. Goodness, that’s quite a bit under median. So that must be a young area. Um, race ethnicity, variables, etc. Um, how I put them up, I’ve got 135 total columns in this, uh, in this data frame right now. I can write it to a CSV right here. Whoops. I called it Hillsboro, Florida. Sacramento. Don’t get confused now. My Hillsborough file is messed up, but, uh, that was, uh, that was from somebody else. So Sacramento tracts and ACS can just open it up in Excel in a comma-separated values format, um, and, um, manipulate that however you like.
So there you go. You’ve got, um, uh. Uh, you can also write it to a shapefile here. Um, Again, make sure you name it the right thing so you don’t forget that that’s Cook County, Illinois. Um, and, uh, you know, you can do some plotting. Um, here is median median home value in Sacramento County. I’m not super familiar with the urban geography of Sacramento, but I’m assuming this is a little bit more kind of an inner ring neighborhoods in the downtown core and then the fringe, you see some higher income as well. This is all in the SF package. So there are a lot of parameters that you can do here.
Uh, the nice thing is, well, by doing this workflow is that you can just do math right here. So what if I want to know if the the share of commuters who work from home. Uh, a question that we get asked all the time. Uh, so I could just do the, uh, number who work from home divided by the total population of commuters. Do a little math here and then plot that variable. So, okay, the work from home share in Sacramento County is way high out here, fairly high in somewhat of the downtown core, and a little bit mixed. Again, you can do quite a bit of a different analysis here if you’d like.
Um. And then if you want to plot the variable a little bit more neatly, um, I’ve got median home value pulled up here with the Jenks optimization so that it gets some nice natural breaks. You can do a reasonable looking plot just right here in R without having to open up GIS or anything else.
Two more quick tricks here before the getting in under the gun at 12:30, uh, Pacific time. that is, um, is a task we often need is to get longitudinal ACS data. Um, I find this a little bit tricky, um, because you do have to iterate quite a bit. Um, can somebody, let’s see. I’m going to pull, um, Milwaukee County, Wisconsin, from, from the chat here for this example. But basically what I’m doing here, um, is I’m making a sequence of all the ACS years that are available. Um, sending, I use a lot of one-year data because I tend to work in big counties. Um, so it’s a little bit tricky because it didn’t exist for 2020. So you have to make sure to make a list that has that gap in there. Um, five year, that’s not an issue.
But in any case, um, what I’ve kind of given here is a not quite as sleek of a, of a loop as, as earlier, but a mechanism to, uh, go through and enter whatever I’d like to here, Milwaukee County. So, um, this is going to take a couple of seconds, in fact, to run this because it’s pulling, um, well, that’s what I’ve come across. Oh, I don’t think that. I think there we go. So now you can see as this runs here in the red text, it’s 2008, 2009. It’s just looping through, uh, all of the available ACS years to get me, um, two variables here. I put them in. I kind of snuck it in here. One is, it’s what I just showed you earlier, the number of people who work from home versus the total commuters. So, um, and what this can give you right here is total commuters in 2005, the number who work from home, and then a really nice time series of how work from home has evolved since the ACS started collecting data on it, uh, in 2005.
So again, you can write that, you can use it later. Um, I can plot it here, make a little plot and see. Goodness, that’s what happened here during COVID. Uh, and then in the most recent year, a little bit of a dip. I can make a better line graph that I’ve put a few bells and whistles into. Uh, whoops, I forgot to change this to Milwaukee County, Wisconsin. I’ll do that in just a second here. Um, and I can even make a, um, a comparative graph. Change that to Milwaukee, just so I don’t get confused. So an example of how to do a little bit of these edits here.
And what I’m also going to do is I’m going to, I’m going to make a comparative graph here. I’m going to also extract Sangamon County, Illinois, which is Springfield, which is kind of a smallish mid-sized city. Uh, and then, um, and then run through this again. And once I run through this again, I’ll be able to have a graph that compares two different places in their work from home trajectories, which is kind of interesting. And this is probably the slowest part of the Census API, at least the way I built this here.
All right. So now I can see Milwaukee County work from home. Goodness, shot up during COVID and went down, but a much smaller, um, you know, uh, metro area, uh, had not only a lower level overall but didn’t see a kind of a drop in 2022 as a return to office happened. So again, just an example of some of the analysis you might be able to do with this.
I’ll share one final tip and trick in the last couple of minutes that I have with you here. Um, and it’s something that we just, just figured out. Um, my colleague Echo Xiang, who’s also on the call, and I, um, is to do a tract-level map of something in a single city. So while I’m doing this, if somebody can, um, tell me a city and the county it’s in, uh, to make a tract-level map, something that actually has not just a few tracts, something that’s a little bit at least medium size.
And this is going to, um, uh, this is going to require a few new packages: terra, readr, and mapview. All right. Let’s do, uh, let’s do, um, Oklahoma City. Actually, it has city twice. I’m not 100% sure it’s going to work. Um, how about, um, Tempe, Arizona, Maricopa County. Tempe, Arizona.
Um, I’m just going to work with median household income right now to show you this. And, um, you know, also one, one thing that I’ve given you here, um, in the GitHub is a file, that’s a relationship file developed from geo core that I use to relate tracts to census places, because, again, it’s not on that main spine of the census geographic hierarchy. Um, so, you know, it gives you the percentage, you know, tracts don’t necessarily nest within cities or places. And this, this tells you, for example, uh, Autauga County, Alabama, which we always see when we’re doing census work nationwide. Uh, nine, 98.42% is in this tract, and 1.5% is apparently outside of Prattville, Alabama. Um, so just, that’s all to say that you can define a threshold, um, to kind of get rid of some of the superfluous stuff that’s, you know, 99% outside of the city.
So I’m going to declare a place, a variable household income. I’m going to make sure that I asked for Maricopa County, Arizona. Uh, solicit this tract data here. Make sure everything works. Okay. Looks like it all works. And then I’m going to use this neat mapview feature here, see. All right. Some, some issues here. So I’m going to go back to, uh, press the old Riverside County, California. What is this for? Apologies for the work. If you troubleshoot, I’m sure.
All right, here we go. A dynamic map of Riverside County, California, by median household income. Uh, mapview even allows you to hover and see what the household incomes are. You can do a pretty yeoman’s job of exporting the image. And, uh, there you go. There is your analysis.
So anyways, check the GitHub. Um, hope this was a helpful demonstration. A little bit sloppy, albeit, but, um, uh, enjoy. And thanks for participating. I think I’ll turn it back to, uh, Lillian and/or Mark for the kind of the closing.
Mark Mather: Great. Thanks so much, Kevin. Um, we are we, it’s 3:20, it’s 3:29 East Coast time. So I know we’re almost at the end of the time for the webinar, but, um, and this was an incredible amount of information. So just as a reminder, we will be sending out a recording and the slides that have all of the relevant links. I think that, um, flew by in many of these, in many of these presentations.
Um, I think because of the time we are going to officially close the webinar, but the panelists have agreed to, I think that you all agreed to stay for a few more minutes. If anybody wants to stay behind, uh, more informally and ask them some questions, we can, um, unmute you and, um, you know, five or 10 more minutes, I think, and we can, uh, turn off the recording so we can just speak more informally. But, uh, with that, I do want to officially close the webinar. I’ll stop recording. And thank you all for joining.

New data released today by PRB and the Appalachian Regional Commission shows that rates of labor force participation, educational attainment, income, and poverty continue to improve in Appalachia.
The 14th annual update of The Appalachian Region: A Data Overview from the 2018-2022 American Community Survey draws from the latest American Community Survey and comparable 2022 Census Population Estimates. Known as “The Chartbook,” the report contains more than 300,000 data points comparing Appalachia’s regional, subregional, state, and county economic status with the rest of the nation.
Key improvements in the region’s economic indicators are as follows.
Increased income and lower poverty rates
Higher educational attainment and labor force participation
Increased population growth in south
Increase in broadband access
“We celebrate the progress Appalachia has made, including declined poverty rates and increased broadband access. However, we know that there is still much work to be done for our entire region to reach economic parity with the rest of the country,” said ARC Federal Co-Chair Gayle Manchin. “ARC will continue to prioritize the quality of life of Appalachia’s 26 million residents, and remains committed to continued collaboration across federal, state, and local levels to ensure our people have a bright future.”
Despite positive trends, several data points revealed vulnerabilities that emphasize the inequities in Appalachia compared to the rest of the nation:
Overall population decline
Poverty rates for children and families and specific counties
Disability and poverty in older adults
Despite gains in access, digital divides persist
“The data in this year’s Chartbook highlight strides being made in the Appalachian Region, with noteworthy improvements across economic, educational, and health-related measures,” said Sara Srygley, a senior research analyst at PRB. “Yet, these data also emphasize considerable variation throughout the region—particularly the persistent challenges facing rural communities.”
The data show that Appalachia’s rural areas continue to be more vulnerable than its urban areas. Appalachia’s 107 rural counties are also more uniquely challenged, compared to 841 similarly designated rural counties across the rest of the U.S. Though rural Appalachians did have higher health insurance coverage than the rest of rural America, rural Appalachian counties continue to lag behind on educational attainment, labor force participation, broadband access, household income and population growth.
The Appalachian Region: A Data Overview from the 2018-2022 American Community Survey was written by PRB and the Appalachian Regional Commission.
In addition to the written report, ARC offers companion web pages on Appalachia’s population, employment, education, income and poverty, computer and broadband access, and rural Appalachian counties compared to the rest of rural America’s counties. For more information, visit www.arc.gov/chartbook.
The Appalachian Regional Commission is an economic development entity of the federal government and 13 state governments focusing on 423 counties across the Appalachian Region. ARC’s mission is to innovate, partner, and invest to build community capacity and strengthen economic growth in Appalachia to help the region achieve socioeconomic parity with the nation.

What are the barriers to conducting abortion-related research in the United States today?
June 7, 2024
In 2022 the Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization decision, which overturned Roe v. Wade, ended the Constitutional right to an abortion and dramatically changed the health care landscape in the United States. Researchers on abortion, fertility, and reproductive health have been working to understand the implications of the Supreme Court decision, including access to care, birth rates, and health outcomes.
In this webinar expert panelists discussed questions including: What are the barriers to conducting abortion-related research today? What have we learned from the data so far? Where are the data gaps and how can we fill them?
Panelists included:
Beth Jarosz, PRB: Hello, everyone. I’m Beth Jarosz, Senior Program Director at the Population Reference Bureau and Vice President of the Association of Public Data Users. And with both of those hats on, I want to welcome you to what will be a very engaging discussion.
As you all know, it’s been nearly two years since the Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization decision changed the abortion health care landscape in the United States, and researchers have been working to understand the implications of Dobbs on access to care, birth rates, health, and other outcomes.
In addition to hearing a bit about that research, today we’re going to tackle questions like: What are the barriers to conduct abortion-related research? What have we learned from the data so far? What are the data gaps, and how can we fill them?
To help answer those questions, I’m joined by an all-star cast: Abigail Aiken, Associate Professor of Public Affairs at UT Austin; Jane Seymour, Research Scientist at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, Collaborative for Reproductive Equity; Alison Gemmill, Assistant Professor at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health; and Laura Lindberg, Professor of the Rutgers School of Public Health.
We’ll hear from all four researchers and will round out the hour with a Q&A. If you have questions, please type them into the Q&A box, and I’ll ask as many of your questions as I can during the Q&A session at the end. So without further ado, I’m going to invite Abigail to begin.
Abigail R.A. Aiken, University of Texas at Austin: Thank you very much, Beth. It’s wonderful to be here with everybody today. I’m just going to share my screen so you can see my slides. And then I’m going to give a short, 10-minute overview of some of the work that we’ve been doing trying to measure self-managed abortion and shield law abortion provision in the post-Dobbs landscape.
I want to say that the work I’ll present to you is the result of a lot of people’s work. So everybody here has been involved with Project SANA, that’s our project, the Self-managed Abortion Needs Assessment Project, at some point over the past five years. And so want to, um, say thank you to everybody who’s been involved in trying to get an effort to look at the who, what, and why of self-managed abortion in the U.S. off the ground. When we started this project back in 2018, we knew so very little in the research sense about self-managed abortion, and we really come a long way since then.
So to be clear on terms, I’m mostly going to be talking about self-managed medication abortion this afternoon. And that’s the process of obtaining medication abortion pills. It could be mifepristone and misoprostol or misoprostol alone, and managing your own abortion outside of the formal health care setting, so with no U.S. licensed provider or clinic involved. And, of course, self-managed abortion can also be done via other methods: herbs, botanicals, self-harm. There’s lots of different ways. It’s really a spectrum of things. Most of what I’ll talk about today will focus on medication self-management, but in the Q&A, I’m also happy to talk about some of the other methods as well.
So self-managed abortion is really hard to study. It’s hard to study because by definition, it’s something that’s happening in private settings. It’s usually in people’s homes. It’s not something where there’s an administrative record that you can request or track easily. And so since 2018, we have been thinking hard in Project SANA about how to, uh, count self-managed abortion, how to explore self-managed abortion, how to get a sense of how often this might occur and why it might occur.
And a lot of work has been done since then, and we really have focused a lot of our work on the nonprofit organization Aid Access. And that’s because since 2018, Aid Access has been providing self-managed medication abortion through online telemedicine. Now, the model of Aid Access has changed in recent times, and we’re going to talk about that later in the presentation. But for about five years this was considered self-managed medication abortion because it was happening entirely outside the formal U.S. health care setting.
We formed a collaboration with Aid Access, having worked with their sister organization, Women on Web, in Ireland and Northern Ireland prior to 2018. And so we were able to look at the trends in the number of people that were making requests to Aid Access. We established the safety, effectiveness, and acceptability to the user of this model. Um, please check out our papers if you’re interested in that.
And we also had a look of, at the question of, Would we expect there to be a relationship between abortion bans and self-managed abortion? You can imagine that when states put, um, abortion restrictions in place and people have less access to clinics that they might more often look to self-manage outside of the formal health care setting. And it’s also evident from our research and the work of others that people sometimes also self-manage from a point of view of being their preference. It’s not just an alternative to lack of clinical access; it’s also something people might prefer to do for a variety of reasons.
So the first part of what I’m going to talk about looks at this question of is there a relationship between SMA and abortion bans? Because leading up to Dobbs, we wanted to know, can we use data from Aid Access to find out whether when states ban abortion post-Dobbs, are we going to see an increase in people self-managing? And we had good reason to expect that that would probably be the case based on a number of prior studies that I’m going to talk about super quickly because I’ve only got 10 minutes. But I just want to show you the strength of data behind this relationship.
So this first paper looked at what happened when Texas, back at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, banned abortion essentially for a period of two weeks by saying that abortion was a non-essential medical procedure. And we looked at what happened at, to request to Aid Access during that admittedly short time period. But it was a really quick and evident increase. You’re looking here at a graph of cumulative requests, so you’re seeing the actual data before the ban. They’re in black. Then you see the data after in the orange line, and the model fit, um, compared to what was forecast. And we saw this doubling of requests over the two-week time period after abortion services were shut down in Texas.
Staying in Texas, we saw what happened in September of 2021, when Senate Bill 8, that was essentially the six-week ban, uh, went into effect. And again, we saw that compared to a long baseline of what Aid Access had been doing, requests for self-managed abortion really spiked when people knew what was about to happen. But even out several months afterwards, you were seeing a tripling over the baseline numbers.
Again then after Dobbs, we saw states with total abortion bans. And again, we saw, when you compare to this baseline of what access had been seeing from these states, a doubling or sometimes even a tripling of requests in those banned states, which is more than what was happening in states without bans. So over and over again, and this is really, I think, in keeping with what we’re seeing, we see in the global context, what we’ve seen historically in other places with abortion bans, when you make clinical abortion access harder, you see this increase in people looking to self-manage.
So now what I want to talk about is going beyond requests and trying to actually count, because the question that, you know, people often ask is, okay, but we see that relationship, but how many self-managed abortions do we think are happening in the U.S. post-Dobbs? And that’s a really hard question to answer. Looking here though, this is from WeCount, and people maybe hope are familiar with the effort from Society of Family Planning to count and make a census of abortions provided within the formal health care setting after the Dobbs decision.
And this is early on, right? We’re only looking out here to six months post the Dobbs decision. But initially there was a decrease. There was a decrease in the number of abortions being provided within the formal health care setting, which raises the question of did we see a concurrent rise in people self-managing? Do we know how much of that decrease of approximately 32,000 abortions provided within the formal health care setting might get offset by abortion outside of the formal health care setting?
Now, the post-op landscape really changed what self-managed abortion looked like. That’s another issue for us. We had worked with Aid Access for a long time and continued to do that because they were an online clinic mailing pills. But there was such a response to the Dobbs decision from community support networks. So based on accompaniment models, oftentimes in Mexico or Latin America, and we knew that model’s been so prevalent in South America for so long, coming to the U.S. to try to secure access for people through volunteer networks and then also websites selling pills. So not online, um, telemedicine operations, but simply online vendors that were like, yep, we’ve got misoprostol/mifepristone. You can order it from us, and we’ll send it to your house.
So trying to, first of all, map this is a large effort, right? Trying to figure out how many different providers out there, out there, as particularly with online vendors, they tend to change a lot. And different people may run multiple websites. They may pop up and go away. It’s hard to keep track of all this. So part of the work that we’ve been doing is trying to figure out how many pathways are there, how many providers are there, and then what does each provider provide.
And in an attempt to do that, we published the first kind of findings out of that looking out six months post-Dobbs. Um, you can find this paper also online. We saw this increase in self-managed abortions provided in that six-month period post-Dobbs, when you saw the decrease that was found within the formal health care setting and now this increase in self-managed abortion. And this chart attempts to break it down by the different types of provider, the community networks, the telemedicine org, and the online vendors. So you can see the baseline.
There was, of course, provision beforehand before Dobbs. People were, of course, self-managing then, too, partly as a result of abortion restrictions, partly as a result of preference. But it really changed post-Dobbs in mostly in states that enacted bans. And approximately 26,500 abortions is our estimate for the six-month post-Dobbs that took place outside the formal health care setting. Lots more methodological details on that in the paper that I don’t have time to cover right now.
I wanted to highlight that these different types of organization, um, play a critical role, partly because of cost. Um, from our qualitative work, we know that even the $90 that a service like Aid Access was asking for in donation is too much for a lot of people, and many of the accompaniment networks are able to provide at no cost, which is really important for people.
Secondly, these options are out there. They are, they’re, they’re becoming more known about. But that doesn’t mean that people don’t often look to other ways, too, maybe as part of their journey to getting what they need or as the ultimate end of their journey. And for some people, this could even be something that’s unsafe or harmful to them. So I haven’t talked a lot about that today, but I don’t want to overlook it completely. It comes up in our qualitative work quite a lot.
Then finally we’ve got this shifting post-Dobbs landscape. We’re now looking at numbers coming in from WeCount showing abortion numbers increasing. And we also see from the Guttmacher map project also, um, similar counts in the monthly provision data as well. So there seems to be an increase in access overall.
And what Aid Access are now doing we wouldn’t call self-managed abortion anymore because they’re now providing, um, entirely through U.S.-based clinicians, through shield laws. So getting medication abortion to banned states from providers that are working in states that have shield laws, that allow that to be within their scope of practice. So now we have a different, um, challenge on top of the counting of self-managed abortion, which is this new definition of shield law provision, and trying to count that alongside, um, the self-managed, uh, medication abortions too.
So I like to leave it there because I only have those 10 minutes. Uh, that’s a summary, a very high-level summary of what we’ve been up to and what we’ve been trying to do. Uh, please check out our site to look at our papers. Um, I’m looking forward to your questions in the Q&A as well. Thanks so much for your time.
Beth Jarosz: Thank you so much for setting the stage and for covering a lot of information in a very short time. And I’m going to invite Jane up next.
Jane Seymour, University of Wisconsin–Madison CORE: Wonderful. Thank you all so much. Um, I’m really delighted to be here today to talk about some of the ways that we’re measuring the impact of Dobbs in Wisconsin at the University of Wisconsin Collaborative for Reproductive Equity, or UW CORE. CORE is a research initiative focused on abortion, contraception, and other aspects of reproductive autonomy that’s housed at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, which is Wisconsin’s largest and only public medical school.
Okay, there we go. So given our focus, one of CORE’s goals both pre- and post-Dobbs is to document the health, well-being, and social consequences to Wisconsinites of barriers to wanted abortion care.
As you may know, post-Dobbs, an 1849 state law here in Wisconsin was interpreted as banning abortion, and as a result, all abortion services in the state were halted, and data from the Society of Family Planning’s WeCount effort, which Abigail referenced, shows here that the, in the year after Dobbs, roughly 7,000 fewer abortions occurred in Wisconsin compared to the prior year.
And while abortion services have resumed in Wisconsin as of last fall, we know that many barriers that predate Dobbs remain in place, and providers are still ramping up services to pre-Dobbs levels. In other words, there are still significant barriers to abortion in Wisconsin.
So naturally, this leads us to ask what happens to Wisconsinites who want abortion services given these bans and restrictions. And we can imagine three scenarios for these folks. First, we can imagine that some likely cross state lines for abortion, as was already the case prior to Dobbs, given Wisconsin’s extreme abortion restrictions. However, data from, excuse me, data from WeCount, um, shows us that the increases in haven states, such as some of the other Midwestern states shown here, don’t make up for the bans in states such as Wisconsin. Um, second, we can imagine that some people self-managed an abortion, obtaining pills from a variety of sources, including places like Aid Access. And finally, we imagine that some Wisconsinites who wanted an abortion did not have one and instead carried their pregnancy to term.
So although we can imagine these scenarios, it’s important to understand the lived experiences and trajectories of abortion seekers in this restrictive environment as well as the impact on their health and well-being.
So to understand these experiences, we must get information from Wisconsinites who considered abortion. As many on this call know, prior to Dobbs our field often recruited for studies from abortion clinics, which may have induced a selection bias, as we failed to include those who face barriers to care such that they never made it to a clinic. Some researchers in our field have made attempts to overcome this limitation by recruiting from prenatal care clinics and/or online via social media or, or Google ads.
Post-Dobbs, especially in states where there were no longer abortion clinics, including Wisconsin for a time, this method, methodological challenge has only been amplified. In other words, we have to search in many different places for research participants to fully answer our questions about barriers to care.
Here at CORE, we’re taking a multi-pronged approach to understanding the impact of Dobbs on abortion seekers, which we call the post-Roe impact research portfolio. In this portfolio, there are three studies shown here, which we refer to as the Turnaway, prenatal, and MAP studies. I’ll briefly note that the Turnaway work is comprised of interviews with those who participate in Dr. Diana Greene Foster’s post-Roe, uh, work.
But today I’m going to focus on our other two studies, which recruit from prenatal care clinics and online, respectively. And both include longitudinal surveys as well as in-depth interviews. Overall, this portfolio builds on Dr. Foster’s original Turnaway Study as well as pre-Dobbs work that sought to recruit those who considered abortion outside of the clinical setting.
Here’s a bit more detail about these two studies. In brief, the prenatal study recruits patients from UW Health prenatal care clinics, after which they complete a baseline survey. Those who report having considered abortion are invited to participate in an in-depth interview two weeks after the baseline survey, as well as for 10- and 18-month follow-up surveys. Additionally, at baseline, we ask all participants to agree to use of their electronic medical record, or EMR. We pull EMR data for all study participants to compare outcomes between those who did and did not consider abortion care.
Oops. Excuse me. Uh, currently, we’re still recruiting, and the first participants have received their 10-month follow-up survey. As you’ve already seen, the MAP Study, or the Midwest Abortion Pathways Study, is a partnership between CORE, Ibis Reproductive Health, and Indiana University and recruits participants via Google and Microsoft internet search engine advertisements. Participants are eligible if they’re pregnant, live in Wisconsin, and report having considered abortion for their current pregnancy. They complete a baseline survey after clicking through the advertisement and then are invited to complete 4-, 10-, and 18-month follow-up surveys, as well as an interview post-4-month survey. Currently, we’re still recruiting in the first. Participants are about to receive the 10-month survey.
Now, typically this is where I would share a few nuggets of our results, but instead I’m going to share some challenges we’ve encountered as those feel particularly relevant to today’s conversation.
First, as is likely no surprise, abortion seekers who were hard to find pre-Dobbs are even harder to find now, likely due in part to concerns about the legality of abortion and related increases in conversations about digital security. Second, the legal and health care delivery context for abortion is extremely dynamic. We’ve had to be very flexible and in some cases act quickly to update our survey instruments to understand the current legal or political context in Wisconsin.
Finally, and perhaps most notably, bad actors and bots abound in this work. We’ve been overwhelmed by the number of fraudulent responses we’ve received and, in turn, the time and effort it takes to parse the good responses from the bad. In the cases of bots that churn out thousands of responses each week, identification is fairly easy, as, for example, their open-ended responses and their email addresses are completely nonsensical. But for those duplicate responses from legitimate participants who are likely trying to obtain additional remuneration and individuals posing as eligible when they’re not, the process is much more art than science.
Through this process we’ve learned a lot about how to proactively prevent fraud and handle it when it slips past our checks. First, the thoughtful, capable data scientists on our team have been an invaluable resource. Their efforts have allowed us to analyze data quickly and again, pretty proactively and quickly, identify appropriate data flags with relative ease and pivot our processes accordingly.
Additionally, having checks in our data collection tools that help identify bad actors and bots has been crucial to our success. I’m happy to talk more about those in detail during the question and answer period, but for now, I’ll highlight to you. Um collecting IP addresses and asking questions for which responses can be compared, both within a single survey and across multiple survey waves has been crucial in helping us catch fraud. With that said, I’ll say that our team remains hopeful in this really is a team effort.
Through the process, we’ve developed even stronger partnerships, and we’ve learned so much. We’re better scientists because of the challenges we’ve encountered. And while our progress may be slower than we hoped in some regards and much more challenging than we expected, our methods are working. We’re finding Wisconsinites who considered abortion and never made it to a clinic and are willing to share their experiences with our team.
So I’ll leave, leave it at that except for two asks. My first is that we continue to fill the gap in finding folks who consider abortion but don’t make it to care. They’re a crucial population within, uh, that should be a focus of our work more often, and I’d ask that we all continue to work collaboratively to build effective anti-fraud strategies that can be applied across contexts. I know there are many folks in the field and in other fields working on this effort, and our collaborative efforts have already been so fruitful, and I welcome more investment.
So with that, thank you very much. And I’ll welcome questions during the question and answer or at this email address at any time.
Beth Jarosz: Thank you so much, Jane. And we will move on to Alison.
Alison Gemmill, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health: Okay. Great. So thank you so much for organizing this. Um, I’m really happy to talk about the, see, it’s working, the data component here. So, um, for those of you who don’t know me, I’m a demographer and a reproductive perinatal epidemiologist, and I am studying the health impacts. And I’m going to talk about some of the challenges of using secondary data sources in this work.
Um, so I wanted to highlight two current projects. Uh, and this is collaborative work with Dr. Suzanne Bell. The first of these is to look at the impact of highly restrictive abortion policies on fertility: so birth rates, uh, severe maternal morbidity and mortality, if possible, and birth outcomes. And then the second project is to look at the impact of these highly restrictive abortion policies on changes in high-risk pregnancy care. And this work is currently funded through the Society of Family Planning.
So what are the data sources that we use? Um, for the first project where we look at birth rates, we obviously use birth certificate data. So we, we rely on vital statistics data a lot. Um, we are also looking at some infant outcomes like infant mortality. So we rely on death certificates as well. The good thing about vital statistics data is that they are virtually complete. So for births, for example, they represent over 99% of all births in the U.S., including home births, and all states participate. So we have good coverage over time and space.
Um, for maternal health outcomes or pregnancy-related outcomes, we can’t really rely on vital statistics for those. And I’ll explain more why shortly. So we’re going to rely on state-level hospitalization data, um, and specifically this is through a database through AHRQ. And what we do is we use ICD 9 or 10 codes for diagnosis and procedure, procedures to identify these types of outcomes.
And then, uh, potential projects in the pipeline might actually be using some of our typical survey data. So, for example, some of you are familiar with the National Survey of Family Growth, or NSFG, and the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring Survey, or PRAMS, and I’ll talk about those in a bit.
So I wanted to actually highlight some data challenges, uh, because I think it’s really important in this work, and it’s what we’re dealing with. The number one challenge: everybody wants to know what’s happening on the ground right now, but we do not yet know, and that’s because our data are lagged in terms of when they are released. So in the case of vital statistics data here, um, usually final birth and death certificate data are lagged by a year. So we have to play the waiting game. However, uh, I’ll talk about this at the end, uh, there have been changes in that they’re making provisional data more available to researchers. And this has been an amazing change.
Um, in terms of hospitalization data, these take a lot of time to come out as well. So I can’t tell you yet what’s happening to an outcome like severe maternal morbidity. Um, so these are lagged by about two years. So data on 2023 births will not be available until early 2025, for example. Um, in terms of those two surveys I mentioned, CDC’s PRAMS, they interview people who are postpartum, so these are among people who gave birth, data on 2023 births will not be available until 2025. And then for the National Survey of Family Growth, they did resume data collection in 2022. So there is a potentially an opportunity to use these data, but they won’t be released for some time.
The second challenge is about varying data availability, availability across states or limited geographic identifiers, and to conduct the kinds of studies that we want to conduct that have very strong causal inference embedded in them. We need data for states, each state. So the state inpatient databases that I talked about, the hospitalization data, those are great because we can get those at the state level. However, one of the big states that we’re interested in, Texas, does not participate, at least in the HCUP Central Distributor where we access these data typically. And then for the NSFG, they do not include state identifiers, nor do they include month year of important reproductive events. To access those data, you actually have to go to a restricted data center, which is associated with time and cost burdens.
The third challenge I want to note is that there’s varying data quality across states. And this is very, or this is, um, specific to birth certificates here. Um, so not all items on the birth certificate have high validity. And this validity varies by state. So because I have a captive audience, I wanted to highlight one of the papers that we wrote. Um, so what you see down here is a section of the birth certificate where there is something known as the maternal morbidity checkbox. So on the birth certificate we can capture information about some of these common maternal morbidities like maternal transfusion or ruptured uterus. However, we did a validation study where we compared the data on the birth certificate to the hospitalization data, and the estimates do not match up. And what our conclusion was is that the birth certificate data for these specific maternal mortality, morbidity indicators, the validity is quite low. So I recommend not using them.
Another challenge: the data are cost prohibitive. So I mentioned that we’re going to be using these state inpatient databases. These are really expensive. So one year of data for one state can cost anywhere from $200 in the case of Florida to about $1,600 in the case of Mississippi. So for our project where we need data for several states and several years, this is going to be quite costly. Thankfully, we have funding to support this work. Um, but again, this is a big barrier, right? Um, I mentioned the NSFG. You have to go to that restricted data center, and that costs a lot of time and a lot of money.
And then finally, I think a really great data source are Medicaid claims data. However, I will not be using them because they are very expensive to use. And you kind of need an existing data infrastructure. So you need, so you need to be linked to universities that are already kind of using Medicaid data because it’s a big, um, what’s the word, it’s a big barrier to overcome to get started with the Medicaid data, is what my understanding.
And then finally, this is my last data challenge, and it’s more of a statistical challenge. It’s about how do we estimate impacts among subgroups. And we know this is a very important question. However, the numbers can be quite small and this comes with lower statistical power. So, for example, how do we measure fertility rates among smaller or, yes, subgroups in smaller geographies? Or how do we measure events of very rare maternal outcomes that really matter, but they might just be so rare they’re hard to study.
So we need to expand our causal inference toolkit to detect these effects. We don’t want them, we don’t want them to go unnoticed, right? We want to detect some signal. So how do we do that? And that’s where I think a lot of the work needs to be done in terms of population health outcomes.
And then finally I’ll close with some data opportunities. Um, the one that I briefly touched on is that the CD, or the National Center of Health Statistics has made this release of provisional data in terms of birth certificate data and death certificate data. Um, and it’s been a game changer. I think what happened is COVID prompted the release of this data because we needed to know in real time, especially with mortality, what was going on. Um, and as of 2023, provisional birth and death certificate data are now available on CDC Wonder. So if you don’t know about CDC Wonder, this is a great interactive, um, platform that you could use online to download data. It’s an amazing resource.
So one of the first things that we did, um, while we’re still waiting for, uh, to study impacts of Dobbs, is we could study the impact of Texas SB8 policy using that provisional data from NCHS. And so this is a paper that my colleagues and I wrote, um, looking at what happened to fertility after SB8. And we did find a 3% increase in live births.
And I believe this is the last thing I want to say. So I just wanted to know other potential data sources for those of you in the audience that are thinking about doing this work. Uh, one colleague at Hopkins, he’s a current student, has actually used the behavioral risk factor surveillance system, which does have data by state. And he looked at outcomes related to self-reported anxiety and depression and found that those were elevated in respondents in banned states following the Dobbs decision.
I know other people might be looking at changes in the workforce. So there’s potential data, um, from some organizations that might be possible. I know people have looked at Reddit forums. Um, so there’s some rich qualitative there, data there potentially. And then I think we’re just going to be, have to be innovative in terms of other types of digital data that might be used.
So, um, I think that was it. And I look forward to any questions you might have. Thank you so much.
Beth Jarosz: Thank you so much, Alison. And last but certainly not least, I will invite Laura to present.
Laura Lindberg, Rutgers School of Public Health: Okay. Thank you all for having me here today. And, um, Alison really set this up because I want to focus on a subpopulation, which is adolescence. And I want to move my slides. There we go.
So adolescents are experiencing disproportionate legal, financial, logistical, and social barriers to abortion. This policy environment impacts not just adolescents seeking abortion, but all adolescents. And the experience of adolescence itself may have fundamentally changed. Adolescents are thinking differently about many aspects of their lives: their relationships, health, where to go to college, where to live, and what their future might look like.
Adolescents are impacted by new abortion laws aimed at all pregnancy capable people, as well as those such as abortion trafficking laws that specifically target minors’ access to abortion. And abortion access remains difficult for minors, even in states where access is protected, whether it’s because of parental involvement requirements, financial logistical challenges, or forms of abortion stigma.
It’s against this backdrop that I’m going to draw on a new report, Adolescence Post-Dobbs: A Policy-Driven Research Agenda for Minor Adolescence and Abortion. And I’d like to take this opportunity to acknowledge and thank my incredible co-authors, Julie Maslowsky and Emily Mann. While we focus on minors because of their unique standing in the law, our recommended action steps would benefit adolescents of all ages, their families, and their communities. And today, I’m going to focus on the data agenda that we developed in this report.
This report was produced under the auspices of Youth Reproductive Equity, a national multidisciplinary research collaborative composed of both researchers and clinician scientists. We formed in 2021 in anticipation of the Dobbs decision and its disproportionate impact on young people, and we continue to expand our work.
So, we found that minors are systematically underrepresented in research about abortion. Far too often, studies start at age 18, excluding the experiences of younger adolescents. Failing to produce needed research on minor adolescents and abortion is an equity issue, and the large knowledge gap has become a liability as the data gap allows for non-evidence-based policies.
A key call to action of our research agenda is to ensure that research designs and analyses include the experiences of minors. We make a distinction between studying the direct impacts of changing abortion policies on pregnant minors and the indirect impacts of abortion policies on the total population of minors.
So currently we lack the data needed to study the direct impacts of the new restricted abortion policies on minors. For example, it’s well established that federal and state abortion surveillance is incomplete. For example, California doesn’t participate in these systems, and states don’t always collect data by age. Studies of abortion patients, usually based out of clinics, even when they do include minors, are often limited by small numbers, and the new real-time data collection of abortion counts, such as that from Guttmacher or the Society of Family Planning, doesn’t even collect patient age, leaving critical gaps in the surveillance of minors’ receipt of abortion care.
Thus, we recommend expanding data collection to increase and improve the inclusion of minors in clinical studies, as well as state and national surveillance, and this may include a need targeted oversampling of minors.
Further, where there is data, we need to expand again our approach so that we present age-specific data in ways that we can identify minors’ unique experiences and not group them with all adolescents up to age 19 or, worse, with the general population.
In addition to expanding our research, we call for approaches that use tailoring, which is to tailor direct collection to provide an in-depth examination of those experiences that are unique to minors. This allows for focused attention to policies, focus on this age group’s abortion access, experience, access and experiences separate from those of adults. And a key recommendation around tailoring is to field a new longitudinal study of pregnant minors across different policy environments to better understand their pregnancy, abortion, and parenting experiences.
Now, I want to turn to the data needed to examine the indirect effect of abortion policies on minors. And here we propose the need for what we call contextualizing, calling for population representative as well as targeted studies of minors that aren’t so focused on abortion but capture the context of adolescents’ lives as abortion access is changing.
So as we think about contextualizing, we can see many gaps in existing federal, state, and national data collection efforts that limit our, our ability to do needed research. So let me just talk about a few. There’s obviously other data sources out there, but I think these are some major ones that are worthy of discussion.
So the Youth Risk Behavior Survey, or YRBS: these are state surveys of high school students. And they should allow us to compare between different abortion policy environments. But an increasing number of states are choosing not to participate in the YRBS, and this is likely to only get worse over time. Still, there are opportunities here to abortion policies by knowing the state that the student resides in to outcomes such as their mental health, their experience of intimate partner violence, and contraceptive use patterns.
Alison mentioned the National Survey of Family Growth. This is a household survey that starts at age 15 and goes through age 49. However, the sample size of adolescence is relatively small, and especially if you want to do analyses limited to sexually experienced teens. Um, Alison noted that the geographic identifiers in the study are not made publicly available, which I’ll talk about more in a minute. She also mentioned BRFSS, and this is a good resource because it does provide state representative health data that could be of interest, but it only samples adults. And this is an example of the exclusion of minors from research that an expansion of the survey could address and improve.
And finally, we lack a current longitudinal study of adolescent lives. Add Health has been probably the most influential source, source of longitudinal data on teens, but it was started in the 1990s, and those adolescents are now adults. Indeed, it’s the National Institute of Aging that now funds this project, so it doesn’t help us to study today’s teens in today’s post-Dobbs world.
The National Longitudinal Survey of Youth, or NLSY, faces similar aging as the 1997 cohort, which was the most recent cohort, is now in middle age. The Bureau of Labor Statistics is currently designed designing a new NLSY, and this is really an opportunity, I hope, for collaboration to ensure that relevant health and psychosocial and other effects are, and measures are included in addition to the conventional labor force and work and education measures that this survey has usually focused on.
These gaps lead to key recommendations to improve and expand current data collection and start new efforts in the field. So we’re calling for both new cross-sectional and longitudinal survey of the general population of adolescents. These surveys should include not only sexual and reproductive health behavior, but adolescents’ knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors related to changing abortion access. And they should allow for the longitudinal study of the impact of the Dobbs environment of living in this, at this time on their behaviors, their education, their economic and their health, health outcomes into adulthood. Now is the time to design and implement these studies.
And we recognize that part of the context of minors’ lives are the adults in them. Be it parents, health care providers, caseworkers, teachers, even policymakers whose views on adolescence color their approaches. And studies of these adolescents who are influential in minors’ abortion experiences are also needed to understand the context of these experiences.
Finally, I want to remind everyone that in our country right now, your zip code determines your access to abortion care. And to help researchers study the influence of location, we need to make geographic data more readily accessible. This could include strategically collecting state representative data as well as making existing geocodes on surveys more available. So Alan, Alison pointed out the challenges of the difficult to access NSFG geocodes through the research data centers. I’ve lived through that; I call it often the, um, circles of hell, um, and it is not easy. But one approach to facilitating needed research with these geocodes could be to create publicly available aggregated geocodes that group states according to their state policy environment but don’t run these kinds of risk of disclosure, disclosure that the RDC is trying to protect from.
So in conclusion, all adolescents are impacted by the changing abortion policies, even if they aren’t seeking an abortion. And there’s a need, there’s substantial need for more research and data for this population. The historic exclusion or blind eye to minors’ experiences as compared to adults leaves us with inadequate data systems. Excluding and overlooking minors is both an equity and a rigor issue. We need quality science that includes marginalized populations, including those treated differently because of their age. Expanding, tailoring, and contextualizing data collection for minors and improving how researchers can access key data offers us a needed path forward.
I’ve shared here a QR code so you can access, download our entire report. It has not just these data and research needs, but also a deep dive into the changing legal and policy environment. I also invite you to contact us at Youth Repro. We are available for consultation, collaboration, and thought partnership, and my email is up here as well. Thank you.
Beth Jarosz: Thank you so much. All of these presentations have been fantastic, and I want to take a moment to acknowledge all of the great work that you are all doing, and also to suggest that our audience members seem to think so, too, because we have a ton of questions. Um, I will try to get to as many of these as we can, and that’s the 15 minutes that we have left.
And so I want to start with, um, and this is probably for Abigail, but for any of these, any of you can answer, um, and the question is, Is it legal for women in banned states to receive the pill in the mail? And I think maybe talk a little bit about shield laws, which you mentioned in your talk.
Abigail R.A. Aiken: Yes. Thanks for the question. Um, it’s a complicated one because it depends, um, on who we’re talking about being the subject of the laws. Um, it is the case that, um, most states don’t have laws on the books currently that would explicitly criminalize the person using the medications or receiving the medications for a self-managed abortion, although that doesn’t mean that people won’t be surveilled and won’t be subject to investigation or even times prosecution, um, unlawfully. And so, um. That’s one where I would also, if you’re interested in that question, check out the resources of If/When/How: Lawyering for Reproductive Justice because they’re extremely knowledgeable on this issue. So that’s one, um, where it’s, you know, not explicitly criminalized, but doesn’t mean that people couldn’t face, um, legal jeopardy.
For those who are delivering the pills, and I see the question about, um, is it, uh, legal for the person sending them. Now, technically, that would be against the laws of most states who had to have abortion bans or have restrictions on, uh, telemedicine provision of abortion. But the idea of the shield laws is to protect providers in states where they reside and where they practice. So there’s a great article in The New England Journal, uh, written by David Cohen, that lays out shield laws. It’s a really interesting and informative read, and it tells you about some of the protections, uh, that providers residing in states with shield laws would have in terms of protecting their license and protecting them from states that want to enforce their own state laws outside of their state boundaries.
Beth Jarosz: You know, and that kind of leads into, I love someone posted a question that I already had on our list, and I think it dovetails nicely with this. And it’s speaking to privacy and confidentiality. I think that’s one of, it’s sort of the, the elephant in the room when we’re thinking about this, that we need really good, high-quality data for a topic that is sort of legally challenging. Um, and, uh, so can you speak, I know we talked a little bit about that with geography, but I think each of you probably have a perspective on this. Who wants to go first, Abigail, do you want to take us off?
Abigail R.A. Aiken: Yeah. I can kick off there. Yeah. From the self-managed abortion and also the shield law perspective, um, it’s extremely difficult, right. And, you know, we know that, as I said, just because people don’t live in states with state laws that explicitly criminalize them doesn’t mean they won’t be, uh, surveilled and harassed and sometimes even unjustly prosecuted.
And so we really limit our data collection, and we are really limited in terms of what we can collect. So we never collect anything identifying. And even then, we don’t collect a lot of the things that, you know, I appreciated Laura’s call for this more detailed data, and I think we absolutely need that. It’s really hard with self-managed abortion. Um, and so far we have really stuck to the idea of firstly, anyway, counting right, getting information on volumes on prevalence.
Um, before Dobbs, we did quite a lot of qualitative work looking at people’s experiences and their motivations. And I’m not saying we won’t go there again. Um, but it is an even more difficult environment in which to, uh, do this work than it was before. And so, um, right now we’re really very much, when we get data directly from providers, we ask for as little as possible.
Beth Jarosz: Thank you. And I think Alison and Laurie, you both mentioned, um, sort of geographic specificity, which we know is really important in this context. And, Jane, I have a follow-up related to privacy for you, too, but I want to talk a little bit about the challenge of balancing geographic access with confidentiality in these cases. If either of you want to speak to that.
Alison Gemmill: Well, I was actually thinking about some of the rarer outcomes that we’re going to be studying, which you could inadvertently disclose somebody’s identity in a given state, you know, in a given age range. And they have a very rare pregnancy-related outcome. And so one of the challenges we’re going to have is that data are made available to us, and we have a data use agreement where we will make sure that we protect the data at all, at all costs.
But, um, it’s, it might be challenging for us in how we disseminate the information. So we have to make sure that we’re not going to, you know, report only five cases of something. So there’s certain rules. So that’s how I’m thinking about it with the secondary data that I use.
Laura Lindberg: Yeah. And I just want to mention, I mean, there certainly are real risks here. And our role as researchers, we have to take those seriously. But we also need to be educating our IRBs about the reality of the extent of those risks. And what we’re hearing from a lot of research these days is that IRB, IRB members don’t know much about abortion. They’re getting their news from wherever they’re getting it. Um, and they may be concerned in ways that doesn’t reflect the true risk, and their solutions may not be true solutions.
So being the person in your university or in your setting who can work with the IRB to educate them, um, can be helpful. And the Society of Family Planning is in the process of preparing and will be disseminating a series of, um, guidance documents that people can use with their IRBs, both for general sexual and reproductive health research and focused on doing research with minors. So that should be useful to the field.
Beth Jarosz: Wonderful. Thank you. And that’s actually a really nice lead into the question that came in for Jane. And it was thinking of privacy, actually, from the flip side is that, um, you’re finding ways to remove cases that are fraudulent using IP addresses, but does that cause any IRB or confidentiality concerns?
Jane Seymour: Thanks so much for this question. This is something I think about pretty much constantly, it feels like. Um, I think it’s a really, really important conversation, and the tension is really real. So I don’t, I don’t pretend to have any of the answers.
Um, with that said, I really appreciate Laura’s call to, for high-quality data. And we as researchers have a responsibility to ensure that the data that we put out into the world, the results that we put into the world are as real as possible. And in the case where we’re dealing with hundreds and thousands of cases of people who in some cases, like, I think they’re, they’re kind of the two groups I spoke about, there’s like the bots and things that are really, really easy to weed out. You know, when it’s like Abcdefg and a string of 14 letters at mymail.com. That’s pretty easy.
There are some people who have, like, really done their homework and have really convincing stories. And in some cases, we’ve gotten as far as getting them on the phone for an in-depth interview, and it’s become clear that there’s no way that this is a real story that they’re telling. They’re talking about getting pills over the counter in Wisconsin in a time period when, like, pills are not available over the counter, abortion wasn’t available in Wisconsin, you know, just and, and when we probe that, it’s clear that that’s not the case. We’re not talking about issues of stigma where somebody might be changing their story due to abortion stigma.
At any rate, I think it’s incumbent upon us to balance participant safety and security with the rigor and validity of our data. And we feel pretty strongly that IP address is one of those data points we can collect that helps us significantly. We’re really lucky at our institution to work with an IRB that’s very supportive of our work.
One thing I’ll flag here that I didn’t have time to talk about in my presentation was the challenges that we’re working with, um, as it relates to certificates of confidentiality from the National Institutes of Health. There have been changes to that program, and many third-party platforms, including Qualtrics, which I imagine many of us use for data collection, are no longer acceptable, uh, third-party platforms to use under a certificate of confidentiality. So we’re really again struggling with how much does the rigor, how do we balance the rigor with the data protection. And again, I haven’t figured this out, but I think it is a real tension that we’re going to have to continue to work with as a field.
Beth Jarosz: So, um, so, so many more questions. We have time for one, maybe two more. So let’s see if I can package these together. Um, I have sort of a very broad question. I think all of you have touched on this, and that is, What’s a research question you really wish you could answer but don’t have the data now? And one specific question from an audience member is, Do you have statistics on covert delivery? Um, sort of these, uh, abortions that are happening in the states that, that perhaps that have banned abortion, um, in the wake of Dobbs.
Alison Gemmill: Um, I guess I’ll start. And mine is a pretty easy ask. I think I talked about state inpatient data, so that’s people who are hospitalized. I think the next step would be thinking about emergency room departments as a source of care. Um, and those data do exist, but again, not for every state. So that’s a big challenge. And then I think, like what Laura said about longitudinal data, I would love to have longitudinal data to link people over time, whether that’s within administrative claims data or a survey using secondary data. So I, I would love to see data like that eventually to answer some of the questions that we have.
Beth Jarosz: Laura, I know you had a call for data on adolescents. Do you want to renew or repeat them?
Laura Lindberg: Yeah. I mean, I think for, for adolescents, from a research perspective, from an IRB perspective, from a policy perspective, we need to be thinking more about what the harms are for adolescents who wanted an abortion and couldn’t get it, who want and were not telling their stories in our research, that the harm that when we think we’re protecting them by not including them in our research. In fact, so many harms happen when we can’t tell the stories and they’re not included.
And this happens not just for abortion research, by the way, but sexual reproductive health research more generally. So do we, if we don’t include minors in our contraceptive studies, we can’t show that contraception is safe for them because they weren’t in the study to begin with. They need to be included more to in fact increase their safety, not harm it.
Beth Jarosz: And I think I have one more question for Alison. And it’s, you know, you talked about the maternal morbidity data and the research that you’ve done around the challenges with that on the birth certificate record. Um, if you could make recommendations for how to improve, and you probably have that in your paper, but if you could make recommendations about how to improve that data collection system, what would you say?
Alison Gemmill: Yeah. I think, thank you. That’s great. And it was a research letter so I couldn’t say much, but I would, I mean, my understanding is that the National Center for Health Statistics has not had the resources to really check the validity of items. Um, and so first of all, I would want an evaluation of the validity of items on the birth certificate. That would be number one. But then second, it’s really a state’s issue, right? And the data are collected within states at their health departments. And it seems like there is varying data quality. So if there’s a way to train people that fill out the birth certificate to improve the way that they do that, I think that would go really far, because there’s some pretty potential rich data on maternal health there that we could be using.
Beth Jarosz: I think we have time for one more question, and I think this one is for Jane. And it’s, How does a researcher assure that a source for qualitative data like Reddit is reliable and meaningful?
Jane Seymour: That’s a fabulous question. Um, I think that in qualitative data, you know, the aim is not to be generalizable. The aim is to understand the experiences of those people for whom data exists. Um, you know, unfortunately, this is, I have not worked, some of my colleagues at CORE have worked with Reddit. Um, I have not worked directly, worked with Reddit data, but know that there’s quite a literature, which Alison you’ve referenced here. And Alison, forgive me, I’m not sure if you’ve worked with Reddit data, so please feel free to chime in if you have, or anyone else on the panel.
But I think that that Reddit data is a source of data that we can use to understand the experiences of some people who are searching for abortion, have had abortion, or have been denied abortion. And it’s never going to give us the full picture of the experience of everyone, but I want to be really clear that a lot of our quantitative research also doesn’t do that. So these are all important pieces to a larger puzzle that we can put together when we work effectively together to, to gather high-quality, rigorous data.
Beth Jarosz: Thank you. So I want to thank you again for sharing your expertise and your time with us today.
